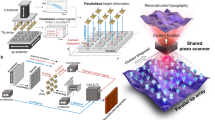
Abstract
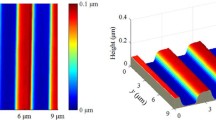
High-speed atomic force microscopy permits the capture of static, as well as the dynamic, processes present in various physical phenomena. Unlike visualizing static processes, capture of dynamic processes requires high-speed scanning in all three dimensions. Despite the recent increased interest in high-speed atomic force microscopy, relatively few reports concerning piezoelectric actuator-driven scanners for high-speed scanning have been published. In this paper, we propose a novel design for a high-speed two-dimensional piezoelectric scanner unit by combining the positive features developed from works published in the literature. The proposed design ensures high vertical stiffness by utilizing compliant double-hinged flexure that minimizes cross-coupling and parasitic motions. Any high-speed scanner design requires a compromise between the two main competing parameters: maximum scan size and speed. The performance of the proposed scanner was evaluated by using numerical simulations with finite element analyses in terms of the mechanical resonance frequencies and the scan range. Finally, the results from the numerical simulations are compared with the experimental measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Binnig, C. F. Quate and Ch. Gerber, Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 930 (1986).
P. N. Adrian, W. E. Blake, H. Nahid, D. A. Jonathan and E. F. Georg, Sci. Rep. 15, 11987 (2015).
G. E. Fantner, R. J. Barbero, D. S. Gray and A. M. Belcher, Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 280 (2010).
J. Loos, Adv. Mater. 17, 1821 (2005).
D. Masoud, S. Samira, U. B. Leila and S. Soheil, Optics 3, 15 (2014).
B. Wolf and P. Paufler, Cryst. Res. Techno. 31, 505 (1996).
J. Sangmin, T. Thomas and B. Yehuda, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 214102 (2006).
X. Li-Chong, H. P. F. Herbert and C. Kwong-Yu, J. Electrochem. Soc. 146, 4455 (1999).
R. Mahlberg, H. E. M. Niemi, F. S. Denes and R. M. Rowell, Langmuir 15, 2985 (1999).
G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, Ch. Gerber and E. Weibel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 57 (1982).
G. Binnig and D. P. E. Smith, Phys. Rev. Lett. 57, 1688 (1986).
D. Croft, G. Shed and S. Devasia, J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. 123, 35 (2001).
M. J. Rost, G. J. C. Van Baarle, A. J. Katan, W. M. Van Spengen, P. Schakel, W. A. Loo, T. H. Oosterkamp and J. W. M. Frenken, Asian J. Control 11, 110 (2009).
A. Mohammadi, A. G. Fowler, Y. K. Yong and S. O. R. Moheimani, J. Microelectromech. Syst. 23, 610 (2014).
S. Wadikhaye, Y. K. Yong and S. O. R. Moheimani, Rev. Sci. Intsrum. 85, 105104 (2014).
A. Toshio, Curr. Opin. Struc. Biol. 28, 63 (2014).
B. J. Kenton and K. K. Leang, IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 17, 356 (2012).
Y. Shan and K. K. Leang, IEEE Control. Syst. Mag. 86 (2013).
T. Ando, K. Noriyuki, N. Yasuyuki, T. Kinoshita, K. Furuta and Y. Y. Toyoshima, Chem Phys Chem 4, 1196 (2003).
T. Ando, U. Takayuki and K. Noriyuki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 51, 08KA02 (2012).
V. E. Gough and S. G. Whitehall, in Proceedings of the 9th International Technical Congress (FISITA, April-May, 1962), p. 117.
G. Schitter, J. T. Philipp and K. H. Paul, Mechatronics 18, 282 (2008).
G. Schitter, K. J. Astrom, B. E. DeMartini, P. J. Thurner, K. L. Turner and P. K. Hansma, IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 15, 906 (2007).
K. Y. Yuen and S. O. R. Moheimani, in Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (Montreal, Canada, July 6-9, 2010), p. 225.
T. Ando, T. Uchihashi and T. Fukuma, Prog. Surf. Sci. 83, 337 (2008).
T. Fukuma, Y. Okazaki, N. Kodera, T. Uchihashi and T. Ando, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 243119 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alunda, B.O., Lee, Y.J. & Park, S. A novel two-axis parallel-kinematic high-speed piezoelectric scanner for atomic force microscopy. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 69, 691–696 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.69.691
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.69.691