Abstract
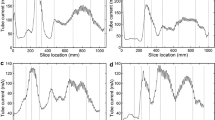
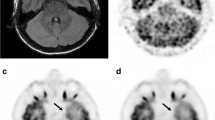
This study examined whether scanning could be performed with minimum dose and minimum exposure to the patient after an attenuation correction. A Hoffman 3D Brain Phantom was used in BIO_40 and D_690 PET/CT scanners, and the CT dose for the equipment was classified as a low dose (minimum dose), medium dose (general dose for scanning) and high dose (dose with use of contrast medium) before obtaining the image at a fixed kilo-voltage-peak (kVp) and milliampere (mA) that were adjusted gradually in 17–20 stages. A PET image was then obtained to perform an attenuation correction based on an attenuation map before analyzing the dose difference. Depending on tube current in the range of 33–190 milliampere-second (mAs) when BIO_40 was used, a significant difference in the effective dose was observed between the minimum and the maximum mAs (p < 0.05). According to a Scheffe post-hoc test, the ratio of the minimum to the maximum of the effective dose was increased by approximately 5.26-fold. Depending on the change in the tube current in the range of 10–200 mA when D_690 was used, a significant difference in the effective dose was observed between the minimum and the maximum of mA (p < 0.05). The Scheffe posthoc test revealed a 20.5-fold difference. In conclusion, because effective exposure dose increases with increasing operating current, it is possible to reduce the exposure limit in a brain scan can be reduced if the CT dose can be minimized for a transmission scan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Nakamoto, M. Osman, C. Cohade, L. T. Marshall, J. M. Links, S. Kohlmyer and R. L. Wahl, J. Nucl. Med. 43, 1137 (2002).
R. Bar-Shalom, N. Yefremov, L. Guralnik, D. Gaitini, A. Frenkel, A. Kuten, H. Altman, Z. Keidar and O. Lsrael, J. Nucl. Med. 44, 1200 (2003).
G. Antoch, N. Saoudi, H. Kuehl, G. Dahmen, S. P. Mueller, T. Beyer, A. Bockisch, J. F. Debatin and L. S. Freudenberg, J. Clin. Oncol. 22, 4357 (2004).
P. E. Kinahan, D. W. Townsend, T. Beyer and D. Sashin, Med. Phys. 25, 2046 (1998).
C. Cohade, M. Osman, L. N. Marshall and R. N. Wahl, Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 30, 721 (2003).
E. Z. Xu, N. A. Mullani, K. L. Gould and W. L. Anderson, J. Nucl. Med. 32, 161 (1991).
V. Bettinardi, E. Pagani, M. C. Gilardi, C. Landoni, C. Riddell, G. Rizzo, I. Castiqlioni, D. Belluzzo, G. Luciqnani, S. Schubert and F. Fazio, Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 26, 447 (1999).
R. Loevinger and M. Berman, J. Nucl. Med. 9, 7 (1968).
L. Michael, S. Sven-Erik and A. K. Michael, Montecarlo Calculations in Nuclear Medicine, 2nd ed. (Taylor and Francis, NY, 2012).
F. C. Robiller, K. D. Stumpe, T. Kossmann, D. Weishaupt, E. Bruder and G. K. von Schulthess, Eur. Radiol. 10, 855 (2000).
J. S. Kim, J. S. Lee and G. J. Cheon, Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 42, 112 (2008).
J. Czernin, M. Allen-Auerbach and H. R. Schelbert, J. Nucl. Med. 48, 78S (2007).
T. Beyer, D. W. Townsend, T. Brun, P. E. Kinahan, M. Charron, R. Roddy, J. Jerin, J. Young, L. Byars and R. Nutt, J. Nucl. Med. 41, 1369 (2000).
H. K. Son, T. G. Turkington, Y. Y. Kwon, H. J. Jung and H. J. Kim, Korean J. Med. Phys. 16, 192 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, EJ., Jeong, MT., Jang, SJ. et al. Evaluation of the dependence of the exposure dose on the attenuation correction in brain PET/CT scans using 18F-FDG. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 64, 114–121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.64.114
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.64.114