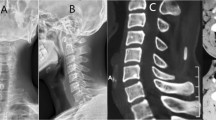
Abstract
Bardet–Biedl syndrome (BBS) is a rare, autosomal-recessive, debilitating genetic disorder, which can present with multitudinous systemic clinical features including rod-cone dystrophy, polydactyly, Frohlich-like central obesity, mental retardation, hypogonadism, and renal anomalies. Diverse neuromuscular manifestations in patients afflicted by this heterogeneous disorder include ataxia, cervical, and thoracic canal stenoses, presenting as spastic quadriparesis and other gait disturbances. We report a young patient with BBS, who had presented with acute flaccid paraparesis due to severe primary lumbar canal stenosis. She underwent immediate lumbar decompression and discectomy following which she recovered significantly. Acute cauda equina syndrome due to primary lumbar canal stenosis has not been reported as a clinical feature of BBS previously.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beales PL, Elcioglu N, Woolf AS, Parker D, Flinter FA. New criteria for improved diagnosis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome: Results of a population survey. J Med Genet 1999;36:437–46.
Green JS, Parfrey PS, Harnett JD, Farid NR, Cramer BC, Johnson G, et al. The cardinal manifestations of Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a form of Laurence-Moon-Biedl syndrome. N Engl J Med 1989;321:1002–9.
Lo KT, Remulla J, Santiago AP. Manifestations of Bardet Biedl syndrome. Philipp J Ophthalmol 2004;29:94–8.
Laurence JZ, Moon RC. Four cases of “retinitis pigmentosa” occurring in the same family, and accompanied by general imperfections of development. Ophthalmol Rev 1866;2:32–41.
Nyska M, Mozes G, Howard C, Bar-Ziv J, Dekel S. Quadriparesis in the Laurence-Moon-Biedl-Bardet syndrome: Case report. Paraplegia 1991;29:350–4.
Moses G, Howard C, Bar-Ziv J, Dekel S, Nyska M. ‘Epiphyseal dysgenesis’ in Laurence-Moon-Biedl-Bardet syndrome. J Pediatr Orthop B 1998;7:193–8.
Uçar T, Mutlucan UO, Göksu E, Taçoy S, Kazan S, Fırat SC. Paraparesis results from spinal stenosis in Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Biedl syndrome: Case report. Türk Nöroşirürji Derg 2012;22:26–9.
Gitelman A, Hishmeh S, Morelli BN, Joseph SA Jr., Casden A, Kuflik P, et al. Cauda equina syndrome: A comprehensive review. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 2008;37:556–62.
Iliescu B, Gaivas S, Apetrei C, Poeată I. Severe spinal stenosis in an adult achondroplastic dwarf: Case report. Rom Neurosurg 2010;17:445–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viswanathan, V.K., Kanna, R.M., Shetty, A.P. et al. Acute flaccid paraparesis (cauda equina syndrome) in a patient with Bardet–Biedl syndrome. IJOO 51, 330–333 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.205682
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.205682