Abstract
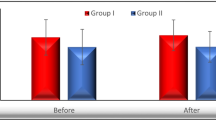
Background and aims: Several studies investigated the possible role of adipokines during chronic viral hepatitis, not producing defined results neither clearly establishing their behavior in course of anti-viral treatment. Our study evaluated blood concentrations of adiponectin and resistin in patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC), B (CHB), and D (CHD) receiving anti-viral treatment, at baseline and after therapy. Methods: We examined 122 subjects, divided into two groups: 64 patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (38 males and 26 females, mean age 47.25 yr) and 58 patients including 39 ones with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection (26 males and 13 females, mean age 48.46 yr) and 19 ones with chronic HBV-hepatitis D virus (HDV) infection (15 males and 4 females, mean age 45.79 yr). Serum levels of adiponectin and resistin were assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results: In the group of CHC patients we observed a significant decrease in resistin after therapy (p=0.006), while not a significant increase in adiponectin after treatment (p=0.32). Evaluation of changes in adiponectin and resistin levels after anti-viral treatment, both in responders and non-responders, revealed no significant variations. In the group of HBV+ and HBV-HDV+ patients, we found a decrease in resistin after therapy (p=0.0016) and a not significant reduction in adiponectin after treatment (p=0.13). Furthermore, we noticed a significant reduction of resistin (p=0.006) in the sub-group of responders. Conclusions: Our data suggested the possible marker role of adiponectin and resistin in the inflammatory process in course of chronic viral hepatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alter HJ, Seeff LB: Recovery, persistence, and sequelae in hepatitis C virus infection: a perspective on long-term outcome. Semin Liver Dis 2000, 20: 17–35.
World Health Org. Hepatitis B, Fact Sheet No 204. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2000.
Tsai SM, Lin SK, Lee KT, et al. Evaluation of redox statuses in patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Clin Biochem 2009, 46: 394–400.
Mohamadkhani A, Jazii FR, Poustchi H, et al. The role of mutations in core protein of hepatitis B virus in liver fibrosis. Virol J 2009, 6: 209.
Rabe K, Lehrke M, Parhofer KG, Broedl UC. Adipokines and insulin resistance. Mol Med 2008, 14: 741–51.
Bertolani C, Marra F. The role of adipokines in liver fibrosis. Pathophysiology 2008, 15: 91–101.
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Hara K, Ueki K, Tobe K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 2006, 116: 1784–92.
Marra F, Bertolani C. Adipokines in liver diseases. Hepatology 2009, 50: 957–69.
Matsuzawa Y, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Shimomura I. Adiponectin and metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004, 24: 29–33.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003, 423: 762–9.
Powell EE, Jonsson JR, Clouston AD. Steatosis: co-factor in other liver diseases. Hepatology 2005, 42: 5–13.
Gustafson B, Hammarstedt A, Andersson CX, Smith U. Inflamed adipose tissue: a culprit underlying the metabolic syndrome and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2007, 27: 2276–83.
Bo S, Ciccone G, Durazzo M, Gambino R, Massarenti P, Baldi I Efficacy of antioxidant treatment in reducing resistin serum levels: a randomized study. PloS Clin Trials 2007, 2: e17.
Myers MG, Cowley MA, Münzberg H. Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 2008, 70: 537–56.
Bertolani C, Sancho-Bru P, Failli P, et al. Resistin as an intrahepatic cytokine: over-expression during chronic injury and induction of proinflammatory actions in hepatic stellate cells. Am J Pathol 2006, 169: 2042–53.
Petta S, Camma C, Di Marco V, et al. Retinol-binding protein 4: a new marker of virus-induced steatosis in patients infected with hepatitis c virus genotype 1. Hepatology 2008, 48: 28–37.
Marchesini G, Moscatiello S, Di Domizio S, Forlani G. Obesity-associated liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008, 93: S74–80.
Musso G, Gambino R, Durazzo M, et al. Adipokines in NASH: postprandial lipid metabolism as a link between adiponectin and liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 42: 1175–83.
Floreani A, Variola A, Niro G, et al. Plasma adiponectin levels in primary biliary cirrhosis: a novel perspective for link between hypercholesterolemia and protection against atherosclerosis. Am J Gastroenterol 2008, 103: 1959–65.
Durazzo M, Niro G, Premoli A, et al. Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis and adipokines:new markers for activity and disease progression? J Gastroenterol 2009, 44: 476–82.
Sato S, Furuta K, Mishiro T, et al. Serum adiponectin concentration in patients with hepatitis C virus. J Clin Gastroenterol 2005, 39: 744–5.
Grigorescu M, Radu C, Crisan D, et al. Metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance and adiponectin levels in chronic hepatitis C. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 2008, 17: 147–54.
Zografos TA, Liaskos C, Rigopoulou EI, et al. Adiponectin: a new independent predictor of liver steatosis and response to IFN-alpha treatment in chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol 2008, 103: 605–14.
Palmer C, Hampartzoumian T, Lloyd A, Zekry A. A novel role for adiponectin in regulating the immune responses in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2008, 48: 374–84.
Lo Iacono O, Venezia G, Petta S, et al. The impact of insulin resistance, serum adipocytokines and visceral obesity on steatosis and fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Alim Pharmacol Ther 2007, 25: 1181–91.
Yagmur E, Tratwein C, Gressner AM, Tacke F. Resistin serum levels are associated with insulin resistance, disease severity, clinical complications and prognosis in patients with chronic liver diseases. Am J Gastroenterol 2006, 101: 1244–52.
Tiftikci A, Atug O, Yilmaz Y, et al. Serum levels of adipokines in patients with chronic HCV infection: relationship with steatosis and fibrosis. Arch Med Res 2009, 40: 294–8.
Tacke F, Wüstefeld T, Horn R, et al. High adiponectin in chronic liver disease and cholestasis suggests biliary route of adiponectin excretion in vivo. J Hepatol 2005, 42: 666–73.
Siagris D, Vafiadis G, Michalaki M, et al. Serum adiponectin in chronic hepatitis C and B. J Viral Hepat 2007, 14: 577–83.
Liu CJ, Chen PJ, Lai MY, et al. High serum adiponectin correlates with advanced liver disease in patients with cronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatol Int 2009, 3: 364–70.
Hui CK, Zhang HY, Lee NP, et al. Serum adiponectin is increased in advancing liver fibrosis and declines with reduction in fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B J Hepatol 2007, 47: 191–202.
Wong VW, Wong GL, Yu J, et al. Interaction of adipokines and hepatitis B virus on histological liver injury in the Chinese. Am J Gastroenterol 2010, 105: 132–8.
Degawa-Yamauchi M, Bovenkerk JE, Juliar BE, et al. Serum resistin (FIZZ 3) protein is increased in obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 5452–5.
McTernan PG, Fisher FM, Valsamakis G, et al. Resistin and type 2 diabetes: regulation of resistin expression by insulin and rosiglitazone and the effects of recombinant resistin on lipid and glucose metabolism in human differentiated adipocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 6098–106.
Tsochatzis E, Papatheodoridis GV, Hadziyannis E, et al. Serum adipokine levels in chronic liver diseases: association of resistin levels with fibrosis severity. Scand J Gastroenterol 2008, 43: 1128–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durazzo, M., Belci, P., Niro, G. et al. Variations of serum levels of adiponectin and resistin in chronic viral hepatitis. J Endocrinol Invest 36, 600–605 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3275/8883
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3275/8883