Abstract
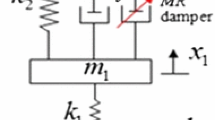
The vehicle semi-active suspension with magneto-rheological damper(MRD) has been a hot topic since this decade, in which the robust control synthesis considering load variation is a challenging task. In this paper, a new semi-active controller based upon the inverse model and sliding mode control (SMC) strategies is proposed for the quarter-vehicle suspension with the magneto-rheological (MR) damper, wherein an ideal skyhook suspension is employed as the control reference model and the vehicle sprung mass is considered as an uncertain parameter. According to the asymptotical stability of SMC, the dynamic errors between the plant and reference systems are used to derive the control damping force acquired by the MR quarter-vehicle suspension system. The proposed modified Bouc-wen hysteretic force-velocity (F-v) model and its inverse model of MR damper, as well as the proposed continuous modulation (CM) filtering algorithm without phase shift are employed to convert the control damping force into the direct drive current of the MR damper. Moreover, the proposed semi-active sliding mode controller (SSMC)-based MR quarter-vehicle suspension is systematically evaluated through comparing the time and frequency domain responses of the sprung and unsprung mass displacement accelerations, suspension travel and the tire dynamic force with those of the passive quarter-vehicle suspension, under three kinds of varied amplitude harmonic, rounded pulse and real-road measured random excitations. The evaluation results illustrate that the proposed SSMC can greatly suppress the vehicle suspension vibration due to uncertainty of the load, and thus improve the ride comfort and handling safety. The study establishes a solid theoretical foundation as the universal control scheme for the adaptive semi-active control of the MR full-vehicle suspension decoupled into four MR quarter-vehicle sub-suspension systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
MARGOLIS D L. Procedure for comparing passive, active, and semi-active approaches to vibration isolation[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 1983, 315(4): 225–238.
ZHAO Yanshui, ZHOU Kongkang, LI Zhongxing, et al. Time Lag magnetorheological damper semi-active suspensions[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(7): 221–227. (in Chinese)
ZHU Maofei, CHEN Wuwei, ZHU Hui. Time-delay variable structure control for semi-active suspension based on magneto-rheological damper[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 12(46): 113–120.
LI Rui, YU Miao, CHEN Weiming, et al. Control of automotive suspensions vibration via magneto rheological damper[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2005, 41(6): 128–132. (in Chinese)
LEE H G, SUNG K G, CHOI S B, et al. Performance evaluation of a quarter-vehicle MR suspension system with different tire pressure[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2011, 12(2): 203–210.
HONG K S, SOHN H C, HEDRICK J K. Modified skyhook control of semi-active suspensions: a new model, gain scheduling, and hardware-in-the-loop tuning[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2002, 124: 158–167.
YOKOYAMA M, HEDRICK J K, TOYAMA S. A model following sliding mode controller for semi-active suspension systems with MR dampers[J]. Proceedings of American Control Conference, 2001, 4: 2652–2657.
YAO Jialing, ZHENG Jiaqiang, GAO Weijie, et al. Sliding mode control of vehicle semi-active suspension with magnetorheological dampers having polynomial model[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2009, 21(8): 2400–2404. (in Chinese)
GUO Dalei, HU Haiyan, YI Jianqiang. Neural network control for a semi-active vehicle suspension with a magnetorheological damper[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2004, 10(3): 461–471.
CHOI S B, LEE H S, PARK Y P. H∞ control performance of a full-vehicle suspension featuring magneto-rheological dampers[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2002, 38(5): 341–360.
SONG Hui, QIU Wei, WANG Enrong. The sliding model-following control for semi-active MR-vehicle suspension[C/CD]//Processings of 2010 IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (IEEE ICNSC 2010), Chicago, USA, April 11–13, 2010.
WANG Enrong, SONG Hui, YAN Wei, et al. The hybrid sliding model-following control for semi-active MR-vehicle suspension: China, CN102004443A[P]. 2011-04-06.
WANG Wanjun, YING Liang, WANG Enrong. Comparison on models of controllable magneto-rheological dampers[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(9): 100–108. (in Chinese)
WANG Enrong, YING Liang, WANG Wanjun, et al. Semi-active control of vehicle suspension with MR-damper: Part I-controller synthesis and evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 21(1): 13–19.
WANG Enrong, YING Liang, WANG Wanjun, et al. Semi-active control of vehicle suspension with MR-damper: Part II-evaluation of suspension performance[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 21(2): 52–59.
WANG Enrong, YING Liang, WANG Wanjun, et al. Semi-active control of vehicle suspension with MR-damper: Part III-experimental validation[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 21(4): 93–100.
ZHANG Hailong, WANG Enrong, MIN Fuhong, et al. Skyhook-based semi-active control of full-vehicle suspension with magneto-rheological dampers[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 26(3): 511–518.
SPENCER B F, DYKE D J, SAIN K M, et al. Phenomenological model of a magnetorheological damper[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanic., 1997, 123(3): 230–238.
WANG D H, LIAO Wei Hsin. Magneto-rheological fluids dampers: A review of parametric modeling[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2011, 20(2): 1–34.
SANKARANARAYANAN V, EMEKLI M E, GÜVENÇ B A, et al. Semiactive suspension control of a light commercial vehicle[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2008, 13(5): 598–604.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51475246, 51277098)
ZHANG Hailong, born in 1988, is currently a PhD candidate at School of Physics and Technology, Nanjing Normal University, China. He received his master degree from School of Electric and Automation Engineering, Nanjing Normal University, China, in 2010. His research interests include the semi-active control for implementing intelligent vehicle suspension with MR dampers.
WANG Enrong, obtained his BS and MS degrees in 1985 and 1988, respectively, both from Southeast University, China and obtained his PhD degree in 2006 from Concordia University, Canada. He joined Nanjing Normal University in 1988, where he is currently professor and dean of School of Electric and Automation Engineering. His research interests focus on the semi-active control for implementing intelligent vehicle suspension with MR dampers, and the related subjects in fields of electrical engineering and automation.
ZHANG Ning, is currently a professor at School of Physics and Technology, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China. His research interests focus on magnetic materials and magnetism, condensed matter and related area.
MIN Fuhong, is currently a associate professor at School of Electric and Automation Engineering, Nanjing Normal University, China. Her research interests focus on the bifurcation and stability of discontinuous dynamic systems and its application in secure communication.
SUBASH Rakheja, is currently a professor of mechanical engineering at Concordia University, Canada. His research interests include advanced transportation systems and highway safety, human responses to workplace vibration, and driver-vehicle interactions.
SU Chunyi, is currently a professor of mechanical engineering at Concordia University, Canada. His research interests focus on automatic control theory and application about non-smooth dynamic system, hysteresis nonlinearities in smart actuators, robots.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Wang, E., Zhang, N. et al. Semi-active sliding mode control of vehicle suspension with magneto-rheological damper. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 28, 63–75 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2014.0918.152
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2014.0918.152