Abstract
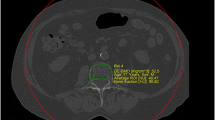
Measurements of osteoporosis might contain errors caused by the calcium drug used in the prevention and the treatment of osteoporosis. This study conducted a lumbar spine phantom experiment to examine whether a calcium drug can influence the measured values of the bone mineral density (BMD) because of the drug taken by a real patient remaining undigested in the stomach. Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) was used to measure the BMD for a calcium-drug in an equipment-dedicated lumbar spine phantom and 10 patients selected for the BMD measurement. Three types of drugs that are prescribed in actual clinical practice calcium drugs were used for the phantom experiment, and the drugs were divided into a fixed dose, 1/2 of the fixed dose, 1/4 of the fixed dose and 1/8 of the fixed dose. Without the drugs included, the phantom was scanned 60 times continuously to calculate the baseline BMD. The BMD was measured as the calcium drug coated with paraffin was placed in the lumbar vertebra 2 and the soft tissue region of the phantom. To determine when the drug was invisible to the naked eye are measured, the BMD at different drug dilutions. The measurements were conducted three times to calculate the mean. In the patient experiment, patients were selected who visited hospital after taking the drug before measuring the BMD. After a certain time had passed, the BMD was measured again to examine the difference in images and the change in BMD values due to the calcium-drug intake. The BMD measurements of lumbar 1–4 in the phantom were higher, with statistical significant, than the least significant change (LSC) in the bone region for all three drugs (Ca carbonate, Ca citrate and Ca cholecalciferol), showing a significant increase. On the other hand, there was no significant change in the soft tissue. When Ca Cholecalciferol was used in a fixed dose, the BMD of L2 increased by 11.6%, showing the largest increase among the drugs examined, but only a 2.8% increase in the BMD of L1–L4 was observed. The dependence of the results on the degree of dilution of the calcium drug showed that the three drugs had values that exceeded the LSC significantly. The measured the BMD was higher in 7 out of 10 patients when the patients took the calcium drug than when they did not. In addition, one of the patients showed a 3.6% increase in BMD. In addition, the calcium drug appeared in the image in two of the patients who showed an increase in the BMD. This confirmed that the drug remained undigested, with a certain amount of it remaining in the body system. Overall, the measured BMD is affected when the calcium drug taken by a real patient remains undigested in the stomach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Fauci, E. Braunwald, D. Kasper, S. Hauser, D. Longo, J. Jameson and J. Loscalzo, Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2008).
K. R. Dong, H. S. Kim and W. K. Chung, J. Radiol. Sci. Technol. 31, 17 (2008).
J. W. Pugh, R. M. Rose and E. L. Radin, J. Biomech. 6, 657 (1976).
NIH Consensus Development Panel on Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy, JAMA 285, 785 (2001).
S. L. Bonnick, The Osteoporosis Handbook: The Comprehensive Guide to Prevention and Treatment (Taylor Trade, New York, 1994).
S. L. Bonnick and P. D. Miller, Bone Densitometry in Clinical Practice, 2nd ed. (Humana Press, New Jersey, 2003).
International Society for Clinical Densitometry, NGC 006915, Clinical use of quantitative computed tomography and peripheral quantitative computed tomography in the management of osteoporosis in adults: the 2007 ISCD official positions, 2008.
International Society for Clinical Densitometry, NGC 006918, Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry technical issues: the 2007 ISCD official positions, 2008.
W. A. M. Brekelmans, H.W. Poort and T. J. J. H. Slooff, Acta. Orthop. Scand. 43, 301 (1972).
E. H. Kim, D. O. Shim, K. R. Dong, H. S. Kim, D. C. Kweon, E. H. Goo, S. H. Choi and W. K. Chung, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 57, 1263 (2010).
H. S. Kim and K. R. Dong, J. Korea Cont. Assoc. 9, 174 (2009).
D. Krueger, M. Checovich, D. Gemar, X. Wei and N. Binkley, J. Clin. Densitom. 9, 159 (2006).
C. E. Cann, H. K. Genant, F. O. Kolb and B. Ettinger, Bone 6, 1 (1985).
H. S. Kim, K. R. Dong and Y. H. Ryu, J. Radiol. Sci. Technol. 32, 361 (2009).
H. S. Kim, K. R. Dong and C. B. Kim, J. Korea Cont. Assoc. 9, 228 (2009).
D. L. Kendler, G. M. Kiebzak, C. G. Ambrose, C. Dinu, S. Robertson, P. Schmeer and J. L. Van Pelt, J. Clin. Densitom. 9, 97 (2006).
G. Liu, M. Peacock, O. Eilam, G. Dorulla, E. Braunstein and C. C. Johnston, Osteoporosis Int. 7, 564 (1997).
P. J. Drinka, A. A. DeSmet, S. F. Bauwens and A. Rogot, Calcified Tissue Int. 50, 507 (1992).
J. Frohn, T. Wilken, S. Falk, H. J. Stutte, J. Kollath and G. Hor, J. Nucl. Med. 32, 259 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, EH., Kim, HS., Dong, KR. et al. A study on the effects of a calcium drug on the bone mineral density (BMD) by using dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA). Journal of the Korean Physical Society 61, 1889–1897 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.61.1889
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.61.1889