Abstract
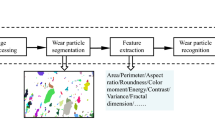
Condition based maintenance(CBM) issues a new challenge of real-time monitoring for machine health maintenance. Wear state monitoring becomes the bottle-neck of CBM due to the lack of on-line information acquiring means. The wear mechanism judgment with characteristic wear debris has been widely adopted in off-line wear analysis; however, on-line wear mechanism characterization remains a big problem. In this paper, the wear mechanism identification via on-line ferrograph images is studied. To obtain isolated wear debris in an on-line ferrograph image, the deposition mechanism of wear debris in on-line ferrograph sensor is studied. The study result shows wear debris chain is the main morphology due to local magnetic field around the deposited wear debris. Accordingly, an improved sampling route for on-line wear debris deposition is designed with focus on the self-adjustment deposition time. As a result, isolated wear debris can be obtained in an on-line image, which facilitates the feature extraction of characteristic wear debris. By referring to the knowledge of analytical ferrograph, four dimensionless morphological features, including equivalent dimension, length-width ratio, shape factor, and contour fractal dimension of characteristic wear debris are extracted for distinguishing four typical wear mechanisms including normal, cutting, fatigue, and severe sliding wear. Furthermore, a feed-forward neural network is adopted to construct an automatic wear mechanism identification model. By training with the samples from analytical ferrograph, the model might identify some typical characteristic wear debris in an on-line ferrograph image. This paper performs a meaningful exploratory for on-line wear mechanism analysis, and the obtained results will provide a feasible way for on-line wear state monitoring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG Yonghong. The study of wear particle recognition based on ferrography[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2002.
MACIAN V, PAYRI R, TORMOS B, et al. Applying analytical ferrography as a technique to detect failures in Diesel engine fuel injection systems[J]. Wear, 2006, 260(4–5):562–566.
RAADNUI S. Wear particle analysis-utilization of quantitative computer image analysis: A review[J]. Tribology International, 2005, 38(10):871–878.
ZHANG Yali, MAO Junhong, Xie Youbai. Engine wear monitoring with OLVF[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2011, 54(2):201–207.
WU Tonghai, WANG Junqun, WU Jiaoyi, et al. Wear characterization by an on-line ferrograph image[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2011, 225(1):23–34.
YUAN Chengqing, JIN Zhongmin, TIPPER J L, et al. Numerical surface characterization of wear debris from artificial joints using atomic force microscopy[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(24):4583–4588.
WU Tonghai, WANG Weigan, WU Jiaoyi, et al. Improvement on on-line ferrograph image identification[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 23(1):1–5.
WU Tonghai, MAO Junhong, WANG Jintao, et al. A new on-line visual ferrograph[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2009, 52(5):623–631.
XIAO Hanliang. The development of ferrography in China-some personal reflections[J]. Tribology International, 2005, 38(10):904–907.
WU Tonghai, WANG Junqun, PENG Yeping, et al. Description of wear debris from on-line ferrograph images by their statistical color[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2012, 55(5):606–614.
WU Tonghai, QIU Huipeng, WU Jiaoyi, et al. Image digital processing technology for visual on-line ferrograph sensor[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 44(9): 83–87. (in Chinese)
KONG N S P, IBRAHIM H. Color image enhancement using brightness preserving dynamic histogram equalization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2008, 54(4):1962–1968.
LIU Tonggang, TANG Xiaohuang, YANG Ziyi. The theory of debris group in ferrographic analysis[C]//Technical Sessions—Proceedings of CIST2008 & ITS-IFToMM2008, Beijing, China, 2009: 361–365.
YAM JYF, CHOW TWS. A weight initialization method for improving training speed in feedforward neural network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2000, 30(1–4):219–232.
HUANG Chuanhui, ZHU Hua, GE Shirong. Study on relevance between contour fractal dimension of wear debris and wear state[J]. Tribology, 2003(4): 336–339. (in Chinese)
STACHOWIAK G W, PODSIADLO P. Surface characterization of wear particles[J]. Wear, 1999, 225–229(2):1171–1185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant Nos. 50905135, 51275381)
WU Tonghai, born in 1976, is currently an associate professor at Theory of Lubrication and Beating Institute, Key Laboratory of Education Ministry for Modern Design and Rotor-Beating Systems, Xi’an Jiaotong University, China. He obtained his PhD degree from Xi’an Jiaotong University, China, in 2006. His research interests include tribology system and intelligent monitoring.
PENG Yeping, born in 1988, is currently a master candidate at Theory of Lubrication and Bearing Institute, Key Laboratory of Education Ministry for Modern Design and Rotor-Bearing Systems, Xi’an Jiaotong University, China. His research interests include tribology system and intelligent monitoring.
SHENG Chenxing, born in 1969, is currently an associate professor at Reliability Engineering Institute, School of Energy and Power Engineering, Key Laboratory of Marine Power Engineering and Technology, Wuhan University of Technology, China. He obtained his PhD degree from Wuhan University of Technology, China, in 2009. His research interests include machinery condition monitoring, fault diagnosis and control.
WU Jiaoyi, born in 1984, is currently a PhD candidate at Theory of Lubrication and Bearing Institute, Key Laboratory of Education Ministry for Modern Design and Rotor-Bearing Systems, Xi’an Jiaotong University, China. His research interests include tribology system and intelligent monitoring.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, T., Peng, Y., Sheng, C. et al. Intelligent identification of wear mechanism via on-line ferrograph images. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 27, 411–417 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2014.02.411
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2014.02.411