Abstract
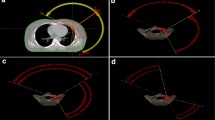
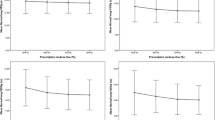
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical usefulness of modulated arc (mARC) treatment techniques. The mARC treatment plans for non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients were made in order to verify the clinical usefulness of mARC. A pre-study was conducted to find the best plan condition for mARC treatment, and the usefulness of the mARC treatment plan was evaluated by comparing it with other Arc treatment plans such as tomotherapy and RapidArc plans. In the case of mARC, the optimal condition for the mARC plan was determined by comparing the dosimetric performance of the mARC plans developed by using various parameters, which included the photon energy (6 MV, 10 MV), the optimization point angle (6°- 10°intervals), and the total number of segments (36 - 59 segments). The best dosimetric performance of mARC was observed at a 10 MV photon energy, a point angle 6 degrees, and 59 segments. The treatment plans for the three different techniques were compared by using the following parameters: the conformity index (CI), homogeneity index (HI), the target coverage, the dose to the OARs, the number of monitor units (MU), the beam on time, and the normal tissue complication probability (NTCP). As a result, the three different treatment techniques showed similar target coverages. The mARC plan had the lowest V20 (volume of lung receiving > 20 Gy) and MU per fraction compared with both the RapidArc and the tomotherapy plans. The mARC plan reduced the beam on time as well. Therefore, the results of this study provide satisfactory evidence that the mARC technique can be considered as a useful clinical technique for radiation treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ashenafi, R. A. Boyd, T. K. Lee, K. K. Lo, J. P. Gibbons, I. I. Rosen, J. D. Fontenot and K. R. Hogstrom, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 77, 836 (2010).
W. Duthoy, W. De Gersem, K. Vergote, T. Boterberg, C. Derie, P. Smeets, C. De Wagter and W. De Neve, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 60, 794 (2004).
S. Clemente, B. Wu, G. Sanguineti, V. Fusco, F. Ricchetti, J. Wong and T. McNutt, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 80, 1248 (2011).
B. J. Salter, V. Sarkar, B. Wang, H. Shukla, M. Szegedi and P. Rassiah-Szegedi, Phys. Med. Biol. 56, 1931 (2011).
K. Kainz, G. P. Chen, Y. W. Chang, D. Prah, X. Sharon Qi, H. P. Shukla, J. Stahl and X. Allen Li, Med. Phys. 38, 5104 (2011).
K. Otto, Med. Phys. 35, 310 (2008).
Y. Dzierma, F. Nuesken, N. Licht and C. Ruebe, Radiat. Oncol. 8, 193 (2013).
L. Feuvret, G. Noel, J. J. Mazeron and P. Bey, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 64, 333 (2006).
Q. Wu, R. Mohan, M. Morris, A. Lauve and R. Schmidt-Ullrich, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 56, 573 (2003).
C. Burman, G. J. Kutcher, B. Emami and M. Goitein, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 21, 123 (1991).
J. T. Lyman, Radiat. Res. Suppl. 8, S13 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.K., Jang, H.S., Kim, Y.S. et al. Evaluation of the clinical usefulness of modulated arc treatment. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 67, 232–236 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.67.232
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.67.232