Abstract
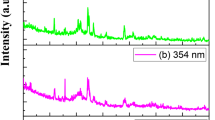
We report on the control of the electrical and the piezoelectric properties of ZnO nanorods (NRs) by incorporation of arsenic (As) elements via a low-temperature processed spin-on-dopant (SOD) method. The structural investigations for the SOD-treated ZnO NRs at different temperatures show a negligible change in morphology at temperatures up to 550 °C and melting of the ZnO NRs at 600 °C. Low-temperature photoluminescence (PL) spectra show gradual development of acceptor-related emission peaks with increasing SOD treatment temperature from 450 to 550 °C, which indicates the successful incorporation of As atoms into the ZnO NRs. An As Zn -2V Zn shallow acceptor model is suggested by considering the formation energy of the interstitial point-defect complex for the modification of the electrical properties of ZnO NRs. A ZnO NR/n-Si heterojunction showed better rectifying behavior with increasing SOD treatment temperature, indicating better incorporation of As-dopants at higher SOD treatment temperatures. A piezoelectric nanogenerator was fabricated as a device application of the electrical-property-modified ZnO NRs. The nanogenerator showed enhanced piezoelectric output potential after doping due to the elimination of the screening effect by free charge carriers in the ZnO NRs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Zhuang, Q. Peng and Y. Li, Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 5492 (2011).
Ü. Özgür, Ya. I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, M. A. Reshchikov, S. Doğan, V. Avrutin, S-J. Cho and H. Morkoç, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005).
Z. L. Wang, J. Phys.: Conden. Matt. 16, R829 (2004).
D. C. Look, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 80, 383 (2001).
D. K. Hwang, M. S. Oh, J. H. Lim and S. J. Park, J. Phys. D 40, R387 (2007).
J. H. Lim, C. K. Kang, K. K. Kim, I. K. Park and S. J. Park, Adv. Mater. 18, 2720 (2006).
Z. L. Wang, Nano Today 5, 540 (2010).
S. Kwon, S. Bang, S. Lee, S. Jeon, W. Jeong, H. Kim, S. C. Gong, H. J. Chang, H. Park and H. Jeon, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 24, 035015 (2009).
S. Chu, G. Wang, W. Zhou, Y. Lin, L. Chernyak, J. Zhao, J. Kong, L. Li, J. Ren and J. Liu, Nature Nanotech. 6, 506 (2011).
Z. L. Wang and J. H. Song, Science 312, 242 (2006).
W-J. Lee, J. Kang and K. J. Chang, J. Kor. Phys. Soc. 53, 196 (2008).
J. Y. Zhang, P. J. Li, H. Sun, X. Shen, T. S. Deng, K. T. Zhu, Q. F. Zhang and J. L. Wu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 021116 (2008).
B. Xiang, P. W. Wang, X. Z. Zhang, S. A. Dayeh, D. P. R. Aplin, C. Soci, D. P. Yu and D. L. Wang, Nano Lett. 7, 323 (2007).
J. S. Lee, S. N. Cha, J. M. Kim, H. W. Nam, S. H. Lee, W. B. Ko, K. L. Wang, J. G. Park and J. P. Hong, Adv. Mater. 23, 4183 (2011).
B. Bazer-Bachi, E. Fourmond, P. Papet, L. Bounaas, O. Nichiporuk, N. Le Quang and M. Lemiti, Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells 105, 137 (2012).
U. Gangopadhyay, K. Kim, S. K. Dhungel and J. Yi, J. Kor. Phys. Soc. 47, 1035 (2005).
J. I. Sohn, Y-I. Jung, S-H. Baek, S. Cha, J. E. Jang, C-H. Cho, J. H. Kim, J. M. Kim and I-K. Park, Nanoscale 6, 2046 (2014).
Y-I. Jung, B-Y. Noh, Y-S. Lee, S-H. Baek, J. H. Kim and I-K. Park, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 1 (2012).
X. Su, Z, Zhang and M. Zhu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 061913 (2006).
J. W. M. Frenken and J. F. van der Veen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 54, 134 (1985).
F. Decremps, J. Pellicer-Porres, A. M. Saitta, J.-C. Cheervin and A. Polian, Phys. Rev. B 65, 092101 (2002).
D. K. Hwang, H. S. Kim, J. H. Lim, J. Y. Oh, J. H. Yang, S. J. Park, K. K. Kim, D. C. Look and Y. S. Park, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 151917 (2005).
S. Limpijumnong, S. B. Zhang. S. H. Wei and C. H. Park, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 155504 (2005).
M. Dutta and D. Basak, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 212112 (2008).
R. L. Anderson, Solid-State Electron. 5, 341 (1962).
J. A. Aranovich, D. G. Golmayo, A. L. Fahrenbruch and R. H. Bube, J. Appl. Phys. 51, 4260 (1980).
S. M. Sze, Semiconductor Devices: Physics and Technology, 2nd edition (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 2001), Chap. 13.
S. N. Cha, J. S. Seo, S. M. Kim, H. J. Kim, Y. J. Park, S. W. Kim and J. M. Kim, Adv. Mater. 22, 4726 (2010).
J. I. Sohn et al., Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 97 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sohn, J.I., Cha, S.N., Kim, J.M. et al. Modification of electrical and piezoelectric properties of ZnO nanorods based on arsenic incorporation via low temperature spin-on-dopant method. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 67, 930–935 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.67.930
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.67.930