Abstract
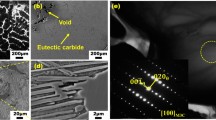
The remanufacturing blanks with cracks were considered as irreparable. With utilization of detour effect and Joule heating of pulsed current, a technique to arrest the crack in martensitic stainless steel FV520B is developed. According to finite element theory, the finite element(FE) model of the cracked rectangular specimen is established firstly. Then, based on electro-thermo-structure coupled theory, the distributions of current density, temperature field, and stress field are calculated for the instant of energizing. Furthermore, the simulation results are verified by some corresponding experiments performed on high pulsed current discharge device of type HCPD-I. Morphology and microstructure around the crack tip before and after electro pulsing treatment are observed by optical microscope(OM) and scanning electron microscope(SEM), and then the diameters of fusion zone and heat affected zone(HAZ) are measured in order to contrast with numerical calculation results. Element distribution, nano-indentation hardness and residual stress in the vicinity of the crack tip are surveyed by energy dispersive spectrometer(EDS), scanning probe microscopy(SPM) and X-ray stress gauge, respectively. The results show that the obvious partition and refined grain around the crack tip can be observed due to the violent temperature change. The contents of carbon and oxygen in fusion zone and HAZ are higher than those in matrix, and however the hardness around the crack tip decreases. Large residual compressive stress is induced in the vicinity of the crack tip and it has the same order of magnitude for measured results and numerical calculation results that is 100 MPa. The relational curves between discharge energies and diameters of the fusion zone and HAZ are obtained by experiments. The difference of diameter of fusion zone between measured and calculated results is less than 18.3%. Numerical calculation is very useful to define the experimental parameters. An effective method to prevent further extension of the crack is presented and can provide a reference for the compressor rotor blade remanufacturing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LIU Zhengdao, ZHANG Xiancheng, XUAN Fuzhen, et al. Effect of laser power on the microstructure and mechanical properties of TiN/Ti3Al composite coating on Ti6Al4V[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 26(4): 714–721.
TAN Jun, CHEN Jianmin, LIU Min, et al. Surface engineering towards green manufacturing and remanufacturing[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 47(20): 95–103. (in Chinese)
XU Binshi, DONG Shiyun, ZHU Sheng, et al. Prospects and developing of remanufacture forming technology[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(15): 96–105. (in Chinese)
TU J F, PALEOCRASSAS A G. Fatigue crack fusion in thin-sheet aluminum alloys AA7075-T6 using low-speed fiber laser welding[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2011, 211: 95–102. (in Chinese)
SCHNUBEL D, HORSTMANN M, VENTZKE V, et al. Retardation of fatigue crack growth in aircraft aluminium alloys via laser heating-Experimental proof of concept[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2012, 546: 8–14.
SONG P S, SHIEH Y L. Stop drilling procedure for fatigue life improvement[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2004, 26: 1333–1339.
ZHAO Yuguang, MA Bingdong, GUO Haicha, et al. Electropulsing strengthened 2GPa boron steel with good ductility[J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 43: 195–199.
YIN Zhenxing, LIANG Dong, CHEN Yue, et al. Effect of electrodes and thermal insulators on grain refinement by electric current pulse[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 92–97.
LIU Yan, ZHOU Hong, SU Hang, et al. Effect of electrical pulse treatment on the thermal fatigue resistance of bionic compacted graphite cast iron processed in water[J]. Materials and Design, 2012, 39: 344–349.
ZHOU Y Z, GAO J D, GAO M. Crack healing in a steel by using electropulsing technique[J]. Materials Letters, 2004, 58: 1732–1736.
GOLOVIN Y I, FINKEL V M, SLETKOV A. A. Effects of current pulse on crack propagation kinetics in silicon iron[J]. Problemy Prochnosti, 1975 (2): 86–91.
FAN Hualin, CHEN Ping. Crack arrest effect in thin plates[J]. Acta Arm Amentarii, 2005, 26(6): 791–794. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Hongchao, YU jing, HAO Shengzhi, et al. Application of electro-magnetic heat effect on arresting the crack in remanufacturing blank[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(7): 21–28. (in Chinese)
FU Yuming, TIAN Zhengguo, ZHENG Lijuan. Analysis on the thermal stress field when crack arrest in an axial symmetry metal die using electromagnetic heating[J]. Applied of Mathematics and Mechanics, 2006, 8(3): 53–55.
ZHENG Lijuan, FU Yuming, TIAN Zhenguo, et al. Analysis on temperature field on a metal component with a circle half-embedding crack at the moment when the current is switched on[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2004, 40(11): 90–93. (in Chinese)
FU Yuming, ZHOU Hongmei, WANG Junli, et al. Analysis of crack arrest by electromagnetic heating in metal with oblique-elliptical embedding crack[J]. Key Engineering Materials, Advances in Fracture and Damage Mechanics XI, 2012, 525–526: 404–408.
FU Yuming, CHAI Xuan, ZHENG Lijuan, et al. Pulse discharge strengthening of 16Mn welded joint and mechanical performance[J]. Advanced Materials Research, Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 197–198: 1460–1463.
WANG Ping, BAI Xiangzhong. Phase transformation stress and its influence for arresting crack propagation using electro-heating effect[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 22(8): 980–984. (in Chinese)
GAO Diankui, LI Hui, FU Yuming, et al. Acted a pulse current to prevent the thermal fatigue crack subcritical extending[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2001, 37(11): 28–31. (in Chinese)
LIU T J C. Thermo-electro-structural coupled analyses of crack arrest by Joule heating[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2008, 49: 171–184.
LIU T J C. Application of Thermo-Electric Joule Heating for Crack Detection[C]//International Conference on Mechanical and Electronics Engineering, Kyoto, Japan, August 1–3, 2010: 103–107.
LIU T J C. Finite element modeling of melting crack tip under thermo-electric Joule heating[J] Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2011, 78: 666–684.
CAI G X, YUAN F G. Stresses around the crack tip due to electric current and self-induced magnetic field[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 1998, 29: 297–306.
CAI G X, YUAN F G. Electric current-induced stresses at the crack tip in conductors[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1999, 96: 279–301.
CHENG D K. Field and wave electromagnetics[M]. MA: Addison-Wesley, 1983.
INCROPERA F P, DEWITT D P. Fundamentals of heat and mass transfer[M]. 5th edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2002.
BORESI A P, CHONG K P. Elasticity in engineering mechanics[M]. 2th ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2000.
ANSYS 10. 0: online documentation[DB / OL]. Canonsburg, PA: ANSYS Inc, 2005. http://www.ansys.com/Support/Documentation/.
SOSNIN O V, GROMOVA A V, FLVANOV Y, et al. Control of austenite steel fatigue strength[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2005, 27: 1186–1191.
QIN Rongshan, SU Shengxia. Thermodynamics of crack healing under electropulsing[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2002, 17(8): 2048–2052.
MA Bingdong, ZHAO Yuguang, BAI Hui, et al. Gradient distribution of mechanical properties in the high carbon steel induced by the detour effect of the pulse current[J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 49: 168–172.
NISHIMURA Toshihiko. Experimental and numerical evaluation of crack arresting capability due to a dimple[J]. Transactions of the ASME, 2005, 127: 244–250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Basic Research Program of China(973 Program, Grant No. 2011CB013402)
YU Jing, born in 1984, is currently a PHD candidate at Institute of Sustainable Design and Manufacture, Dalian University of Technology, China. Her research interests include remanufacturing technology, crack arrest technology, etc.
ZHANG Hongchao, born in 1953, is currently a professor and a doctoral supervisor at Dalian University of Technology, China. His main research interests are sustainable design and manufacturing, life cycle assessment, green manufacturing, remanufacturing.
DENG Dewei, born in 1974, is currently an associate professor at Dalian University of Technology, China. He received his PhD degree from Dalian University of Technology, China, in 2003. His main research interests are surface material microscopic structure analysis and test, nuclear pump material research and application, sustainable manufacturing and remanufacturing.
HAO Shegnzhi, born in 1970, is currently an associate professor at Dalian University of Technology, China. He received his PhD degree from Dalian University of Technology, China, in 2000. His main research interest is surface treatment by high current pulsed electron beam.
IQBAL Asif, born in 1975, is currently an associate professor at Dalian University of Technology, China. He received his PhD degree from Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China, in 2006. His main research interests are high-speed milling, intelligent manufacturing, energy modeling of machining processes for sustainability.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Zhang, H., Deng, D. et al. Numerical calculation and experimental research on crack arrest by detour effect and joule heating of high pulsed current in remanufacturing. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 27, 745–753 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2014.0414.075
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2014.0414.075