Abstract
Background: Pedicle screw instrumentation of the deformed cervical and thoracic spine is challenging to even the most experienced surgeon and associated with increased incidence of screw misplacement. Iso-C3D based navigation has been reported to improve the accuracy of pedicle screw placement, however, there are very few studies assessing its efficacy in the presence of deformity. We conducted a study to evaluate the accuracy of Iso-C3D based navigation in pedicle screw fixation in the deformed cervical and thoracic spine.
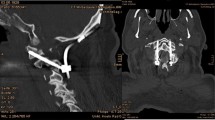
Materials and Methods: We inserted 98 cervical pedicle screws (18 patients) and 242 thoracic pedicle screws (17 patients) using Iso-C3D based navigation for deformities of spine due to scoliosis, ankylosing spondylitis, post traumatic and degenerative disorders. Two independent observers determined and graded the accuracy of screw placement from postoperative computed tomography (CT) scans.
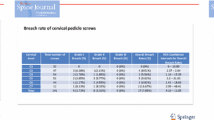
Results: Postoperative CT scans of the cervical spine showed 90.8% perfectly placed screws with 7 (7%) grade I pedicle breaches, 2 (2%) grade II pedicle breaches and one anterior cortex penetration (< 2mm). Five lateral pedicle breaches violated the vertebral artery foramen and three medial pedicle breaches penetrated the spinal canal; however, no patient had any neurovascular complications. In the thoracic spine there were 92.2% perfectly placed screws with only six (2%) grade II pedicle breaches, eight (3%) grade I pedicle breaches and five screws (2%) penetrating the anterior or lateral cortex. No neuro-vascular complications were encountered.
Conclusion: Iso-C3D based navigation improves the accuracy of pedicle screw placement in deformities of the cervical and thoracic spine. The low incidence of pedicle breach implies increased safety for the patient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boos N, Webb JK. Pedicle screw fixation in spinal disorders: A European view. Eur Spine J 1997;6:2–18.
Gaines RW Jr. The use of pedicle-screw internal fixation for the operative treatment of spinal disorders. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2000;82:1458–76.
Liljenqvist UR, Halm HF, Link TM. Pedicle screw instrumentation of the thoracic spine in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1997;22:2239–45.
Barr SJ, Schuette AM, Emans JB. Lumbar pedicle screws versus hooks: Results in double major curves in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 1997;22:1369–79.
Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Mazel C. Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1986;203:7–17.
Suk SI, Lee CK, Min HJ, Cho KH, Oh JH. Comparison of Cotrel-Dubousset pedicle screws and hooks in the treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. Int Orthop 1994;18:341–6.
Belmont PJ Jr, Klemme WR, Dhawan A, Polly DW Jr. In vivo accuracy of thoracic pedicle screws. Spine 2001;26:2340–6.
Richter M, Cakir B, Schmidt R. Cervical pedicle screws: Conventional versus computer-assisted placement of cannulated screws. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30:2280–7.
Liljenqvist UR, Link TM, Halm HF. Morphometric analysis of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000;25:1247–53.
Amiot LP, Lang K, Putzier M, Zippel H, Labelle H. Comparative results between conventional and computer-assisted pedicle screw installation in the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spine. Spine 2000;25:606–14.
Kosmopoulos V, Schizas C. Pedicle screw placement accuracy: A meta-analysis. Spine 2007;32:E111–120.
Kotani Y, Abumi K, Ito M, Minami A. Improved accuracy of computer-assisted cervical pedicle screw insertion. J Neurosurg 2003;99:257–63.
Kotani Y, Abumi K, Ito M, Takahata M, Sudo H, Ohshima S, et al.. Accuracy analysis of pedicle screw placement in posterior scoliosis surgery: Comparison between conventional fluoroscopic and computer-assisted technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:1543–50.
Laine T, Lund T, Ylikoski M, Lohikoski J, Schlenzka D. Accuracy of pedicle screw insertion with and without computer assistance: A randomised controlled clinical study in 100 consecutive patients. Eur Spine J 2000;9:235–40.
Merloz P, Tonetti J, Pittet L, Coulomb M, Lavallee S, Sautot P. Pedicle screw placement using image guided techniques. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1998;354:39–48.
Rajasekaran S, Vidyadhara S, Shetty AP. Iso-C3D fluoroscopy-based navigation in direct pedicle screw fixation of Hangman fracture: A case report. J Spinal Disord Tech 2007;20:616–9.
Rajasekaran S, Vidyadhara S, Ramesh P, Shetty AP. Randomized clinical study to compare the accuracy of navigated and non-navigated thoracic pedicle screws in deformity correction surgeries. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:E56–64.
Esses SI, Sachs BL, Dreyzin V. Complications associated with the technique of pedicle screw fixation: A selected survey of ABS members. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1993;18:2231–8; discussion 2238-9.
Jones EL, Heller JG, Silcox DH, Hutton WC. Cervical pedicle screws versus lateral mass screws: Anatomic feasibility and biomechanical comparison. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1997;22:977–82.
Kotani Y, Cunningham BW, Abumi K, McAfee PC. Biomechanical analysis of cervical stabilization systems: An assessment of transpedicular screw fixation in the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1994;19:2529–39.
Lonstein JE, Denis F, Perra JH, Pinto MR, Smith MD, Winter RB. Complications associated with pedicle screws. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1999;81:1519–28.
Ebraheim N, Rollins JR Jr, Xu R, Jackson WT. Anatomic consideration of C2 pedicle screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996;21:691–5.
Ebraheim NA, Xu R, Knight T, Yeasting RA. Morphometric evaluation of lower cervical pedicle and its projection. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1997;22:1–6.
Miller RM, Ebraheim NA, Xu R, Yeasting RA. Anatomic consideration of transpedicular screw placement in the cervical spine: An analysis of two approaches. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996;21:2317–22.
Stanescu S, Ebraheim NA, Yeasting R, Bailey AS, Jackson WT. Morphometric evaluation of the cervico-thoracic junction: Practical considerations for posterior fixation of the spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1994;19:2082–8.
Brown CA, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Geideman WM, Hasan SA, Blanke K. Complications of pediatric thoracolumbar and lumbar pedicle screws. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1998;23:1566–71.
Ebraheim NA, Xu R, Ahmad M, Yeasting RA. Projection of the thoracic pedicle and its morphometric analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1997;22:233–8.
Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Balderston RA, Allardyce TJ, Garfin SR, Dolinskas C, et al.. Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine: Part II: An anatomical and radiographic assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995;77:1200–6.
Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Allardyce TJ, Ramsey M, Salvo J, Balderston RA, et al.. Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine: Part I: Morphometric analysis of the thoracic vertebrae. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995;77:1193–9.
Zindrick MR, Wiltse LL, Doornik A, Widell EH, Knight GW, Patwardhan AG, et al.. Analysis of the morphometric characteristics of the thoracic and lumbar pedicles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1987;12:160–6.
Belmont PJ Jr, Klemme WR, Robinson M, Polly DW Jr. Accuracy of thoracic pedicle screws in patients with and without coronal plane spinal deformities. Spine 2002;27:1558–66.
Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, Chung YJ, Park YB. Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995;20:1399–405.
Xu R, Ebraheim NA, Ou Y, Yeasting RA. Anatomic considerations of pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: Roy-Camille technique versus open-lamina technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1998;23:1065–8.
Abumi K, Shono Y, Ito M, Taneichi H, Kotani Y, Kaneda K. Complications of pedicle screw fixation in reconstructive surgery of the cervical spine. Spine 2000;25:962–9.
Ludwig SC, Kowalski JM, Edwards CC 2nd, Heller JG. Cervical pedicle screws: Comparative accuracy of two insertion techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000;25:2675–81.
Ludwig SC, Kramer DL, Balderston RA, Vaccaro AR, Foley KF, Albert TJ. Placement of pedicle screws in the human cadaveric cervical spine: Comparative accuracy of three techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000;25:1655–67.
Rampersaud YR, Lee KS. Fluoroscopic computer-assisted pedicle screw placement through a mature fusion mass: An assessment of 24 consecutive cases with independent analysis of computed tomography and clinical data. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:217–22.
Richter M, Amiot LP, Neller S, Kluger P, Puhl W. Computerassisted surgery in posterior instrumentation of the cervical spine: An in-vitro feasibility study. Eur Spine J 2000;9:S65–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajan, V.V., Kamath, V., Shetty, A.P. et al. Iso-C3D navigation assisted pedicle screw placement in deformities of the cervical and thoracic spine. IJOO 44, 163–168 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.62083
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.62083