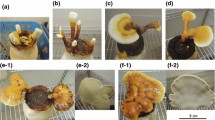
Abstract
The content of ginsenosides in ginseng is known to differ based on the parts, including root, leaf, and flower buds. Ginseng flower buds cultivated in Korea and China contain the highest amount of Re of 3.455 and 2.727%, respectively. However, Sanchi flower bud cultivated in China contained the highest amount of ginsenoside-Rb1 (3.738%).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jang JG, Lee KS, Kwon DW, Nam KY, and Choi JH (1983) Study on the changes of saponin contents in relation to root age of Panax ginseng. Korean J Food Nutr 12, 37–40.
Kaku T, Miyata T, Uruno T, Sako I, and Kinoshita A (1975) Chemico-pharmacological studies on saponins of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. Arzneimittelforschung 25, 539–547.
Kitagawa I, Taniyama T, Shibuya H, Nota T, and Yoshikawa M (1987) Chemical studies on crude drug processing. V. On the constituents of ginseng radixrubra (2): Comparison of the constituents of white ginseng and red ginseng prepared from the same Panax ginseng root. Yakugaku Zasshi 107, 495–505.
Ko SK, Lee KH, Hong JK, Kang SA, Sohn UD, Im BO, Han ST, Yang BW, Chung SH, and Lee BY (2005) The change of ginsenoside composition in ginseng extract by the vinegar process. Food Sci Biotechnol 14, 509–513.
Mochizuki M, Yoo YC, Matsuzawa K, Sato K, Saiki I, Tonooka S, Samukawa K, and Azuma I (1995) Inhibitory effect of tumor metastasis in mice by saponins, ginsenoside-Rb2, 20(R)- and (S)-ginsenoside-Rg3, of red ginseng. Biol Pharm Bull 18, 1197–1202.
Shibata S, Tanaka O, Ando T, Sado M, Tsushima S, and Ohsawa T (1966) Chemical studies on oriental plant drugs (XIV). Protopanaxadiol, a genuine sapogenin of ginseng saponins. Chem Pharm Bull 14, 595–600.
Yokozawa T, Kobayashi T, Oura H, and Kawashima Y (1985) Studies on the mechanism of the hypoglycemic activity of ginsenoside-Rb2 in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Chem Pharm Bull 33, 869–872.
Yoon SH and Joo CN (1993) Study on the preventive effect of Ginsenosides against hypercholesterolemia and its mechanism. J Ginseng Res 17, 1–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, S.K., Cho, O.S., Bae, H.M. et al. Quantitative analysis of ginsenosides composition in flower buds of various ginseng plants. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 54, 154–157 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2011.025
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2011.025