Abstract
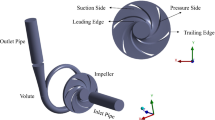
Current research on the operational reliability of centrifugal pumps has mainly focused on hydrodynamic instability. However, the interaction between the fluid and structure has not been sufficiently considered; this interaction can cause vibration and dynamic stress, which can affect the reliability. In this study, the dynamic stresses in a single-blade centrifugal pump impeller are analysed under different operating conditions; the two-way coupling method is used to calculate the fluid-structure interaction. Three-dimensional unsteady Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equations are solved with the SST k-ω turbulence model for the fluid in the whole flow passage, while transient structure dynamic analysis is used with the finite element method for the structure side. The dynamic stresses in the rotor system are computed according to the fourth strength theory. The stress results show that the highest stress is near the loose bearing and that the equivalent stress increases with the flow rate because the dynamic stresses are closely related to the pressure load. The stress distributions on the blade pressure side, suction side, leading edge, and trailing edge are each analysed for different flow rates; the highest stress distribution is found on the pressure side. On the blade pressure side, a relatively large stress is found near the trailing edge and hub side. Based on these results, a stress distribution prediction method is proposed for centrifugal pumps, which considers the interaction between the fluid and structure. The method can be used to check the dynamic stress at different flow rates when optimising the pump design to increase the pump reliability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
XING Jingtang, ZHOU Sheng, CUI Erjie. A survey on the fluid-solid interaction mechanics[J]. Advanced in Mechanics, 1997, 27(1): 19–38. (in Chinese)
ZIENKIEWICZ O C, TAYLOR R L. The finite element method[M]. Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, 2000.
ZHANG Lixiang, GUO Yakun, WANG Wenquan. FEM simulation of turbulent flow in a turbine blade passage with dynamical fluid-structure interaction[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluid, 2009, 61(12): 1299–1330.
ZHANG Lixiang, GUO Yakun, WANG Wenquan. Large eddy simulation of turbulent flow in a true 3D Francis hydro turbine passage with dynamical fluid-structure interaction[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluid, 2007, 54(5): 517–541.
CAMPBELL R L, PATERSON E G. Fluid-structure interaction analysis of flexible turbomachinery[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2011, 27(8): 1376–1391.
MUENCH C, AUSONI P, BRAUN O, et al. Fluid-structure coupling for an oscillating hydrofoil[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2010, 26(6): 1018–1033.
ZHOU Lingjiu, WANG Zhengwei, XIAO Ruofu, et al. Analysis of dynamic stresses in Kaplan turbine blades[J]. Engineering Computations, 2007, 24(8): 753–762.
PEI J, DOHMEN H J, YUAN S Q, et al. Investigation of unsteady flow-induced impeller oscillations of a single-blade pump under off-design conditions[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2012, 35: 89–104.
PEI J, BENRA F-K, DOHMEN H J. Application of different strategies of partitioned fluid-structure interaction simulation for a single-blade pump impeller[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part E: Journal of Process Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 226(4): 297–308.
YUAN Shouqi, PEI Ji, YUAN Jianping. Numerical investigation on fluid structure interaction considering rotor deformation for a centrifugal pump[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 24(4): 539–545.
KATO C, YAMADE Y, WANG H, et al. Prediction of the noise from a multi-stage centrifugal pump[C]//ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting, Houston, Texas, USA, 2005, PART B: 1273–1280.
LANGTHIEM M A, OLHOFF N. A numerical study of flow-induced noise in a two-dimensional centrifugal pump, part I: hydrodynamics[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2004, 19(3): 349–368.
FELIPPA C A, PARK K C. Staggered transient analysis procedures for coupled mechanical systems: formulation[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1980, 24(1): 61–111.
PIPERNO S, FARHAT C. Partitioned procedures for the transient solution of coupled aeroelastic problems-part II: energy transfer analysis and three-dimensional applications[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2001, 190(24–25): 3147–3170.
BATHE K J. Finite element procedures[M]. Prentice Hall: New Jersey, 1996.
BATHE K J, ZHANG H, JI S H. Finite element analysis of fluid flows fully coupled with structural interactions[J]. Computers and Structures, 1999, 72(1): 1–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant Nos. 51239005, 51009072), and National Science & Technology Pillar Program of China(Grant No. 2011BAF14B04)
PEI Ji, born in 1984, is currently an assistant research fellow at Research Center of Fluid Machinery Engineering and Technology, Jiangsu University, China. He received his doctoral degree from Jiangsu University, China, in 2013. His research interests include flow instability phenomena and fluid-structure interactions in turbomachines.
YUAN Shouqi is currently a professor and a PhD candidate supervisor at Research Center of Fluid Machinery Engineering and Technology, Jiangsu University, China. He has received 16 prizes for science and technology advancement at the province or ministry level. He has published three books and more than 240 papers. His research interests include the theory, design, and CFD of pumps and fluid machinery.
YUAN Jianping is currently a professor and a PhD candidate supervisor at Research Center of Fluid Machinery Engineering and Technology, Jiangsu University, China. His research interests include drainage and irrigation machinery.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, J., Yuan, S. & Yuan, J. Dynamic stress analysis of sewage centrifugal pump impeller based on two-way coupling method. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 27, 369–375 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2014.02.369
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2014.02.369