Abstract
When we respond to a stimulus, our ability to quickly execute this response depends on how combinations of stimulus and response features match to previous combinations of stimulus and response features. Some kind of memory representations must be underlying these visuomotor repetition effects. In this paper, we tested the hypothesis that visual working memory stores the stimulus information that gives rise to these effects. Participants discriminated the colors of successive stimuli while holding either three locations or colors in visual working memory. If visual working memory maintains the information about a previous event that leads to visuomotor repetition effects, then occupying working memory with colors or locations should selectively disrupt color–response and location–response repetition effects. The results of two experiments showed that neither color nor spatial memory load eliminated visuomotor repetition effects. Since working memory load did not disrupt repetition effects, it is unlikely that visual working memory resources are used to store the information that underlies visuomotor repetitions effects. Instead, these results are consistent with the view that visuomotor repetition effects stem from automatic long-term memory retrieval, but can also be accommodated by supposing separate buffers for visual working memory and response selection.
Similar content being viewed by others
When we make a response to a stimulus, the speed of that response is dependent on whether stimulus properties repeat across trials. However, such repetition effects can depend on whether the response repeats as well, such that the repetition of feature–response pairings affects speeded responses. For example, if the location of a stimulus repeats along with the response to the previous stimulus across subsequent trials, observers’ response times (RTs) are faster than if one of these two features (location or response) changes across back-to-back trials. Given that these visuomotor repetition effects are defined as an effect of the past on present behavior, some kind of memory storage must be at work. The goal of this study was to test the hypothesis that visual working memory stores the representations that cause visuomotor repetition effects. Before discussing the potential role of visual working memory in visuomotor repetition effects, we will briefly review what they are and how they are explained.
Visuomotor repetition effects are one of many kinds of repetition effects that can be observed in speeded decision-making. Repetition of a stimulus location (inhibition of return: Posner & Cohen, 1984; position priming: Maljkovic & Nakayama, 1994), repetition of stimulus category, color, or shape (stimulus repetition effect: Pashler & Baylis, 1991; priming of pop-out: Maljkovic & Nakayama, 1994), and repetition of the motor response (response repetition effect: Bertelson, 1965) can independently affect the speed of responses. However, whether the repetition of a single stimulus feature (such as the location or color of a stimulus) affects response time often depends on whether the response also repeats (Hommel, 1998; Hommel, Proctor & Vu, 2004; Hommel, Memelink, Zmigrod, & Colzato, 2014; Kleinsorge, 1999; Rothermund, Wentura, & De Houwer, 2005). These visuomotor repetition effects have been explained by the theory of event coding, as we describe next.
The theory of event coding borrows the concept of incidental feature-binding from object-file theory (Kahneman, Treisman, & Gibbs, 1992) and includes response codes as features that can be bound with stimulus codes into what are called event files (Henson, Eckstein, Waszak, Frings, & Horner, 2014; Hommel, 1998, 2005; Hommel & Colzato, 2004; Hommel et al., 2004; ). The core idea is that responding to a stimulus causes features of that stimulus (i.e., its location, color, or shape) to be automatically associated with, or bound to, the response codes that co-occurred during that stimulus-processing episode. These event files can then influence how quickly we can respond to a subsequent stimulus, leading to partial repetition costs. Partial repetition costs occur when a current event contains information that partially matches an event file. For example, producing a response to a leftward stimulus requiring an index-finger response is typically slower after having recently produced a middle-finger response to a leftward stimulus. This is because, in this case, the left location code is bound to the index response code in the current event file, and this binding must be updated to produce the correct response (Hommel, 2004). When all stimulus and response features repeat, the match between the current event and the features in an event file can facilitate response time, although in some cases response times are no faster than when no features match (a full switch; Hommel, 1998). Whether or not full-repeats facilitate responding relative to the intuitive baseline of full-switches may depend on the number of feature–response alternatives, as many-to-one stimulus–response mappings tend to show full-repeat advantages (cf. Experiments 1 and 2 from Hilchey, Rajsic, Huffman, & Pratt, 2017a).
Despite considerable research, there have been few investigations into what memory system stores event files. On the one hand, the event files that lead to visuomotor repetitions effects are hypothesized to be relatively transient, which may suggest that a temporary information storage system is responsible (Hommel, 2004; Hommel & Colzato, 2009; see Hommel, 2019, for a recent summary of this proposal). Such transience is supported by the findings that the magnitude of visuomotor repetition effects does not appear to depend on the relative frequency of specific feature combinations (Colzato, Raffone, & Hommel, 2006), and that manipulations that increase repetition effects do not necessarily lead to larger incidental stimulus–response learning (Moeller & Frings, 2017). In other words, incidental associations between features of events seem not to be represented in long-term memory. More broadly, Pashler and Baylis (1991) found that stimulus–response repetition effects were strongest when a specific stimulus repeated rather than just the response category, but that practice-related response-time improvements were more categorical, which implies that repetition effects are driven by different codes than learning effects. Thus, broadly speaking, repetition effects may occur at least partly because the most recently used stimulus–response link is still actively maintained in working memory between successive decisions (Oberauer, 2009; Schneider & Anderson, 2011). If this is the case, a concurrent working memory load ought to disrupt these repetition effects. It is also, however, plausible that repetition effects are largely independent of working memory. Rather, the repetition effects may reflect the more or less automatic consequence of stimulus processing, and dual-route models of performance tend to associate automaticity with long-term memory (Logan, 1990). Consistent with this possibility, visuomotor repetition effects are robust even when people have to make decisions about one or more stimuli in between two sequentially presented stimulus events (Hilchey et al., 2017a; Rajsic, Bi, & Wilson, 2014; Wilson, Castel, & Pratt, 2006), similar to stimulus–task bindings (Pösse, Waszak, & Hommel, 2006; Waszak, Hommel, & Allport, 2003). If repetition effects depend instead on memory resources that do not overlap with working memory, then we should see that working memory load leaves repetition effects just as potent as in the absence of load.
The logic of our tests is simple; we will fill visual working memory with different types of feature information to assess whether this knocks out the visuomotor repetition effects. That is, the present design takes advantage of the fact that visual working memory is highly capacity limited (Luck & Vogel, 1997; Cowan, 2001). As such, if information about previous stimulus features and locations is represented using these limited-capacity resources, then requiring participants to maintain additional stimulus information in visual working memory should interfere with the maintenance of a previous target’s location or color, thus reducing or eliminating the repetition effects. Furthermore, if visuomotor repetition effects involve codes stored in visual working memory, then it should be possible to selectively disrupt location–response repetition effects and color–response repetition effects using location and color memory load, respectively. We expect this selective disruption because storage of color and location in working memory appears to depend on which features are task relevant (Woodman & Vogel, 2008; Woodman, Vogel, & Luck, 2012, but see Olson, Jiang, & Chun, 2000). To test whether visuomotor repetition effects are supported by visual working memory resources, we conducted two experiments, each of which required two-alternative forced-choice color discrimination responses to sequentially presented stimuli in the presence or absence of visual working memory load (see Fig. 1). In addition to varying the presence of visual working memory load, we varied whether participants were required to maintain locations or colors in memory to assess whether the type of working memory load would selectively disrupt the visuomotor repetition effects. To preview our results, both experiments indicated that visuomotor repetition effects were robust against visual working memory loads, suggesting that visual working memory is not responsible for visuomotor repetition effects.
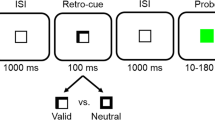
Illustration of a sample trial from Experiment 1. Stimuli are not drawn to scale. The memory probe array depicts a different location, same color probe
Experiment 1
Experiment 1 provided a first test of the role of visual working memory in visuomotor repetition effects. Participants completed a discrimination task where they made key-press responses to serially presented target colors appearing randomly at one of two locations, with and without a concurrent memory load. More specifically, trials consisted of two tasks: a change detection task and a target discrimination task. Each trial started with an array of colored rectangles, which either required memorization (until the end of the trial) or not. This was followed by two sequentially presented colored rectangles, each randomly left or right of fixation, with both requiring an arbitrary key-press discrimination response (e.g., index finger for green and blue, middle finger for red and purple) and with the appearance of the second being temporally contingent on the response to the first. On memory load trials, one group of participants was instructed to remember the locations of three colored squares that appeared at the beginning of trials, whereas another group was instructed to remember their colors for a memory probe task that occurred after the two sequentially presented colored rectangles. The to-be-remembered colors and locations were always different than the target colors and locations used in the key-press discrimination task. Visuomotor repetition effects were measured for color–response combinations (same color/same response, different color/same response, and different color/different response) and location–response combinations (same location/same response, different location/same response, and different location/different response).
Method
Participants
Thirty-five undergraduates enrolled in a first-year psychology course at the University of Toronto volunteered to participate for either course credit or monetary compensation ($10). Seventeen participants completed the color WM version of our task, and eighteen participants completed the spatial WM version of our task. All participants provided informed consent before participating. The average participant age was 20.4 years (SD = 2.2), and 25 participants were female.
Stimuli and apparatus
Stimuli were displayed on the black background (RGB: 0, 0, 0) of a 17-in. CRT monitor, which was connected to a Dell computer running custom Python software. Head position was stabilized with a chin and head rest 50 cm from the monitor. Responses were made on a standard QWERTY keyboard. During experimental trials, there was always a fixation stimulus, a white crosshair (0.15° × 0.15° of visual angle), at the center of the monitor.
Memory preview displays
Three preview colors (1.00° × 1.00° filled squares) were randomly selected, without replacement, from a list that included white, orange, yellow, khaki, brown, and slate gray. These colors appeared at locations on the circumference of an imaginary circle (radius = 4.00°) that was centered on fixation. The color locations were randomly selected, without replacement, from a list of polar coordinates that included 30°, 60°, 90°, 120°, 150°, 210°, 240°, 270°, 300° and 330°. Importantly, the potential locations of color targets were not included in the set of potential memory preview locations. No key-press responses were made during this display.
Color target displays
One gray outline box (1.00° × 1.00°) appeared at the center of the display, and two additional outline boxes were positioned 4.00° away from center on the left (180° in polar coordinates) and right side (0° in polar coordinates). Target colors were red, green, blue and purple. The left or right outline box was filled with the target color. Two colors were responded to with the “o” key (right index finger) and the other two were responded to with the “p” key (right middle finger). These color–response mappings were counterbalanced across participants.
Memory probe displays
A single probe color (1.00° × 1.00° filled square) appeared at one of the possible locations in the memory preview display. On half of all trials, the memory probe appeared at the same location as a preview color, and on the other half it appeared randomly at one of the unused preview locations. On half of all trials, the probe was the same color as a preview color and on the other half it was one of the unused preview colors. Depending on the condition, participants made either no response to the probe (control), or indicated whether the preview and probe color or location matched (“q” key, left middle finger; “w” key, left index finger for mismatch) in the visual and spatial working memory conditions, respectively.
Trial feedback displays
All trials ended with two feedback displays. The first feedback display indicated whether an error had been made to the target colors. If an error was made, an error message appeared along with the color–response mappings. If there were no errors, the message “Successful target identifications” appeared. The second feedback display, which applied only to the memory conditions, indicated whether a correct response was made to the memory probe. If an error was made, an error message appeared along with the probe–response mappings. If there was no error, the message “Successful memory” appeared. All feedback was displayed in white font, was centered on the display and was acknowledged with the spacebar.
Procedure
Possible trial sequences are illustrated in Fig. 1. Each trial began with the appearance of the fixation cross. Half a second later, the memory preview display appeared for 500 ms. In the color working memory condition, participants were told to remember the preview colors without verbalizing them. Participants were also informed that (1) the preview locations were irrelevant, (2) there was a 50% chance that the memory probe color would match a memory preview color, and (3) the target colors were never preview or probe colors. In the spatial working memory condition, participants were told to remember the preview color locations without verbalizing them. Participants were also informed that (1) the preview colors were irrelevant, (2) there was a 50% chance that the memory probe color would match a memory preview color and a 50% chance that the memory probe location would match a memory preview location, and (3) the target locations were never preview or probe locations. In the control condition, participants were told that both the memory preview and probe displays were completely meaningless and should be ignored.
Half a second after the disappearance of the memory preview display, the gray outline boxes appeared, which signaled the beginning of the color target displays. The first target color appeared 500 ms later, in either the left or right box. After the response, the target disappeared. One and a half seconds later, the second target color appeared, in either the left or right box. After the response, the target and outline boxes disappeared. Each target color and location was randomly selected, of which all participants were duly informed. Participants were told to keep their gaze on the fixation stimulus at all times and that their goal was to respond as quickly and accurately as possible to the colors.
Half a second after the disappearance of the color target displays, the memory probe display appeared. In the control condition, the memory probe display remained onscreen for 750 ms, after which the probe disappeared and trial feedback appeared. In the working memory conditions, the memory probe display remained onscreen until a response was made, after which the feedback screen appeared. There was a 500-ms black screen between trials. Participants were told that the goal was to respond as accurately possible to memory probes.
Design
Each participant performed the control condition first, as pilot testing revealed that participants found it very difficult to learn the arbitrary color–response mapping and remember the items in the memory preview display at the same time. Half of the participants completed the visual working memory condition after the control condition, whereas the other half completed the spatial working memory condition after the control. Each condition comprised 192 experiment trials. Prior to the experimental trials, each participant practiced, and was free to ask questions to the experimenter (M.D.H.), until they were ready to begin. Data from practice trials were not recorded.
Analysis
In analyzing RT data, we first excluded participants whose overall memory performance was not statistically different from chance performance (57.29%, n = 2, both from the color memory condition). Following that, we excluded trials with target errors on the color target displays, which accounted for 5.4% of trials. Next, any trial with a RT to the first target or second target that were 2.5 standard deviations above or below each participant’s mean response times to the first and second color targets, respectively, were excluded as outliers, which accounted for 2.4 and 2.5% of the total trials, respectively. Finally, we only analyzed RTs on trials with correct memory responses (75.5% of all trials), to help ensure that the preview stimuli were indeed in working memory. Memory accuracy for included participants was 69.9% (SD = 10.5%) in the color load condition and 80.2% (SD = 7.5%) in the location load condition. Overall, 80% of trials were retained for analysis. First and second target accuracy on trials with target response errors included (but other exclusion criteria applied) was near ceiling, Mfirst = 97.3, SDfirst = 1.5% Msecond = 97.6%, SDsecond = 1.9%.
Results
Mean RTs are shown in Fig. 2. The working memory loads did not reduce either the color–response repetition effect (i.e., the main effect of stimulus–response repetition) or the location–response repetition effect (i.e., the interaction between location repetition and stimulus–response repetition). In fact, working memory load increased the stimulus–response repetition effect (for both location and color load), which is the opposite of what one would expect if event files were held in working memory. These findings suggest that visual working memory does not maintain the representations underlying the speeding of RTs due to repetitions.
Second target response times in Experiment 1 as a function of color–response repetition type (horizontal axes), location repetition (gray lines: location repeat, black lines: location switch), memory load (present: solid lines, absent: dashed lines), and load type (color load, left panel, spatial load, right panel). Error bars depict one standard error of the mean
The data were analyzed with a mixed-model ANOVA, with load type (color or spatial) as a between-subjects factor and load (present or absent), location repetition (repeat or switch), and color–response repetition (both repeat, response repeat, both switch) as within-subjects factors. Greenhouse–Geisser corrections were applied when sphericity assumptions were violated, though these corrections did not change any inferences. We first checked that the expected visuomotor repetition effects were elicited in this task. Color–response repetitions affected RTs, F(1.61, 50.00) = 55.32, p < .001, ηp2 = .64, with faster RTs when the color and response repeated than when only the response repeated or when neither repeated. Location repetition reduced RTs overall, F(1, 31) = 4.68, p = .04, ηp2 = .13, but its effect differed in combination with response repetition, F(1.62, 50.10) = 33.69, p < .001, ηp2 = .52. As expected, location repetitions speeded RT when the response repeated, but slowed it when the response switched. Thus, we indeed observed the visuomotor repetitions effects that we sought to selectively reduce via working memory load.
We next checked whether memory load of either type (location or color) affected visuomotor repetition effects. Memory load slowed overall RTs, F(1, 31) = 23.35, p < .001, ηp2 = .43, but only interacted weakly with color–response repetition, F(2, 62) = 3.20, p = .05, ηp2 = .09. As is shown in Fig. 2, color–response repetition was slightly more advantageous to performance with than without memory load. Without memory load, color–response repetitions were 98 ms (SE = 24 ms) faster than partial repetitions, but with memory load, color–response repetitions were 121 ms (SE = 45 ms) faster than partial repetitions. Load did not interact with location repetition, F(1, 31) = 0.03, p = .88, ηp2 = .001, nor did it interact with the location–response repetition effect (that is, the location × color–response repetition effect), F(2, 62) = 0.55, p = .58, ηp2 = .02. Thus, adding a memory load did not reduce visuomotor repetition effects, and in the case of color–response repetition effects, may have instead increased them.
Most critically for the present study, the type of load made little to no difference to any of the repetition effects, location × load type: F(1, 31) = 3.04, p = .09, ηp2 = .09; color–response repetition × load type: F(1.61, 50.00) = 1.76, p = .19, ηp2 = .05; color–response repetition × location repetition × load type: F(1.62, 50.10) = 0.46, p = .59, ηp2 = .02; location repetition × load × load type: F(1, 31) = 0.14, p = .72, ηp2 = .004; color–response repetition × load × load type: F(2, 62) = 0.01, p = .99, ηp2 < .001; location repetition × color–response repetition × load × load type: F(2, 62) = 1.01, p = .37, ηp2 = .03. This shows that neither the specific kind of information being remembered, nor the instruction to attend to one dimension, affected the robustness of repetition effects. Load type also did not affect overall response time, F(1, 31) = 0.18, p = .68, ηp2 = .006, and there was no load × load type interaction either, F(1, 31) = 1.32, p = .26, ηp2 = .041.
We conducted two additional analyses; one to independently assess the robustness of the visuomotor repetition effects with and without working memory load and another to assess the likelihood of there being no interaction between working memory load and visuomotor repetition effects. First, we analyzed our data separately for the no load and memory load conditions to ensure that visuomotor repetition effects robustly occurred in both conditions. They did: With no memory load, color–response repetition had a strong effect on RT, F(1.50, 46.36) = 49.68, p < .001, ηp2 = .62, and it interacted with location repetition, F(2, 62) = 27.47, p < .001, ηp2 =.47. The same was true with memory load. Color–response repetition strongly affected RT, F(2, 62) = 48.32, p < .001, ηp2 =.61, and it interacted with location repetition, F(1.66, 51.51) = 14.89, p < .001, ηp2 =.32. A careful reader may notice that the ηp2 for the location–response repetition effect in the memory condition is about half of that of the no-memory condition. However, this is due to noisier data, as the mean squared value for this interaction effect is actually larger in the memory condition (0.05, compared with 0.03 in the no-load condition). Our second approach was to calculate Bayes factors using JASP (JASP Team, 2018) for the critical interaction effects. Specifically, we used the Bayes factor for inclusion, which estimates the change in prior probability to posterior probability (given the data) of the set of models including a particular effect. The BFinclusion estimate for the load × location repetition × color–response repetition was 0.013, meaning that this effect was 76.92 times more likely to not exist. Similarly, the BFinclusion estimate for the four-way interaction (including load type) was 6.032 × 10-6, meaning it is 1.66 × 105 times more likely that this interaction does not exist. Thus, we believe the data compel a rejection of the hypothesis that representations in visual working memory underlie these repetition effects.
It is possible that visual working memory load did reduce color–response and location–response repetition effects by way of reducing target–response errors instead of RT, or by affecting how many locations and/or colors could be remembered. Before proceeding we note that this analysis should be read with caution, as the low error rates led to some observations being at ceiling (i.e., 100% performance), which artificially restricts variability and can produce spurious differences. Two conditions contained zero errors, and thus zero variability. The mean error rates for each condition can be seen in Fig. 3.
We found evidence that both color–response repetition, F(1.54, 47.65) = 38.18, p < .001, ηp2 =.55, and location–response repetition, F(2, 62) = 21.49, p < .001, ηp2 =.41, affected errors as they affected response time. However, with respect to color–response repetition, partial repetitions led to uniquely high error rates, unlike with response times. Location switches led to higher errors overall, F(1, 31) = 11.49, p = .002, ηp2 =.27, although this is best interpreted in light of the location–response repetition effect, as partial repetitions of location–response bindings (specifically, repeating a response to a target in a new location) seem to be driving this main effect. The location repetition effect interacted with load type, F(1, 31) = 5.92 p = .02, ηp2 = .16, such that a location switch affected errors more for color-load participants. Load also interacted with location repetition, such that location repetition mattered more with memory load than without load, F(1, 31) = 7.05, p = .012, ηp2 = .19. The location–response repetition effect interacted with load type, F(2, 62) = 2.94, p = .06, ηp2 = .09, such that it was most pronounced for participants in the color load condition. Finally, load and load type interacted, F(1, 31) = 5.92, p = .02, ηp2 = .16, such that spatial memory load lowered, but color memory load slightly increased errors. As is evident in Fig. 3, this is largely attributable to the uniquely low error rates when target location repeated in the spatial memory load condition. Additionally, a Bayesian ANOVA revealed that the BFinclusion for the memory load × color–response repetition × location–response repetition effect was 0.06, meaning a null effect was 16.67 times more probable, and the BFinclusion for the four-way interaction (including load type) was 1.25 × 10-4, meaning a null effect was 8, 000 times more probable. In sum, the accuracy data do not support a reduction in the potency of color–response or location–response repetitions in producing errors under load.
Additionally, we analyzed the effect of repetition type on change-detection performance. Change detection performance was quantified as Cowan’s k using the equation N × (HR − FAR), where N is the number of to-be-remembered items and HR and FAR are the hit rate and false alarm rate, respectively (Rouder, Morey, Morey, & Cowan, 2011). These data are shown in Fig. 4. While there was an effect of load type, F(1, 31) = 8.32, p = .007, ηp2 = .21, reflecting the lower capacity estimates for color memory, there were no effects of color–response repetition, F(2, 62) = 1.71, p = .19, ηp2 = .05, location repetition, F(1, 31) = 0.22, p = .64, ηp2 = .007, or location–response repetition, F(2, 62) = 0.42, p = .66, ηp2 = .01. Load type did not interact with location repetition, F(1, 31) = 0.24, p = .63, ηp2 = .008, or color–response repetition, F(2, 62) = 0.65, p = .53, ηp2 = .02, nor with location–response repetition, F(2, 62) = 1.90, p = .16, ηp2 = .06. A Bayesian ANOVA revealed that the null model was 4.24 times more likely than the next best model (a main effect of color–response repetition).
Memory performance following repetition types in Experiment 1. Error bars depict one standard error of the mean
Discussion
Experiment 1 showed little to no direct relationship between visual working memory and the repetition effects (location repetition × response repetition; color–response repetition) that occur when serially presented stimuli are discriminated. If such information was stored in visual working memory, concurrent memory load ought to have selectively eliminated visuomotor repetition effects depending the information (location or color) held in visual working memory. Instead, both color–response and location–response repetition effects were robust against, and largely unaltered by, visual working memory load.
However, the design of Experiment 1 had some drawbacks. First, memory load (but, critically, not load type) was confounded with block order, in that participants always completed the memory load trials in the second half of the experiment. We did this for practical reasons, but it is a concern no less. Second, the memory load was imposed before the two discrimination stimuli were presented. It is possible that attending to the first discrimination stimulus caused its color and location to be obligatorily encoded into working memory (Bundesen, 1990), displacing stored colors or locations from the memory array presented at the beginning of the trial and remaining in visual working memory until the second target stimulus appeared. If this were the case, then visual working memory representations might still underlie visuomotor repetition effects. Experiment 2 addresses these concerns.
Experiment 2
Experiment 2 modified the design of Experiment 1 in two ways. First, we varied memory load randomly across trials by always presenting a memory array, and cuing participants at the outset of each trial to either remember or ignore the array. Second, the memory array was presented in between the two discrimination stimuli. Hilchey et al. (2017a, 2017b) have shown that location–response repetition effects are largely unaltered by intervening stimulus events, and so we expect that we will be able to observe them even though the display interrupts the sequence of discrimination stimuli compared with Experiment 1.
Method
Participants
Fifty-two participants from the Vanderbilt community completed Experiment 2 for course credit. Twenty-eight participated in the color memory condition, and 24 participants completed the location memory condition. In both conditions, participants were run until 24 participants remained after exclusion criteria were applied (see Results). All participants provided informed consent before participating. The average participant age was 19.4 years (SD = 1.2), and 28 participants were female.
Stimuli, apparatus, and procedure
Stimuli were presented to participants on ASUS VG248 LED monitors using Mac mini computers. Responses were collected using standard USB keyboards. Stimuli were generated using MATLAB and the Psychophysics toolbox (Kleiner et al., 2007). Stimulus sizes were calculated to match those of Experiment 1 using the new apparatus and viewing distance of approximately 80 cm. The only new display type used was the cue display used at the beginning of the trial that instructed participants about whether or not they should complete the memory task on a given trial. All other displays were drawn to match those in Experiment 1. A schematic depiction of a trial is shown in Fig. 5.
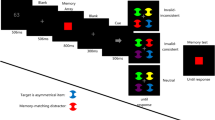
Illustration of a sample trial from Experiment 2. Stimuli are not drawn to scale. The first event of each trial was either “remember” or “ignore.” The memory probe array depicts a different location, same color probe
Cue displays
Each trial began with a word cue that instructed participants about whether or not they should remember the three colors or locations presented in the memory displays on that trial. These word cues were Remember and Ignore, respectively, printed in the center of the screen in 24-point Arial font. Cue displays lasted for 500 ms.
The overall sequence of events in the trial was as follows: 500 ms of a black screen; 500 ms of a cue display; 500 ms of a black screen with a single fixation cross; 500 ms of empty placeholders; the first peripheral color target, presented until a response was entered; the memory display, presented for 500 ms; the empty placeholder display, presented for 500 ms; the second peripheral color target, presented until responses; and the memory test display, presented until response on memory trials and for 750ms for ignore trials. After a trial was completed, participants were informed of their accuracy for each response, and pressed the space bar to initiate the next trial. Participants completed 20 trials of practice on the color target task alone to acquaint themselves with their randomly generated S–R mapping. The practice phase was repeated if participants made three or more response errors. Following practice, participants completed 384 trials where each condition was randomly intermixed, with three repetitions of each combination of memory load, target 1 location, target 2 location, target 1 color, and target 2 color. Breaks were given every 50 trials.
Analysis
Four participants were excluded for having memory performance that could not be distinguished from chance (<57.29%), all of whom had completed the color memory condition. For the remaining participants, average response times for the second color targets were calculated for each condition, excluding trials where the first or second color response was slower or faster than 2.5 standard deviations of all target responses (3.0% for the first color response, 2.5% for the second), and where an error in any response was made (5.0% in target responses, 24.3% errors in memory responses). Overall, 79.2% of all trials were retained for analysis. Memory accuracy in the color load condition was 71.3% (SD = 6.8%) and 80.1% (SD = 9.3%) in the location load condition. Again, accuracy for both first-target and second-target responses on trials with target response errors included (but other exclusion criteria applied) was near ceiling after exclusions were applied, Mfirst = 97.6%, SDfirst = 2.1%, Msecond = 97.3%, SDsecond = 2.2%.
Results
Mean RTs are shown in Fig. 6. These findings replicate the hypothesis-pertinent results of Experiment 1, in that RTs were slower in the dual-task condition in which the working memory load was maintained, but the memory load did not reduce visuomotor repetition effects, selectively or otherwise. The relative insensitivity of the visuomotor repetition effects to working memory load again indicate that these repetition effects are not due to working memory storage. A mixed-model ANOVA showed three repetition effects: color–response repetition speeded responses, F(1.71, 78.85) = 80.65, p < .001, ηp2 = .64, as did location repetitions, F(1, 46) = 27.48, p < .001, ηp2 = .37, but the latter depended on response repetition, F(2, 92) = 15.50, p < .001, ηp2 = .25, as in Experiment 1 and elsewhere (Hilchey et al., 2017a, b). Thus, we again were successful in measuring visuomotor repetitions effect in this task.
Second target response times in Experiment 2 as a function of color–response repetition type (horizontal axes), location repetition (gray lines: location repeat, black lines: location switch), memory load (present: solid lines, absent: dashed lines), and load type (color load, left panel, spatial load, right panel). Error bars depict one standard error of the mean
With respect to working memory’s involvement in visuomotor repetition effects, memory load slowed responses overall, F(1, 46) = 94.91, p < .001, ηp2 = .67, and may have increased the magnitude of the overall location repetition benefit, F(1, 46) = 3.02, p = .09, ηp2 = .06, potentially reflecting a reduction in IOR (Castel, Pratt, & Craik, 2003), which we know to be overshadowed by visuomotor repetition effects (Hilchey, Rajsic, Huffman, Klein, & Pratt, 2018), but this did not interact with load type, F(1, 46) = 0.56, p = .46, ηp2 = .01. Color load seemed to slow responses more than location load, but this effect was not significant, F(1, 46) = 2.79, p = .10, ηp2 = .06. Load did not affect the color–response repetition effect overall, F(2, 92) = 1.21, p = .30, ηp2 = .03, but memory load may have selectively, albeit weakly, modulated the size of the color–response repetition effect, as indicated by a memory load × load type × color–response interaction, F(2, 92) = 2.58, p = .08, ηp2 = .03, such that difference in RT between the partial matching condition (different color, same response) and the full switch condition (different color, different response) was larger under color memory load than location memory load. Interestingly, load type affected color–response repetition effects even when the memory array was irrelevant, F(1.45, 66.48) = 3.67, p = .04, ηp2 = .07, albeit in a different way: the benefit of color–response repeats over the other two color–response conditions was larger under location than color memory instructions. The fact that load type affected color–response repetition effects even when the load was irrelevant makes it difficult to attribute this interaction to memory load per se. Critically, memory load did not modulate the location–response repetition effect, F(2, 92) = 0.06, p = .94, ηp2 = .001, nor did it modulate it differently when load type was considered, F(2, 92) = 0.52, p = .60, ηp2 = .011. Considered separately from whether or not the memory sample needed to be remembered, load type showed a trend of an interaction with the location repetition effect, F(1, 46) = 3.73, p = .06, ηp2 = .08, such that the RT cost for location changes was larger for participants instructed to remember locations. Load type also interacted with the color–response repetition effect, F(1.71, 78.85) = 3.30, p = .05, ηp2 = .07, as noted earlier, Load type did not interact with the location–response repetition effect, F(2, 92) = 1.70, p = .19, ηp2 = .04. Finally, load type did not affect overall RT, F(1, 46) = 1.44, p = .24, ηp2 = .03.
As in Experiment 1, we conducted additional tests to assess whether our data showed evidence for a lack of a relationship between memory load and repetition effects. Analyzed alone, no load trials showed both a color–response repetition effect, F(1.45, 66.48) = 90.48, p < .001, ηp2 = .66, and a location–response repetition effect, F(2, 92) = 14.14, p < .001, ηp2 =.24. Trials with memory load also showed both a color–response repetition effect, F(2, 92) = 47.58, p < .001, ηp2 =.51, and a location–response repetition effect, F(2, 92) = 6.98, p = .002, ηp2 =.13. The mean square estimate was slightly smaller for the memory load condition (MSno load = 0.032, MSload = 0.027), but the MSE was also larger (MSEno load = 0.002, MSEload = 0.004), so the halving of the effect size comes from two sources. Bayesian effects estimates showed a BFinclusion of 0.007 for the load × color–response repetition × location–response repetition effect, meaning it is 143 times more likely that no interaction exists. We found even stronger evidence against the four-way interaction, with BFinclusion = 2.234 × 10-5, meaning it is 4,476 times more likely that no interaction exists, given the data.
Target accuracy painted a similar picture, though again these results should be interpreted with caution due to ceiling performance (see Fig. 7). analyzing target response accuracy revealed a location repetition effect, F(1, 46) = 20.37, p < .001, ηp2 = .31, such that error rates were higher for location switches. This suggests that the location repetition effect in RT may be a speed–accuracy trade-off instead of IOR. However, as before, this main effect may largely reflect the higher error rates for repeated responses following a target location change. We also found a color–response repetition effect, F(1.08, 49.78) = 45.17, p < .001, ηp2 = .50, and a location–response repetition effect, F(1.35, 62.11) = 15.34, p < .001, ηp2 = .25, that revealed a cost for changing a stimulus feature (color or location) when responses repeated. No other effects were significant (Fs < 2.34, p > .13, ηp2s < .05). Using a Bayesian ANOVA, we again calculated the BFinclusion estimate for the memory × color–response repetition × location repetition interaction, which was 7.45 × 10-4 (meaning a null effect was 1,342 times more likely), and for the four-way interaction, which was 2.00 × 10-9 (meaning a null effect was 5.00 × 108 times more likely). Thus accuracy data provided no suggestion of a relationship between visual working memory load and repetition effects.
Finally, we also analyzed visual working memory performance as a function of target repetitions as in Experiment 1. As in Experiment 1, k estimates (see Fig. 8) were lower for participants memorizing colors than locations, F(1, 46) = 15.25, p < .001, ηp2 = .25. However, we found no effects of any repetition type, load type, or interactions (Fs < 2.69, ps > .10). A Bayesian ANOVA showed that the null model was 4.97 times more likely than the next best model (a main effect of color–response repetition).
Memory performance following repetition types in Experiment 2. Error bars depict one standard error of the mean.
Discussion
The results of Experiment 2 are consistent with the conclusion from Experiment 1 that visual working memory load did relatively little to affect visuomotor repetition effects, and in no way disrupted their influence on response time. When memory load varied unpredictably throughout the experiment, and memory encoding occurred between the critical target discrimination events, visuomotor repetition effects were again not disrupted. If anything, Experiment 2 demonstrated a tendency for the color–response repetition effect to slightly increase under color visual working memory load, such that the cost of a partial match (same response but different color) slowed response time more. However, the kind of load mattered even when participants were cued not to store the memory sample in visual working memory, and so it is difficult to attribute this to visual working memory load, as opposed to the need to switch attention between stimulus dimensions (for color-memory participants, color was the relevant dimension on both tasks in each trial, whereas for location-memory participants, location needed to be encoded in the memory task, but color was relevant in the target discrimination task), or even task difficulty (colors were generally remembered more poorly than locations).
The results of Experiment 2 thus strengthen the conclusion that visual working memory does not store the codes that produce visuomotor repetition effects. Having to encode the memory array in between color targets makes it very unlikely that the first target’s color and location were represented in working memory at the time that the second target was processed. While one may argue that three colors and locations could have left spare capacity for representing the features of the first target, the average memory accuracy was decidedly below ceiling for both color and location loads, as can be seen in Fig. 8. This was also true for Experiment 1 (see Fig. 4). If participants were indeed able to store more than the three locations and colors we presented, their performance ought to have been at ceiling. Furthermore, given that all target—target feature relationships were random, it is not obvious that any strategic advantage could be gained from trying to sustain a memory for the first target’s features instead of encoding all three features from the memory array. Thus, we believe that it is most likely that the requirement to encode the locations or colors sufficiently occupied working memory. Nevertheless, maintaining this additional information did not prevent the colors, locations, and responses of previous targets from affecting responses to a subsequent target.
General discussion
When identification responses are made to sequentially presented stimuli, the speed of these responses is affected in systematic ways by feature and response overlap. If these visuomotor repetition effects depended on short-term color and location working memory resources, respectively, then working memory loads should have selectively eliminated their respective location–response and color–response repetition effects. Clearly, this did not happen. Our data suggest that the memory representations of previous events that drive visuomotor repetition effects are likely a different kind of memory representation than the kind used to intentionally store visual information (see also Keizer, Hommel, & Lamme, 2015). These data are thus generally consistent with dual-systems views of visually driven response selection, where response selection based on recently seen stimulus attributes proceeds via an automatic pathway that is not subject to the bottlenecks associated with controlled, rule-based responding (Hommel et al., 2004; Logan, 1979; Schneider & Anderson, 2011). This automatic pathway may instead rely on an implicit episodic memory system (Schmidt, De Houwer, & Rothermund, 2016) that can influence response selection when task settings demand that cue features are processed when responses are being selected (Hommel et al., 2014; Memelink & Hommel, 2013; Huffman, Hilchey & Pratt, 2018).
Our data therefore suggest that the memories leading to visuomotor repetition effects do not rely on the capacity-limited system that is used to intentionally remember visual information (Luck & Vogel, 1997). Unlike long-term memory, visual working memory appears to be capacity limited rather than interference limited (Lin & Luck, 2012; Oberauer, Awh, & Sutterer, 2017; but see Hartshorne, 2008; Makovski & Jiang, 2008). Indeed, our experiments were designed to impose a memory load, but not interference; participants always encoded sets of colors or locations that did not overlap with the colors and locations used for the target task. If the repetition of event features affects responses through a retrieval process (see Memelink & Hommel, 2013), then recycling of target features during the memory task could modulate repetition effects through retrieval interference. Thus, our data support the conclusion that visuomotor repetition effects reflect automatic retrieval of information stored in long-term memory (Logan, 1990; Schneider & Anderson, 2011). The apparent transience of event files could be a consequence of poor long-term memory for specific features and too much retroactive interference for bindings to accumulate over trials, especially when these bindings are not explicitly retrieved (Logie, Brockmole, & Vandenbroucke, 2009).
It is still possible, however, that event files do reflect transient bindings of the sort suggested by Hommel and Colzato (2009). It may be that event files are stored in an implicit visual short-term memory, whose representational basis overlaps minimally with that of voluntary visual short-term memory (i.e., visual working memory; see Carlisle & Kristjánsson, 2018; Maljkovic & Nakayama, 2000, for such a distinction in the context of priming of pop-out). It may also be the case that visuomotor repetition effects solely reflect the operation of a procedural working memory system, and that remembering visual information relies on a declarative working memory system with an entirely separate capacity (Gade, Druey, Souza, & Oberauer, 2014; Oberauer, 2009; Souza, Oberauer, Gade, & Druey, 2012), and with separate stimulus codes (i.e., “red” or “left”) for the procedural and declarative working memory systems.
Although the present results argue against a common representational code for visual working memory and visuomotor repetition effects, they cannot distinguish between long-term memory storage and implicit or procedural short-term memory storage as their representational basis. This is an important issue to be settled, as it bears on the question of whether or not the same memory systems underlying moment-to-moment associations also lead to skilled behavior that comes from long-term associations (Logan, 1990), an assertion which should only be true if repetition effects stem from long-term memory. Additional experiments investigating whether event files can have cumulative and remote (e.g., Rajsic et al., 2014; Wilson et al., 2006) effects would be most informative for this outstanding issue. Whichever the case may be, our results still support the assertion that changes in response efficacy due to visuomotor repetition have little to do with deliberately maintained memory for recently seen visual information.
Expanding upon this latter point, a practical implication of our results is that visuomotor repetition effects do not appear to depend on the number of concurrently active features. In our experiments, participants had to maintain additional colors or locations while processing target colors and, implicitly, locations. While slowing responses overall, additional active features did not reduce the effect of recent stimulus–response associations. In general, then, we can predict that actively remembering some information will not directly affect the different states of preparedness that recent stimulus-driven actions cause for future stimulus-driven actions, even when the stimuli and memories are from the same category. Many real-world situations require the execution of a rapid response depending on changes in input. For example, pilots need to respond to complex symbolic displays whose elements share simple visual features (such as radial positions of needles across different instruments, form or locations of icons in a heads-up display) that may partially overlap with recently processed elements. In such situations, visuomotor repetitions can still affect response speed and accuracy (Yamaguchi & Proctor, 2006). Our results imply that partial overlap of display features will continue to affect performance in systematic ways whether pilots are actively remembering other visual information, such as the positions of other aircrafts, or are attending solely to the task of responding to display changes, though further research on this topic would surely be valuable. The influence of past actions on current actions seems to depend more on which details are needed for a given visuomotor decision than the active contents of memory (Hommel et al., 2014).
Our results also cast some additional doubt on the involvement of visual attention in these visuomotor repetition effects (see also Hilchey, Antinucci, Lamy, & Pratt, in press; Hilchey et al., 2017b; Hilchey et al., 2018). Given that spatial working memory load tends to interact with the operation of spatial attention (Ahn, Patel, Buetti, & Lleras, 2017; Castel et al., 2003; Woodman & Luck, 2004;), spatial WM load ought to have altered visuomotor biases here too if these biases resulted from how spatial attention was deployed during the task. Indeed, Experiment 2 did reveal an interaction between memory load and the benefits of repeating a target location, consistent with a reduction in IOR (Castel et al., 2003; Zhang & Zhang, 2011). Our findings also align well with studies of the failure of visual working memory load to affect priming of pop-out, given that simply loading visual working memory with colors does not reduce color-based priming of pop-out (Ahn et al., 2017; Carlisle & Kristjánsson, 2018; Lee, Mozer, & Vecera, 2009; Kristjánsson, Saevarsson, & Driver, 2013). Our results similarly show that maintaining visual features in working memory does not reduce the impact of recently processed features on response time.
Finally, we should note that in Experiment 1 we found that memory load, regardless of its type, increased the size of the color–response repetition benefit. A similar effect was reported by Keele and Boies (1973) in the context of a task requiring participants to quickly report sequences of target locations while remembering five consonants. However, in Experiment 2, this effect disappeared. Although there were several differences between Experiments 1 and 2, it is tempting to speculate that the critical difference is the position of the memory array in the sequence of a trial’s events, given Keele and Boies’ similar event ordering and results. In Experiment 1, participants maintained a memory load through both target–response episodes, whereas in Experiment 2, participants encoded object features in between target episodes. While the total load at the time of the second target–where repetition effects occur–was the same in both cases, it may be that encoding new colors in between two responses causes interference that simply maintaining information does not.
In sum, although some memory storage system must be responsible for maintaining the event representations that give rise to visuomotor repetition effects, our results suggest that this memory storage system is independent of that used to intentionally remember recently encountered visual information, which is inherently capacity limited.
References
Ahn, J. W., Patel, T. N., Buetti, S., & Lleras, A. (2017). Exploring the contributions of spatial and non-spatial working memory to priming of pop-out. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 79(4), 1012–1026.
Bertelson, P. (1965). Serial choice reaction-time as a function of response versus signal-and-response repetition. Nature, 206(4980), 217-218.
Bundesen, C. (1990). A theory of visual attention. Psychological Review, 97(4), 523–547.
Carlisle, N. B. & Kristjánsson, À. (2018). How visual working memory contents influence priming of visual attention. Psychological Research, 82(5), 1-7.
Castel, A. D., Pratt, J., & Craik, F. I. M. (2003). The role of spatial working memory in inhibition of return: Evidence from divided attention tasks. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 65(6), 970–981.
Colzato, L. S., Raffone, A., & Hommel, B. (2006). What do we learn from binding features? Evidence for multilevel feature integration. Journal of Experimental Psychology, Human Perception and Performance, 32(3), 705–716.
Cowan, N. (2001). The magical number 4 in short-term memory: A reconsideration of mental storage capacity. Behavioral & Brain Sciences, 24(1), 87–114.
Gade, M., Druey, M. D., Souza, A. S., & Oberauer, K. (2014). Interference within and between declarative and procedural representations in working memory. Journal of Memory and Language, 76, 174–194.
Hartshorne, J. K. (2008). Visual working memory capacity and proactive interference. PLOS ONE, 3(7), e2716.
Henson, R. N., Eckstein, D., Waszak, F., Frings, C., & Horner, A. J. (2014). Stimulus-response bindings in priming. Trends in Cognitive Science, 18(7), 376-384.
Hilchey, M. D., Antinucci, V., Lamy, D., & Pratt, J. (in press). Is attention really biased toward the last target location in visual search? Attention, response rules, distractors, and eye movements. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review.
Hilchey, M. D., Rajsic, J., Huffman, G., Klein, R. M., & Pratt, J. (2018). Dissociating orienting biases from integration effects with eye movements. Psychological Science, 29(3), 328-339.
Hilchey, M. D., Rajsic, J., Huffman, G., & Pratt, J. (2017a). Intervening response events between identification targets do not always turn repetition benefits into repetition costs. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 1–13.Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-016-1262-9
Hilchey, M. D., Rajsic, J., Huffman, G., & Pratt, J. (2017b). Response-mediated spatial priming despite perfectly valid target location cues and intervening response events. Visual Cognition, 1–15. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506285.2017.1349230
Hommel, B. (1998). Event files: Evidence for automatic integration of stimulus-response episodes. Visual Cognition, 5(1-2), 183-216.
Hommel, B. (2004). Event files: Feature binding in and across perception and action. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8(11), 494–500.
Hommel, B. (2005). How much attention does an event file need? Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 31(5), 1067–1082.
Hommel, B. (2019). Theory of event coding (TEC) V2.0: Representing and controlling perception and action. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-019-01779-4
Hommel, B., & Colzato, L. S. (2004). Visual attention and the temporal dynamics of feature integration. Visual Cognition, 11(4), 483–521.
Hommel, B. & Colzato, L. S. (2009). When an object is more than the binding of its features: Evidence for two mechanisms of feature integration. Visual Cognition, 17(1/2), 120–140.
Hommel, B., Memelink, J., Zmigrod, S., & Colzato, L. S. (2014). Attentional control of the creation and retrieval of stimulus-response bindings. Psychological Research, 78(4), 520–538.
Hommel, B., Proctor, R. W., & Vu, K. P. L. (2004). A feature-integration account of sequential effects in the Simon task. Psychological Research, 68(1), 1–17.
Huffman, G., Hilchey, M. D., & Pratt, J. (2018). Feature integration in basic detection and localization tasks: Insights from the attentional orienting literature. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 80(6), 1333–1341.
JASP Team. (2018). JASP (Version 0.9) [Computer software]. Retrieved from https://jasp-stats.org/2018/06/20/introducing-jasp-0-9/
Jiang, Y., Olson, I. R., & Chun, M. M. (2000). Organization of visual short-term memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, memory, & cognition, 26(3), 683–702.
Kahneman, D., Treisman, A., & Gibbs, B. J. (1992). The reviewing of object files: Object-specific integration of information. Cognitive Psychology, 24(2), 175–219.
Keele, S. W., & Boies, S. J. (1973). Processing demands of sequential information. Memory & Cognition, 1(1), 85–90.
Keizer, A. W., Hommel, B., & Lamme, V. A. F. (2015). Consciousness is not necessary for visual feature binding. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 22, 453-460.
Kleinsorge, T. (1999). Response repetition benefits and costs. Acta Psychologica, 103(3), 295–310.
Kleiner, M., Brainard, D. H., & Pelli, D. G. (2007). What is new in Psychophysics Toolbox. Perception, 36.
Kristjánsson, À., Saevarsson, S., & Driver, J. (2013). The boundary conditions of priming of visual search: From passive viewing through task-relevant working memory load. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 20(3), 514–521.
Lee, H., Mozer, M. C., & Vecera, S. P. (2009). Mechanisms of priming of pop-out: Stored representations or feature-gain modulations? Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 71(5), 1059–1071.
Lin, P. H., & Luck, S. J. (2012). Proactive interference does not meaningfully distort visual working memory capacity estimates in the canonical change detection task. Frontiers in psychology, 3, 42.
Logan, G. D. (1979). On the use of a concurrent memory load to measure attention and automaticity. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 5(2), 189.
Logan, G. D. (1990). Repetition priming and automaticity: Common underlying mechanisms? Cognitive Psychology, 22, 1–35.
Logie, R. H., Brockmole, J. R., & Vandenbroucke, A. R. (2009). Bound feature combinations in visual short-term memory are fragile but influence long-term learning. Visual Cognition, 17(1/2), 160–179.
Luck, S. J., & Vogel, E. K. (1997). The capacity of visual working memory for features and conjunctions. Nature, 390(6657), 279–281.
Makovski, T., & Jiang, Y. V. (2008). Proactive interference from items previously stored in visual working memory. Memory & Cognition, 36(1), 43–52.
Maljkovic, V., & Nakayama, K. (2000). Priming of popout: III. A short-term implicit memory system beneficial for rapid target selection. Visual cognition, 7(5), 571–595.
Maljkovic, V., & Nakayama, K. (1994). Priming of pop-out: I. Role of features. Memory & Cognition, 22(6), 657–672.
Memelink, J., & Hommel, B. (2013). Intentional weighting: A basic principle in cognitive control. Psychological Research, 77(3), 249–259.
Moeller, B., & Frings, C. (2017). Dissociation of binding and learning processes. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 79(8), 2590–2605. doi:https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-017-1393-7
Oberauer, K. (2009). Design for a working memory. Psychology of Learning and Motivation, 51, 45–100.
Oberauer, K., Awh, E., & Sutterer, D. W. (2017). The role of long-term memory in a test of visual working memory: Proactive facilitation but no proactive interference. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 43(1), 1–22.
Pashler, H., & Baylis, G. (1991). Procedural learning: II. Intertrial repetition effects in speeded-choice tasks. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 17(1), 33–48.
Posner, M. I., & Cohen, Y. (1984). Components of visual orienting. Attention and Performance X: Control of Language Processes, 32, 531–556.
Pösse, B., Waszak, F., & Hommel, B. (2006). Do stimulus-response bindings survive a task switch? European Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 18(4), 640–651.
Rajsic, J., Bi, Y., & Wilson, D. E. (2014). Long-term facilitation of return: A response-retrieval effect. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 21(2), 418–424.
Roper, Z. J. J., & Vecera, S. P. (2014). Visual short-term memory load strengthens selective attention. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 21(2), 549–556.
Rothermund, K., Wentura, D., & De Houwer, J. (2005). Retrieval of incidental stimulus–response associations as a source of negative priming. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 31(3), 482–495.
Rouder, J. N., Morey, R. D., Morey, C. C., & Cowan, N. (2011). How to measure working memory capacity in the change detection paradigm. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 18(2), 324–330.
Schmidt, J. R., De Houwer, J., & Rothermund, K. (2016). The parallel episodic processing (PEP) model 2.0: A single computational model of stimulus-response binding, contingency learning, power curves, and mixing costs. Cognitive Psychology, 91, 82–108.
Schneider, D. W. & Anderson, J. R. (2011). A memory-based model of Hick’s law. Cognitive Psychology, 62(3), 193–222.
Souza, A. S., Oberauer, K., Gade, M., & Druey, M. D. (2012). Processing of representations in declarative and procedural working memory. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 65(5), 1006–1033.
Waszak, F., Hommel, B., & Allport, A. (2003). Task-switching and long-term priming: Role of episodic stimulus-task bindings in task-shift costs. Cognitive Psychology, 46(4), 361–413.
Wilson, D. E., Castel, A. D., & Pratt, J. (2006). Long-term inhibition of return for spatial locations: Evidence for a memory retrieval account. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 59(12), 2135–2147.
Woodman, G. F. & Luck, S. J. (2004). Visual search is slowed when visuospatial working memory is occupied. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 11(2), 269–274.
Woodman, G. F., & Vogel, E. K. (2008). Selective storage and maintenance of an object’s features in visual working memory. Psychonomic bulletin & review, 15(1), 223–229.
Woodman, G. F., Vogel, E. K., & Luck (2012). Flexibility in visual working memory: Accurate change detection in the face of irrelevant variations in position. Visual Cognition, 20(1), 1–28.
Yamaguchi, M., & Proctor, R. W. (2006). Stimulus-response compatibility with pure and mixed mappings in a flight task environment. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 12(4), 207–222.
Zhang, Y., & Zhang, M. (2011). Spatial working memory load impairs manual but not saccadic inhibition of return. Vision Research, 51(1), 147–153.
Acknowledgements
Funding for this project was provided by a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada grant to J.P. (194537), National Institutes of Health grants to G.F.W. (R01-EY025275, R01-EY019882, R01-MH110378, and P30-EY08126), a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada Post-Graduate Scholarship to J.R., and a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada Post-doctoral scholarship to M.D.H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open practices statement
The data for the experiments reported here are available at https://osf.io/d7tr6/, and none of the experiments were preregistered.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 120 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajsic, J., Hilchey, M.D., Woodman, G.F. et al. Visual working memory load does not eliminate visuomotor repetition effects. Atten Percept Psychophys 82, 1290–1303 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-019-01839-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-019-01839-9