Abstract
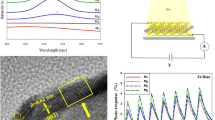
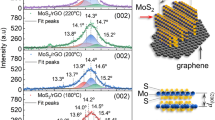
In this study, we have proposed a simple method to produce temperature-dependent variablesize of MoS2 nanodots (NDTs) by using MoS2 powder as a pre-cursor and KNa-tartrate as the intercalant. Due to defects in MoS2, the optical properties are strongly modified and show blue luminescence under UV irradiation of MoS2 NDTs. The temperature variable is used to gradually introduce defects in 2D materials to obtain nanodots with different particle sizes. When the synthesis temperature is increased from 120 °C to 200 °C, the particle size is reduced from ~ 120 nm to ~ 2.5 nm. Next, an enhancement of photoluminescent magnitude and a red shift were observed in photoluminescence spectra from MoS2 NDTs solutions. These results offer a route toward tailoring the optical properties of 2D nanomaterials by controlling the size/temperature/synthesis method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. F. Mattheiss, Phys. Rev. B 8, 379 (1973).
K. F. Mak et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 136805 (2010).
G. Eda et al., Nano Lett. 11, 5111 (2011).
H. D. Ha et al., Small 10, 3858 (2014).
J. Li and J. J. Zhu, Analyst 138, 2506 (2013).
G. U. Siddiqui et al., J. Lumin. 169, 342 (2016).
Y. Zhou et al., Opt. Mater. Express 5, 1606 (2015).
L. Chen et al., Nanoscale 7, 14982 (2015).
J. Benson et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 14113 (2015).
Y. Shi et al., Nano Lett. 12, 2784 (2012).
G. S. Bang et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 7084 (2014).
N. S. Arul and V. D. Nithya, RSC Adv. 6, 65670 (2016).
G. C. Loh, R. Pandey, Y. K. Yap and S. P. Karna, J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 1565 (2015).
M. Javaid, D. W. Drumm, S. P. Russo and A. D. Greentree, Sci. Rep. 7, 9775 (2017).
B. Li et al., Sci. Rep. 7, 1182 (2017).
B. L. Li et al., Nanoscale 6, 9831 (2014).
D. Gopalakrishnan et al., Chem. Commun. 51, 6293 (2015).
X. Ren et al., J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 10693 (2015).
D. Gopalakrishnan, D. Damien and M. M. Shaijumon, ACS Nano 8, 5297 (2014).
Y. Wang and Y. Ni, Anal. Chem. 86, 7463 (2014).
W. Dai et al., Small 11, 4158 (2015).
Y. Xu et al., Chem. Soc. Rev. 47, 586 (2018).
L. Ji, J. Wang, S. Zuo and Z. Chen, J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 4917 (2017).
C. H. Lin et al., Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10, 446 (2015).
L. Lin et al., ACS Nano 7, 8214 (2013).
J. Y. Wu et al., RSC Adv. 5, 95178 (2015).
Y. Wang et al., Kexue Tongbao/Chin. Sci. Bull. 64, 411 (2019).
L. Bao et al., Adv. Mater. 23, 5801 (2011).
V. Štengl and J. Henych, Nanoscale 5, 3387 (2013).
H. Lin et al., New J. Chem. 39, 8942 (2015).
S. H. Song et al., Adv. Opt. Mater. 2, 1016 (2014).
Q. Xue et al., Adv. Mater. 29, 1604847 (2017).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the “Research Base Construction Fund Support Program” funded by Jeonbuk National University in 2019 and by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (NRF-2018R1A2B6006740).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rani, A., Kim, EY., Song, D.S. et al. Effects of the Intercalant and the Temperature in Hybrid-MoS2 Nanodots Fabrication and Their Photoluminescence Enhancement. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 76, 980–984 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.76.980
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.76.980