Abstract
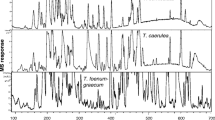
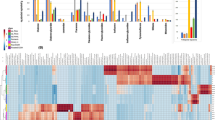
Metabolic profiling of cactus samples collected on Jeju Island (Opuntia ficus-indica) and in Sinan, Jeonnam province (O. Humifusa) was carried out using high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy (HPLC-ESI-MS) and multivariate statistical analysis. The samples were classified into two characteristic groups and the flavonoid glycosides accounting for the observed variations were identified by MS/MS analysis. This approach provided an overview of the differences among plant products originating from differences in the genetic nature of plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESI:
-
electrospray ionization
- HPLC:
-
high performance liquid chromatography
- MS:
-
mass spectroscopy
- PCA:
-
principal component analysis
References
Eriksson L, Johansson E, Kettaneh WN, and Wold S (2001) In Multi- and mega-variate data analysis. Umetrics Academy, Umea, Sweden.
Galati EM, Monforte MT, Tripodo MM, d’Aquino A, and Mondello MR (2001) Antiulcer activity of Opuntia ficusindica (L.) Mill. (Cactaeceae): ultrastructural study. J Ethnopharmacol 76, 1–9.
Ibanez CR and Roman RR (1979) Hypoglycemic effect of Opuntia cactus. Arch Invest Med 10, 223–230.
Jeong SJ, Jun KY, Kang TH, Ko EB, and Kim YC (1999) Flavonoids from the fruits of Opuntia ficus-indica var. saboten. Korean J Pharmacogn 30, 84–86.
Kim JK, Ryu TH, Sohn SI, Kim JH, Chu SM, Tu CY, and Baek HJ (2009) Metabolic fingerprinting study on the substantial equivalence of genetically modified (GM) Chinese cabbage to non-GM cabbage. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 52, 186–192.
Lee EH, Kim HJ, Song YS, Jin C, Lee TK, Cho J, and Lee YS (2003) Constituents of the stems and fruits of Opuntia ficus-indica var. saboten. Arhc Pharm Res 26, 1018–1023.
Lee KS, Kim MG, and Lee KY (2004) Antimicrobial effects of the extracts of the cactus Cheonnyeoncho (Opuntia humifusa) against food borne pathogens. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 33, 1268–1272.
Lee KS, Oh CS, and Lee KY (2005) Antioxidative effect of the fractions extracted from a cactus Cheonnyeoncho (Opuntia humifusa). Korean J Food Sci Technol 37, 474–478.
Lee KY, Lee KS, and Lee CH (2007) Antioxidative and antimicrobial effects of taxifolin isolated from a cactus Cheonnyeoncho (Opuntia humifusa). FASEB J 21, 1083–1084.
Li Z and Taylor NP (2007) Cactaceae. In Flora of China 13, Wu Z and Raven P (eds.), pp. 209–212. Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis, MO, U.S.A.
Lopez D (1995) Use of the fruits and stem of prickly pear cactus (Opuntia spp.) into human food. Food Sci Technol Int 1, 65–74.
Parfitt BD and Gibson AC (2004) Cactaceae. In Flora of North America 4, Flora of North America Editorial Committee (ed.), pp.92–2577. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, U.S.A.
Park EH, Kahng JH, and Paek EA (1998) Studies on the pharmacological actions of cactus: identification of its anti-inflammatory effect. Arch Pharm Res 21, 30–34.
Park SH, Kim H, and Rhyu DY (2007) Flavonoids from the stems of eastern picklypear Opuntia humifusa, Cactaceae. J Appl Biol Chem 54, 254–258.
Saleem M, Kim HJ, Han CK, Jin C, and Lee YS (2006) Secondary metabolites from Opuntia ficus-indica var. saboten. Phytochemistry 67, 1390–1394
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H., Park, S.H. Metabolic profiling and discrimination of two cacti cultivated in Korea using HPLC-ESI-MS and multivariate statistical analysis. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 52, 346–352 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2009.062
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2009.062