Abstract
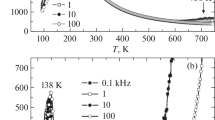
The electric modulus relaxations were considered to be coupled phenomena between the polarization fluctuations < P 2 > due to local symmetry breaking and ionic hopping through nearest neighbor sites. The Nb-rich potassium lithium niobate (K5.595Li3.125Nb11.28O30) crystals exhibited a ferroelectric diffused phase transition around the dielectric maximum temperature T max = 350. The electric modulus relaxations were characterized by using the Cole-Davidson distribution of the electric modulus relaxation times at frequencies ranging from 100 Hz to 1 MHz. Although the lattice constants along the a-axes and the c-axes and the tetragonal unit cell volume showed linear expansions with increasing temperature T, the axial ratio c/a decreased with increasing T at temperatures below the Burn’s temperature TB. The dielectric relaxation accompanied the high ionic conduction in the temperature range above T. The ac conductivity σ'(ω) was analyzed by using the formulae, where ω O is the crossover frequency. It was considered that a double-Arrhenius behavior of the dc conductivity σ dc at temperatures around the Burn’s temperature T B was suspected of thermally activated motions in the random distribution of oxygen vacancies and lithium ions. The ac universality could result in a disordered configuration of the mobile ions, i.e., the dc conductivity at temperatures above T B . The slow relaxations of the nano-sized polar regions may contribute to the dc conductivity σ dc at temperatures below T B . The characteristic relaxation time τ CD showed a change in activation energy from 1.08 eV to 0.80 eV at temperatures around T B . The scaling factor increased in proportion to (T B − T) at T T B , but was almost constant at T >T B , where ε'∞ is the high frequency dielectric constant and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Burns and F. H. Dacol, Phys. Rev. B 28, 2527 (1983).
W. Dmowski, S. B. Vakhrushev, I.-K. Jeong, M. P. Hehlen, F. Trouw and T. Egami, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 137602 (2008).
A. Rotaru, D. C. Arnold, A. Daoud-Aladine and F. D. Morrison, Phys. Rev. B 83, 184302 (2011).
J. A. Bock, S. Trolier-McKinstry, G. D. Mahn and C. A. Randal, Phy. Rev. B 90, 115106 (2014).
T. B. Schrder and J. C. Dyre, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 310 (2000).
J. R. Macdonald, Phys. Rev. B 71, 184307 (2005).
J. C. Dyre, Phys. Rev. B 48, 12511 (1993).
A. S. Nowick, A. V. Vaysleyb and I. Kuskovsky, Phys. Rev. B 58, 8398 (1998).
H. H. P. Gommans, M. Kemerink and W. H. A. Schilders, Phys. Rev. B 72, 165110 (2005).
D. Viehland, S. Jang, L. E. Cross and M. Wuttig, Phil. Mag. 64, 335 (1991).
I. Svare, S. W. Martin and F. Borsa, Phys. Rev. B 61, 228 (2000).
C. Leon, M. L. Lucia and J. Santamaria, Phys. Rev. B 55, 882 (1997).
V. Gupta and A. Mansingh, Phys. Rev. B 49, 1989 (1994).
K. L. Ngai and R. W. Rendell, Phys. Rev. B 61, 9393 (2000).
D. L. Sidebottom, B. Roling and K. Funke, Phys. Rev. B 63, 024301 (2000).
A. K. Jonscher, Dielectric Relaxation in Solids (Chelsea Dielectric Press, London, 1983).
G. A. Niklasson, J. Appl. Phys. 66, 4350 (1989).
L. A. Dissado and R. M. Hill, J. Appl. Phys. 66, 2511 (1989).
D. W. Davidson and R. H. Cole, J. Chem. Phys. 19, 1484 (1951).
K. Pathmanathan and J. R. Stevens, J. Appl. Phys. 68, 5128 (1990).
B.-E. Jun, C. S. Kim, H. K. Kim, J. N. Kim, Y. H. Hwang and D. J. Kim, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 46, 44 (2005)
G. Burns, Phys. Rev. B 13, 215 (1976).
B. M. Jin, A. S. Bhalla, B. C. Choi and J. N. Kim, Phys. Stat. Sol. A 140, 239 (1993)
J. S. Kim and J. N. Kim, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 69, 1880 (2000).
P. B. Jamieson, S. C. Abrahams and J. L. Bernstein, J. Chem. Phys. 15, 2355 (1971).
B.-E. Jun, Ph D thesis, Pusan National University, 2005.
A. W. Smith, G. Burns, B. A. Scott and H. D. Edmonds, J. Appl. Phys. 42, 684 (1971).
F. W. Ainger, J. A. Beswick, W. P. Bickley, R. Clarke and G. V. Smith, Ferroelectrics 2, 183 (1971).
T. Ikeda and K. Kiyohashi, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 9, 1541 (1970).
B. A. Scott, E. A. Giess, B. L. Olson, G. Burns, A. W. Smith and D. F. O’Kane, Mater. Res. Bull. 5, 7 (1970).
L. E. Cross, Ferroelectrics 76, 241 (1987); L. E. Cross and R. R. Neurgaonkar, J. Mater. Sci. 27, 2589 (1992).
A. J. Bell, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 5, 8773 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jun, BE., Jeong, J.H., Choi, B.C. et al. Relaxation and phase-transition characteristics of relaxor ferroelectric potassium lithium niobate. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 66, 1736–1743 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.66.1736
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.66.1736