Abstract
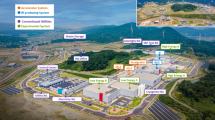
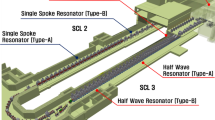
The Rare Isotope Science Project (RISP) in Korea is developing the Rare Isotope (RI) Accelerator, RAON. The RAON is planned to be an advanced RI beam using isotope separation on-line (ISOL) with a high-power target. The main goal of the ISOL facility is to deliver high-quality, intense, neutron-rich (n-rich) beams to the experimental hall; for example 108 atoms per second of the 132Sn n-rich reference isotope. The RAON ISOL facility consists of mainly two systems. One is the RI production system of a high-power uranium fission target combined with the Forced Electron Beam Induced Arc Discharge (FEBIAD) ion source, Surface Ionization (SI) ion source and Resonance Ionization Laser Ion Source (RILIS), in which system the final goal for the RI production rate is 1014 fission per second. The other is the RI beam purification system, which is comprised of an RF beam cooler, a high resolution mass separator (HRMS), a charge breeder and a charge state separator, and the design goal is to deliver the RI beam with a mass resolving power up to 45,000 and with a limit of 6 × 105 background counts per second. The current status of the ISOL facility of the RISP is reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Kofoed-Hansen and K. O. Nielsen, Mat. Fys. Medd. Dan.Vid. Selsk. 26, 1 (1951).
Baseline Design Summary of RISP (2013).
M. S. Ryu, B. H. Kang, Y.-K. Kim, S.-C. Jeong and C. C. Yun, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 60, 19 (2012).
J. H. Hamilton, A. V. Ramayya and H. K. Carter, Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on FISSION AND PROPERTIES OF NEUTRON-RICH NUCLEI. (Sanibel Island, USA, 2007).
P. W. Schmor, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 73, 707 (2002).
L. Penescu, R. Catherall, J. Lettry and T. Stora, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 81, 02A906 (2010).
A. Andrighetto et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 266, 4257 (2008).
J. S. Hendricks et al., MCNPX version 2.5.e, Los Alamos National Laboratory report LA-UR-04-0569, 2004.
M. S. Leitner, PhD. dissertation, UPC-ETSEIB / CERN, 2005.
F. Herfurth et al., Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 469, 254 (2001).
F. Wenander, Nucl. Phys. A 746, 40C (2004).
G. D. Alton, Appl. Rad. Isotop. 64, 1574 (2006).
D. W. Stracener, Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 204, 42 (2003).
LNL, SPES TDR, INFN-LNL-223 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, B.H., Kim, G.D., Woo, H.J. et al. ISOL facility for rare isotope beams at RAON. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 63, 1473–1476 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.63.1473
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.63.1473