Abstract
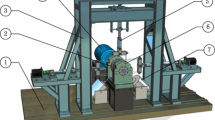
PT fuel injector is one of the most important parts of modern diesel engine. To satisfy the requirements of the rapid and accurate test of PT fuel injector, the self-adaptive floating clamping mechanism was developed and used in the relevant bench. Its dynamic characteristics directly influence the test efficiency and accuracy. However, due to its special structure and complex oil pressure signal, related documents for evaluating dynamic characteristics of this mechanism are lack and some dynamic characteristics of this mechanism can’t be extracted and recognized effectively by traditional methods. Aiming at the problem above-mentioned, a new method based on Hilbert-Huang transform (HHT) is presented. Firstly, combining with the actual working process, the dynamic liquid pressure signal of the mechanism is acquired. By analyzing the pressure fluctuation during the whole working process in time domain, oil leakage and hydraulic shock in the clamping chamber are discovered. Secondly, owing to the nonlinearity and nonstationarity of pressure signal, empirical mode decomposition is used, and the signal is decomposed and reconstructed into forced vibration, free vibration and noise. By analyzing forced vibration in the time domain, machining error and installation error of cam are revealed. Finally, free vibration component is analyzed in time-frequency domain with HHT, the traits of free vibration in the time-frequency domain are revealed. Compared with traditional methods, Hilbert spectrum has higher time-frequency resolutions and higher credibility. The improved mechanism based on the above analyses can guarantee the test accuracy of injector injection. This new method based on the analyses of the pressure signal and combined with HHT can provide scientific basis for evaluation, design improvement of the mechanism, and give references for dynamic characteristics analysis of the hydraulic system in the interrelated fields.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG Linhong, WU Bo, DU Runsheng, et al. Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of moving hydraulic cylinder[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 43(12): 12–19. (in Chinese)
CHEN Zhonghua, PAN Wei, DI Wenfeng. Fault diagnosis of gear pump based on pressure signals analyzing and features extracting[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2007, 35(1): 237–240. (in Chinese)
YANG Tielin, GAO Yingjie, KONG Xiangdong. Investigation on wavelet-based method of fault diagnosis for a piston pump[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2005, 41(2): 112–116. (in Chinese)
CHEN Xiong. Research of multilayer diagnosis based on distributed networks and its application to hydraulic pressure system[D]. Nanjing: PLA University of Science and Technology, 2008. (in Chinese)
HUANG N E, SHEN Z, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and nonstationary time series analysis[C]//Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 1998, London: A 454: 903–995.
LI Helong, YANG Lihua, HUANG Daren. The study of the intermittency test filtering character of Hilbert-Huang transform[J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2005(70): 22–32.
ZHONG Youming, QIN Shuren. Research on the uniform theoretical basis for Hilbert-Huang transform[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2006, 25(3): 40–43. (in Chinese)
PENG Z K, TSE P W, CHU F L. An improved Hilbert-Huang transform and its application in vibration signal analysis[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2005, 286(1): 187–205.
DENIS Donnelly. Enhanced empirical mode decomposition[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2008, 5 073(1): 696–706.
ZHANG Yushan. Hilbert-Huang transform and Hilbert spectrum of earthquake ground motion[D]. Beijing: Instutute of Geophysics, China Seismlogical Bureau, 2003. (in Chinese)
ZHANG R R. Characterizing and quantifying earthquake-induced site nonlinearity[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2006, 26(8): 799–812.
XIANG Lin, TANG Guiji, HU Aijun. Vibration signal’s time-frequency analysis and comparison for a rotating machinery[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2010, 29(2): 42–45. (in Chinese)
PENG Z K, TSE P W, CHU F L. A comparison study of improved Hilbert-Huang transform and wavelet transform: Application to fault diagnosis for rolling bearing[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2005(19): 974–988.
ZHENG Min, SHEN Fan, DOU Yuping, et al. Modal identification based on Hilbert-Huang Transform of structural response with SVD preprocessing[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2009, 25(6): 883–888.
PENG Z K, CHU F L. Application of the wavelet transform in machine condition monitoring and fault diagnostics: a review with bibliography[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signals Processing, 2003(18): 199–221.
ZHANG Jianming, ZHANG Weigang, WANG Yawei, et al. Study on high pressure physical properties of diesel oil[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2005, 19(1): 41–44. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
WANG Xinqing, born in 1963, is currently a professor at University of Science & Technology of Chinese People’s Liberation Army, China. He received his PhD degree from Tianjin University, China, in 1998. His research interests include mechanical-electronic engineering, fault diagnosis and signal processing.
LIANG Sheng, born in 1986, is currently a PhD candidate at University of Science & Technology of Chinese People’s Liberation Army, China. He received his bachelor degree from University of Science & Technology of Chinese People’s Liberation Arm, China, in 2006. His research interests include condition monition and fault diagnosis of the hydraulic system.
XIA Tian, born in 1983, is currently an engineer at Bureau of Navy Engineering Design & Research, China. He received his PhD degree from University of Science & Technology of Chinese People’s Liberation Army, China, in 2010. His research interests include machine design and signal processing.
WANG Dong, born in 1985, is currently a PhD candidate at University of Science & Technology of Chinese People’s Liberation Army, China. e]dyhkxywangdong@163.com
QIAN Shuhua, born in 1964, is currently an engineer at University of Science & Technology of Chinese People’s Liberation Army, China. She received her master degree from University of Science & Technology of Chinese People’s Liberation Army, China, in 2003. Her research interests include automatic control and computer measurement.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Liang, S., Xia, T. et al. Floating clamping mechanism of PT fuel injector and its dynamic characteristics analysis. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 25, 550–556 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2012.03.550
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2012.03.550