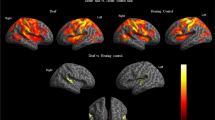
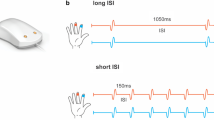
Abstract
A device for measuring signal transfer within and between hemispheres has been developed at the Center for Neuropsychological Research at the University of Trier, Germany. It contains two identical panels allowing both tactile stimulation and motor response with buttons for the fingers of each hand. The buttons have two functions. They can exert a slight tactile stimulation to a finger, and they can be pressed down by the finger to provide a motor response to the tactile stimulation allowing measuring the response time. The device was used for measuring brain asymmetry in tactile processing autistic children. The participants were given a finger tapping test followed by the procedures with unilateral and bilateral processing of tactile stimulation. All participants responded positively to the test procedure and accepted it as a kind of game. The results indicated that brains were more asymmetrical in autistic children than in controls: The right hemisphere functioned quicker than the left hemisphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akshoomoff, N., Corsello, C., & Schmidt, H. (2006). The role of autism diagnostic observation schedule in the assessment of autism spectrum disorders in school and community settings. California School Psychologist, 11, 7–19.
Annett, M. (2002). The puzzle of handedness and cerebral speech. In M. Annett (Ed.), Handedness and brain asymmetry: The right shift theory (pp. 3–20). New York: Taylor & Francis.
Banich, M. T. (1995). Interhemispheric processing: Theoretical considerations and empirical approaches. In R. J. Davidson & K. Hugdahl (Eds.), Brain asymmetry (pp. 427–450). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Barnett, K. J., Corballis, M. C., & Kirk, I. J. (2005). Symmetry of callosal information transfer in schizophrenia: A preliminary study. Schizophrenia Research, 74, 171–178.
Bench, C. J., Frackowiak, R. S. J., & Dolan, R. J. (1995). Changes in regional cerebral blood flow on recovery from depression. Psychological Medicine, 25, 247–251.
Berthier, M. L. (1994). Corticocallosal anomalies in Asperger’s syndrome. American Journal of Roentgenology, 162, 236–237.
Blaxill, M. F. (2004). What’s going on? The question of time trends in autism. Public Health Reports, 119, 536–551.
Boddaert, N., Belin, P., Chabane, N., Poline, J.-B., Barthelemy, C., Mouren-Simeoni, M. C., et al. (2003). Perception of complex sounds: Abnormal pattern of cortical activation in autism. American Journal of Psychiatry, 160, 2057–2060.
Boddaert, N., Chabane, N., Belin, P., Bourgeois, M., Royer, V., Barthelemy, C., et al. (2004). Perception of complex sounds in autism: Abnormal auditory cortical processing in children. American Journal of Psychiatry, 161, 2117–2120.
Bruder, G. E. (2003). Frontal and parietotemporal asymmetries in depressive disorders: Behavioral, electrophysiologic, and neuroimaging findings. In K. Hugdahl & R. J. Davidson (Eds.), The asymmetrical brain (pp. 719–742). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Burroni, L., Orsi, A., Monti, L., Hayek, Y., Rocchi, R., & Vattimo, A. G. (2008). Regional cerebral blood flow in childhood autism: A SPET study with SPM evaluation. Nuclear Medicine Communications, 29, 150–156.
Chiron, C., Leboyer, M., Leon, F., Jambaque, I., Nuttin, C., & Syrota, A. (1995). SPECT of the brain in childhood autism: Evidence for a lack of normal hemispheric asymmetry. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 37, 849–860.
Chugani, D. C., Muzik, O., Rothermel, R., Behen, M., Chakraborty, P., Mangner, T., et al. (1997). Altered serotonin synthesis in the dentatothalamocortical pathway in autistic boys. Annals of Neurology, 42, 666–669.
Cody, H., Pelphrey, K., & Piven, J. (2002). Structural and functional magnetic resonance imaging of autism. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 20, 421–438.
Courchesne, E., Press, G. A., & Yeung-Courchesne, R. (1993). Parietal lobe abnormalities detected with MR in patients with infantile autism. American Journal of Roentgenology, 160, 387–393.
Dane, S., & Balci, N. (2007). Handedness, eyeness and nasal cycle in children with autism. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 25, 223–226.
Dawson, G., Warrenburg, S., & Fuller, P. (1982). Cerebral lateralization in individuals diagnosed as autistic in early childhood. Brain & Language, 15, 353–368.
Dawson, G., Warrenburg, S., & Fuller, P. (1983). Hemisphere functioning and motor imitation in autistic persons. Brain & Cognition, 2, 346–354.
Dollfus, S., Razafimandimby, A., Delamillieure, P., Brazo, P., Joliot, M., Mazoyer, B., & Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. (2005). Atypical hemispheric specialization for language in right-handed schizophrenia patients. Biological Psychiatry, 57, 1020–1028.
Gillberg, C. (1983). Autistic children’s hand preference: Results from an epidemiological study of infantile autism. Psychiatry Research, 10, 21–30.
Gurney, J. G., Fritz, M. S., Ness, K. K., Sievers, P., Newschaffer, C. J., & Shapiro, E. G. (2003). Analysis of prevalence trends of autism spectrum disorder in Minnesota. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 157, 622–627.
Hauser, S. L., DeLong, G. R., & Rosman, N. P. (1975). Pneumografic findings in the infantile autism syndrome. A correlation with temporal lobe disease. Brain, 98, 667–688.
Herbert, M. R. (2005). Large brains in autism: The challenge of pervasive abnormality. Neuroscientist, 11, 417–440.
Herbert, M. R., Harris, G. J., Adrien, K. T., Zeigler, D. A., Makris, N., Kennedy, D. N., et al. (2002). Abnormal asymmetry in language association cortex in autism. Annals of Neurology, 52, 588–596.
Herbert, M. R., Ziegler, D. A., Deutsch, C. K., O’Brien, L. M., Kennedy, D. N., Filipek, P. A., et al. (2005). Brain asymmetries in autism and developmental language disorder: A nested whole-brain analysis. Brain, 128, 213–226.
Hughes, J. R. (2007). Autism: The first firm finding 5 underconnectivity? Epilepsy & Behavior, 11, 20–24.
Just, M. A., Cherkassky, V. I., Keller, T. A., Kana, R. K., & Minshew, N. J. (2007). Functional and anatomical cortical underconnectivity in autism: Evidence from an fMRI study of an executive function task and corpus callosum morphometry. Cerebral Cortex, 17, 951–961.
Kicic, D., Lioumis, P., Ilmoniemi, R. J., & Nikulin, V. V. (2008). Bilateral changes in excitability of sensorimotor cortices during unilateral movement: Combined electroencephalographic and transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Neuroscience, 152, 1119–1129.
McAlonan, G. M., Cheung, V., Cheung, C., Suckling, J., Lam, G. Y., Tai, K. S., et al. (2005). Mapping the brain in autism. A voxelbased MRI study of volumetric differences and intercorrelations in autism. Brain, 128, 268–276.
McCann, B. (1981). Hemispheric asymmetries and early infantile autism. Journal of Autism & Developmental Disorders, 11, 401–411.
Meresse, I. G., Zilbovicius, M., Boddaert, N., Robel, L., Philippe, A., Sfaello, I., et al. (2005). Autism severity and temporal lobe functional abnormalities. Annals of Neurology, 58, 466–469.
Minshew, J., & Williams, D. L. (2007). The new neurobiology of autism. Neurological Review, 64, 945–950.
Mooshagian, E., Iacoboni, M., & Zaidel, E. (2008). The role of task history in simple reaction time to lateralized light flashes. Neuropsychologia, 46, 659–664.
Newschaffer, C. J., & Curran, L. K. (2003). Autism: An emerging public health problem. Public Health Reports, 118, 393–399.
Ogawa, T., Sugiyama, A., Ishiwa, S., Suzuki, M., Ishihara, T., & Sato, K. (1982). Ontogenetic development of EEG-asymmetry in early infantile autism. Brain & Development, 4, 439–449.
Ohnishi, T., Matsuda, H., Hashimoto, T., Kunihiro, T., Nishikawa, T. U., & Sasaki, M. (2000). Abnormal regional cerebral blood flow in childhood autism. Brain, 123, 1838–1844.
Pinkham, A. E., Hopfinger, J. B., Pelphrey, K. A., Piven, J., & Penn, D. L. (2008). Neural bases for impaired social cognition in schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorders. Schizophrenia Research, 99, 164–175.
Plailly, J., d’Amato, T., Saoud, M., & Royet, J. P. (2006). Left temporo-limbic and orbital dysfunction in schizophrenia during odor familiarity and hedonicity judgments. NeuroImage, 29, 302–313.
Rizhova, L. Y., Vershinina, E., Balashov, Y. G., Kulagin, D. A., & Kokorina, E. P. (2006). Relation of behavioral asymmetry to the functions of hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal and reproductive systems in vertebrates. In Y. Malashichev & W. Deckel (Eds.), Behavioral and morphological asymmetries in vertebrates (pp. 160–176). Portland, OR: Book News.
Rutter, M. (2003). Introduction: Autism—The challenges ahead. In G. Bock & J. Goode (Eds.), Autism: Neural basis and treatment possibilities (pp. 1–9). Chichester, U.K.: Wiley.
Rutter, M., Baily, A., & Lord, C. (2003). Social communication questionnaire. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Santangelo, S. L., & Tsatsanis, K. (2005). What is known about autism. American Journal of Pharmacogenomics, 5, 71–92.
Shelton, E. L., & Knight, R. G. (1984). Inter-hemispheric transmission time in schizophrenics. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 23, 227–228.
Siegel, B. V. J., Asarnow, R., Tanguay, P., Call, J. D., Abel, L., Ho, A., et al. (1992). Regional cerebral glucose metabolism and attention in adults with a history of childhood autism. Journal of Neuropsychiatry & Clinical Neurosciences, 4, 406–414.
Soper, H. V., Satz, P., Orsini, D. L., Henry, R. R., Zvi, J. C., & Schulman, M. (1986). Handedness patterns in autism suggest subtypes. Journal of Autism & Developmental Disorders, 16, 155–167.
Steiner, C. E., Guerreiro, M. M., & Marques-de-Faria, A. P. (2004). Brief report: Acrocallosal syndrome and autism. Journal of Autism & Developmental Disorders, 34, 723–726.
Tassinari, G., Aglioti, S., Pallini, R., Berlucchi, G., & Rossi, G. F. (1994). Interhemispheric integration of simple visuomotor responses in patients with partial callosal defects. Behavioural Brain Research, 64, 141–149.
Vidal, C. N., Nicolson, R., DeVito, T. J., Hayashi, K. M., Geaga, J. A., Drost, D. J., et al. (2006). Mapping corpus callosum deficit in autism: An index of aberrant cortical connectivity. Biological Psychiatry, 60, 218–225.
Wilcox, J., Tsuang, M. T., Ledger, E., Algeo, J., & Schnurr, T. (2002). Brain perfusion in autism varies with age. Neuropsychobiology, 46, 13–16.
Williams, J. G., Higgins, J. P. T., & Brayne, C. E. G. (2006). Systematic review of prevalence studies of autism spectrum disorders. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 91, 8–15.
Wittling, W. (1995). In R. J. Davidson & K. Hugdahl (Eds.), Brain asymmetry (pp. 305–358). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Wittling, W., & Wittling, A. R. (2005). Europäische patentschrift EP 1 656 885 B1.
Wong, V. C. N., & Hui, S. L. H. (2008). Epidemiological study of autism spectrum disorder in China. Journal of Child Neurology, 23, 67–72.
Yeargin-Allsopp, M., Rice, C., Karapurkar, T., Doernberg, N., Boyle, C., & Murphy, C. (2003). Prevalence of autism in a US Metropolitan area. Journal of the American Medical Association, 289, 49–55.
Zilbovicius, M., Boddaert, N., Belin, P., Poline, J.-B., Remy, P., Mangin, J. F., et al. (2000). Temporal lobe dysfunction in childhood autism: A PET study. American Journal of Psychiatry, 157, 1988–1993.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wittling, R.A., Schweiger, E., Rizhova, L. et al. A simple method for measuring brain asymmetry in children: Application to autism. Behavior Research Methods 41, 812–819 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.41.3.812
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.41.3.812