Abstract
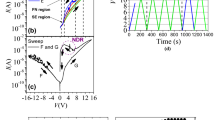
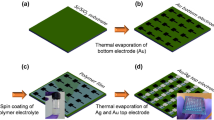
The prediction of the current-voltage (IV) characteristics of resistive switching devices has remained a challenge before their physical realization. This research work addresses the prediction of the IV characteristics and the bipolar switching mechanism of polymer-based resistive switches by examining their structures before their fabrication. The research was carried out through an analytical study of the device structure, thereby correlating the predicted IV curve to the in-situ IV characteristics of the device. Different types of the device structures were considered, depending upon the work function of the top and the bottom electrodes and the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) levels of the sandwiched layer. We concluded that the defects/traps within the sandwiched layer lead to the interface effect being the dominant switching mechanism driving the polymer-based resistive switches. Furthermore, we also found that the devices following the interface effect are driven from trap-limited space-charge-limited current (SCLC) conduction to trap-free SCLC conduction as their current conduction mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. J. Yang, D. B. Strukov and D. R. Stewart, Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 13 (2013).
S. K. Hong, J. E. Kim, S. O. Kim and B. J. Cho, J. Appl. Phys. 110, 044506 (2011).
M. N. Awais and K. H. Choi, Electron. Lett. 51, 2147 (2015).
H. Nili et al., Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 1 (2014).
R. Waser and M. Aono, Nat. Mater. 6, 833 (2007).
R. Waser, R. Dittmann, G. Staikov and K. Szot, Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 2632 (2009).
C. Y. Lin et al., J. Appl. Phys. 102, 094101 (2007).
Y. Yang et al., Adv. Funct. Mater. 16, 1001 (2006).
Q. D. Ling et al., Prog. Polym. Sci. 33, 917 (2008).
M. Mustafa, M. N. Awais, G. Poonia and K. H. Choi, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 61, 470 (2012).
T. Lee and Y. Chen, Mater. Res. Bull. 37, 144 (2012).
M. Lin et al., Polymers 9, 1 (2017).
M. C. Lia et al., Solid State Electronics 148, 1 (2018).
M. A. Lampert and P. Mark, Current Injection in Solids (Academic Press, New York, 1970).
M. Bajpai et al., Synth. Met. 160, 1740 (2010).
M. Arif et al., Phys. Rev. B 75, 195202 (2007).
T. W. Kim et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 253308 (2008).
M. N. Awais and K. H. Choi, Electron. Mater. Lett. 10, 601 (2014).
M. N. Awais et al., Micro Nano Lett. 11, 712 (2016).
C. Wu, F. Li, T. Guo and T. W. Kim, Org. Electron. 13, 178 (2012).
T. Ouisse and O. Stephan, Org. Electron. 5, 251 (2004).
J. A. Rohr et al., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 30, 105901 (2018).
Y. Sadaoka and Y. Sakai, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. II 72, 1911 (1976).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awais, M.N., Shehzad, M.N. Prediction of the Current-Voltage Characteristics and the Bipolar Resistive Switching Mechanism in Polymer-Based Sandwiched Structures. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 75, 409–414 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.75.409
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.75.409