Abstract
Background
There is medium correlation between the current anthropometric method and the radiography in the angle of hallux valgus (AoH) measurement, so this study aimed at designing a reliable and more accurate approach to measure the AoH (AoH).
Materials and Methods
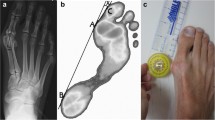
Fifteen age, body weight, and height matched male students were included and those with foot disorders, deformities, or injuries were excluded from the study. The dorsal protrusions of the first metatarsal and the hallux were marked by palpating from three experienced observers; then their barefoot model in standing was collected by a three dimensional laser scanning system. The AoH was defined in the X-Y plane by the angle between the line joining the marks of centre of head and centre of base of metatarsal shaft and the one connecting the marks of the centre of metatarsal head and the hallux. The same procedure was repeated a week later. Besides, other measures based on the footprint, outline, and the radiography were also available for comparisons. Paired t-test, linear regression, and reliability analysis were applied for statistical analysis with significant level of 0.05 and 95% confidence interval.
Results
There were no significant differences recorded between the new method and the radiographic method (P = 0.069). The AoH was superior to the methods of footprint and outline and it displayed a relative higher correlation with the radiographic method (r = 0.94, r2 = 0.89). Moreover both the inter and intraobserver reliabilities of this method were proved to be good.
Conclusion
This new method can be used for hallux valgus inspection and evaluation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonney G, Macnab I. Hallux valgus and hallux rigidus: A critical survey of operative results. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1952;34-B: 366–85.
Spooner SK. Predictors of Hallux Valgus: A Study of Heritability. UK: University of Leicester; 1997.
Brodie BS, Robins DJ, Wilson AF. Wessex Feet: A regional foot health survey. Chiropodist 1988;43:152–65.
Bryant A. Radiographic measurements and plantar pressure distribution in normal, hallux valgus and hallux limitus feet. Foot 2000;10:18–22.
Hardy RH, Clapham JC. Observations on hallux valgus; based on a controlled series. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1951;33-B: 376–91.
Kilmartin TE, Wallace WA. The Significance of Pes Planus in Juvenile Hal-Lux Valgus. J Pediatr Orthop 1992;12:556.
Kilmartin TE, Barrington RL, Wallace WA. The X-ray measurement of hallux valgus: An inter and intraobserver error study. Foot 1992;2:7–11.
Kilmartin TE, Wallace WA. A model for foot health screening. Br J Podiatr Med Surg 1990;2:8–10.
Barnicot NA, Hardy RH. The position of the hallux in West Africans. J Anat 1955;89:355–61.
Sanders AP, Snijders CJ, van Linge B. Medial deviation of the first metatarsal head as a result of flexion forces in hallux valgus. Foot Ankle 1992;13:515–22.
Park JM, Kwon SJ, Lee DW, Im HT. The Comparison of Hallux Valgus Angles between Plain Radiography and Footprint Test. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med 2008;32:689–92.
Kilmartin TE, Bishop A. Hallux abductus angle measurement: Repeatability trials of a clinical measuring instrument. Chiropodist 1988;43:185–7.
De Mits S, Coorevits P, De Clercq D, Elewaut D, Woodburn J, Roosen P. Reliability and validity of the INFOOT three-dimensional foot digitizer for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2011;101:198–207.
Hopkins WG. Measures of reliability in sports medicine and science. Sports Med 2000;30:1–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Hlavacek, P., Xu, B. et al. Approach for measuring the angle of hallux valgus. IJOO 47, 278–282 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.109875
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.109875