Abstract
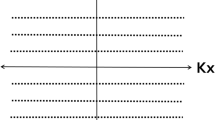
Whole-body diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a useful tool in oncology, which enables fast screening of disseminated tumors, lymph nodes or abscesses in the body. Multistation magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or continuously moving table (CMT) MRI can be performed to overcome the limited field of view (FOV) of the magnet bore in whole-body DWI. Although CMT-MRI is regarded as a more advanced form of whole-body MRI, it cannot be widely used because most of the available MR systems are not equipped with the required hardware/software to perform CMT. Thus, optimizing the multistation approach for whole-body DWI, which is more widely available and easier to perform with the existing MR systems, is worthwhile. To improve the quality of DW images acquired with the multistation approach, we used different combinations of the built-in body RF coil and the phased-array surface RF coils for reception of the signals in whole-body DWI in this work. If different coils are selectively used in the extended FOV and appropriate reconstruction algorithms are exploited, the screening ability of whole-body DWI can be improved while minimizing the patient’s discomfort and the artifacts due to physiological motions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Takahara, Y. Imai, T. Yamashita, S. Yasuda, S. Nasu and M. van Cauteren, Radiat. Med. 22, 275 (2004).
S. Li, F. Sun, Z. Y. Jin, H. D. Xue and M. L. Li, J. Magn. Reson. 26, 1139 (2007).
D. M. Koh and D. J. Collins, Am. J. Roentgenol. 188, 1622 (2007).
T. C. Kwee, T. Takahara, R. Ochiai, R. A. Nievelstein and P. R. Luijten, Eur. Radiol. 18, 1937 (2008).
U. Ludwig, G. Sommer, M. Zaitsev, N. Ghanem, J. Hennig and H.P. Fautz, Magn. Reson. Med. 55, 423 (2006).
G. Sommer, H.P. Fautz, U. Ludwig and J. Hennig, Magn. Reson. Med. 55, 918 (2006).
P. Bornert and B. Aldefeld, J. Magn. Reson. 28, 1 (2008).
Y. Han, S. Huff, M.Weigel and U. Ludwig, Magn. Reson. Med. 65, 1557 (2011).
H. M. van Ufford, T. C. Kwee, F. J. Beek, M. S. van Leeuwen, T. Takahara, R. Fijnheer, R. A. Nievelstein and J. M. de Klerk, Am. J. Roentgenol. 196, 662 (2011).
D. Delbeke, S. Stroobants, E. de Kerviler, C. Gisselbrecht, M. Meignan and P. S. Conti, Oncologist. 14, 30 (2009).
C. Furth et al., J Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 28, 501 (2006).
T. C. Kwee, T. Takahara, T. Niwa, M. K. Ivancevic, G. Herigault, M. van Cauteren and P. R. Luijten, Magn. Reson. Mater. Phy. 22, 319 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y. An adaptive diffusion-weighted whole-body magnetic resonance imaging scheme using the multistation approach. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 68, 467–473 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.68.467
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.68.467