Abstract
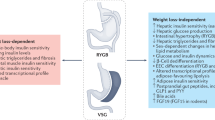
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is increasing over time as result of the obesity epidemics. In fact, the prevalence of Type 2 diabetes across Europe in 2010 was estimated to be 8.2% of the population and its projection for 2030 sees figures of 10.1%. This increase in the number of diabetic individuals has also dramatically raised the health expense, with spending on diabetes in Europe in 2010 accounting for 10% of the total healthcare cost. A meta-analysis of the literature evidenced that the clinical and laboratory manifestations of Type 2 diabetes are resolved in 78.1 %, and are improved in 86.6% of obese patients (body mass index >35 kg/m2) after bariatric surgery. However, a gradation of effects of different surgical techniques in improving glucose control does exist, with the largest and durable effects observed in prevalently malabsorptive procedures. The outcome of bariatric surgery on insulin sensitivity and secretion is different in relation to the type of operation performed. In fact, while Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass enhances insulin secretion after a meal thus improving glucose metabolism, Bilio-Pancreatic Diversion acts through the amelioration of insulin sensitivity allowing a subsequent reduction of insulin hypersecretion, which is a typical feature of the insulin resistance state. Gastric banding action is mediated uniquely through the weight loss, and the effect of sleeve gastrectomy is still to be elucidated. Incretin secretion is dramatically increased under nutrient stimulation after gastric bypass leading, probably, to an overstimulation of pancreatic β-cells resulting in the increase of insulin secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004, 27: 1047–53.
Zhang P, Zhang X, Brown J, et al. Global healthcare expenditure on diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2010, 87: 293–301.
Liebl A, Mata M, Eschwège E; CODE-2 Advisory Board. Evaluation of risk factors for development of complications in Type II diabetes in Europe. Diabetologia 2002, 45: S23–8.
Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, et al. Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med 2009, 122: 248–56.
Dixon JB, O’Brien PE, Playfair J, et al. Adjustable gastric banding and conventional therapy for type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008, 299: 316–23.
Buse JB, Caprio S, Cefalu WT, et al. How do we define cure of diabetes? Diabetes Care 2009, 32: 2133–5.
Dixon JB, Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Rubino F; International Diabetes Federation Taskforce on Epidemiology and Prevention. Bariatric surgery: an IDF statement for obese Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 2011, 28: 628–42.
Gagner M, Inabnet WB, Pomp A. Laparoscopic gastrectomy with second stage biliopancreatic diversion and duodenal switch in the super-obese. In: Inabnet WB, DeMaria EJ, Ikramuddin S Eds. Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2005, 143–9.
Abbatini F, Rizzello M, Casella G, et al. Long-term effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, gastric bypass, and adjustable gastric banding on type 2 diabetes. Surg Endosc 2010, 24: 1005–10.
Rizzello M, Abbatini F, Casella G, et al. Early postoperative insulin-resistance changes after sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg 2010, 20: 50–5.
Lee WJ, Ser KH, Chong K, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for diabetes treatment in nonmorbidly obese patients: efficacy and change of insulin secretion. Surgery 2010, 147: 664–9.
Valderas JP, Irribarra V, Rubio L, et al. Effects of sleeve gastrectomy and medical treatment for obesity on glucagon-like peptide 1 levels and glucose homeostasis in non-diabetic subjects. Obes Surg 2011, 21: 902–9.
Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, Schmidova K, Wisse BE, Weigle DS. A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 2001, 50: 1714–9.
Wren AM, Seal LJ, Cohen MA, et al. Ghrelin enhances appetite and increases food intake in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001, 86: 5992.
Tack J, Depoortere I, Bisschops R, Verbeke K, Janssens J, Peeters T. Influence of ghrelin on gastric emptying and meal-related symptoms in idiopathic gastroparesis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005, 22: 847–53.
Granata R, Settanni F, Biancone L, et al. Acylated and unacylated ghrelin promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis of pancreatic beta-cells and human islets: involvement of 3′, 5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, and phosphatidyl inositol 3-Kinase/Akt signaling. Endocrinology 2007, 148: 512–29.
Papotti M, Ghè C, Cassoni P, et al. Growth hormone secretagogue binding sites in peripheral human tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000, 85: 3803–7.
Tack J, Depoortere I, Bisschops R, Verbeke K, Janssens J, Peeters T. Influence of ghrelin on gastric emptying and meal-related symptoms in idiopathic gastroparesis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005, 22: 847–53.
Vestergaard ET, Gormsen LC, Jessen N, et al. Ghrelin infusion in humans induces acute insulin resistance and lipolysis independent of growth hormone signaling. Diabetes 2008, 57: 3205–10.
Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes. N Engl J Med 2012, 366: 1567–76.
Mari A, Pacini G, Murphy E, Ludvik B, Nolan JJ. A model-based method for assessing insulin sensitivity from the oral glucose tolerance test. Diabetes Care 2001, 24: 539–48.
Matsuda M, DeFronzo RA. Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 1999, 22: 1462–70.
Chambers AP, Jessen L, Ryan KK, et al. Weight-independent changes in blood glucose homeostasis after gastric bypass or vertical sleeve gastrectomy in rats. Gastroenterology 2011, 141: 950–8.
Yin DP, Gao Q, Ma LL, et al. Assessment of different bariatric surgeries in the treatment of obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Ann Surg 2011, 254: 73–82.
Speck M, Cho YM, Asadi A, Rubino F, Kieffer TJ. Duodenal-jejunal bypass protects GK rats from β-cell loss and aggravation of hyperglycemia and increases enteroendocrine cells coexpressing GIP and GLP-1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2011, 300: E923–32.
Laferrère B, Heshka S, Wang K, et al. Incretin levels and effect are markedly enhanced 1 month after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007, 30: 1709–16.
Laferrère B, Teixeira J, McGinty J, et al. Effect of weight loss by gastric bypass surgery versus hypocaloric diet on glucose and incretin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008, 93: 2479–85.
Salinari S, Bertuzzi A, Guidone C, Previti E, Rubino F, Mingrone G. Insulin sensitivity and secretion changes after gastric bypass in normotolerant and diabetic obese subjects. Ann Surg (in press).
Camastra S, Gastaldelli A, Mari A, et al. Early and longer term effects of gastric bypass surgery on tissue-specific insulin sensitivity and beta cell function in morbidly obese patients with and without type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2011, 54: 2093–102.
Roslin M, Damani T, Oren J, Andrews R, Yatco E, Shah P. Abnormal glucose tolerance testing following gastric bypass demonstrates reactive hypoglycemia. Surg Endosc 2011, 25: 1926–32.
Kellogg TA, Bantle JP, Leslie DB, et al. Postgastric bypass hyper-insulinemic hypoglycemia syndrome: characterization and response to a modified diet. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2008, 4: 492–9.
Marsk R, Jonas E, Rasmussen F, Näslund E. Nationwide cohort study of post-gastric bypass hypoglycaemia including 5,040 patients undergoing surgery for obesity in 1986–2006 in Sweden. Diabetologia 2010, 53: 2307–11.
Patti ME, McMahon G, Mun EC, et al. Severe hypoglycaemia post-gastric bypass requiring partial pancreatectomy: evidence for inappropriate insulin secretion and pancreatic islet hyperplasia. Diabetologia 2005, 48: 2236–40.
Service GJ, Thompson GB, Service FJ, Andrews JC, Collazo-Clavell ML, Lloyd RV. Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia with nesidioblastosis after gastric-bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 2005, 353: 249–54.
Goldfine AB, Mun EC, Devine E, et al Patients with neuroglycopenia after gastric bypass surgery have exaggerated incretin and insulin secretory responses to a mixed meal. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007, 92: 4678–85.
Reed MA, Pories WJ, Chapman W, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass corrects hyperinsulinemia implications for the remission of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011, 96: 2525–31.
Salehi M, Prigeon RL, D’Alessio DA. Gastric bypass surgery enhances glucagon-like peptide 1-stimulated postprandial insulin secretion in humans. Diabetes 2011, 60: 2308–14.
Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2012, 366: 1577–85.
Scopinaro N, Marinari GM, Camerini GB, Papadia FS, Adami GF. Specific effects of biliopancreatic diversion on the major components of metabolic syndrome: a long-term follow-up study. Diabetes Care 2005, 28: 2406–11.
Salinari S, Bertuzzi A, Asnaghi S, Guidone C, Manco M, Mingrone G. First-phase insulin secretion restoration and differential response to glucose load depending on the route of administration in type 2 diabetic subjects after bariatric surgery. Diabetes Care 2009, 32: 375–80.
Guidone C, Manco M, Valera-Mora E, et al. Mechanisms of recovery from type 2 diabetes after malabsorptive bariatric surgery. Diabetes 2006, 55: 2025–31.
Mari A, Manco M, Guidone C, et al. Restoration of normal glucose tolerance in severely obese patients after bilio-pancreatic diversion: role of insulin sensitivity and beta cell function. Diabetologia 2006, 49: 2136–43.
Greco AV, Mingrone G, Giancaterini A, et al. Insulin resistance in morbid obesity: reversal with intramyocellular fat depletion. Diabetes 2002, 51: 144–51.
Iaconelli A, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, et al. Effects of bilio-pancreatic diversion on diabetic complications: a 10-year follow-up. Diabetes Care 2011, 34: 561–7.
Halverson JD, Zuckerman GR, Koehler RE, Gentry K, Michael HE, DeSchryver-Kecskemeti K. Gastric bypass for morbid obesity: a medical—surgical assessment. Ann Surg 1981, 194: 152–60.
Amaral JF, Thompson WR, Caldwell MD, Martin HF, Randall HT. Prospective hematologic evaluation of gastric exclusion surgery for morbid obesity. Ann Surg 1985, 201: 186–93.
Brolin RE, Gorman JH, Gorman RC, et al. Are vitamin B12 and folate deficiency clinically important after roux-en-Y gastric bypass? J Gastrointest Surg 1998, 2: 436–42.
Skroubis G, Sakellaropoulos G, Pouggouras K, Mead N, Nikiforidis G, Kalfarentzos F. Comparison of nutritional deficiencies after Rouxen-Y gastric bypass and after biliopancreatic diversion with Rouxen-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg 2002, 12: 551–8.
Koffman BM, Greenfield LJ, Ali II, Pirzada NA. Neurologic complications after surgery for obesity. Muscle Nerve 2006, 33: 166–76.
Marcuard SP, Sinar DR, Swanson MS, Silverman JF, Levine JS. Absence of luminal intrinsic factor after gastric bypass surgery for morbid obesity. Dig Dis Sci 1989, 34: 1238–42.
Vargas-Ruiz AG, Hernández-Rivera G, Herrera MF. Prevalence of iron, folate, and vitamin B12 deficiency anemia after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg 2008, 18: 288–93.
Ruz M, Carrasco F, Rojas P, et al. Iron absorption and iron status are reduced after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Am J Clin Nutr 2009, 90: 527–32.
Dalcanale L, Oliveira CP, Faintuch J, et al. Long-term nutritional outcome after gastric bypass. Obes Surg 2010, 20: 181–7.
Brolin RE, Leung M. Survey of vitamin and mineral supplementation after gastric bypass and biliopancreatic diversion for morbid obesity. Obes Surg 1999, 9: 150–4.
Scopinaro N, Adami GF, Marinari GM, et al. Biliopancreatic diversion. World J Surg 1998, 22: 936–46.
Dolan K, Hatzifotis M, Newbury L, Lowe N, Fielding G. A clinical and nutritional comparison of biliopancreatic diversion with and without duodenal switch. Ann Surg 2004, 240: 51–6.
de Luis DA, Pacheco D, Izaola O, et al. Early clinical and surgical results of biliopancreatic diversion. Obes Surg 2005, 15: 799–802.
Biertho L, Biron S, Hould FS, Lebel S, Marceau S, Marceau P. Is biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch indicated for patients with body mass index <50 kg/m2? Surg Obes Relat Dis 2010, 6: 508–14.
Gracia JA, Martínez M, Elia M, et al. Obesity surgery results depending on technique performed: long-term outcome. Obes Surg 2009, 19: 432–8.
Slater GH, Ren CJ, Siegel N, et al. Serum fat-soluble vitamin deficiency and abnormal calcium metabolism after malabsorptive bariatric surgery. J Gastrointest Surg 2004, 8: 48–55.
Lancaster RT, Hutter MM. Bands and bypasses: 30-day morbidity and mortality of bariatric surgical procedures as assessed by prospective, multi-center, risk-adjusted ACS-NSQIP data. Surg Endosc 2008, 22: 2554–63.
Mognol P, Chosidow P, Marmuse JP. Laparoscopic gastric bypass versus laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in the super-obese: a comparative study of 290 patients. Obes Surg 2005, 15: 76–81.
Galvani C, Gorodner M, Moser F, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric band versus laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: ends justify the means? Surg Endosc 2006, 20: 934–41.
Ponce J, Fromm R, Paynter S. Outcomes after laparoscopic adjustable gastric band repositioning for slippage or pouch dilation. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2006, 2: 627–31.
Pontiroli AE, Morabito A. Long-term prevention of mortality in morbid obesity through bariatric surgery. a systematic review and metaanalysis of trials performed with gastric banding and gastric bypass. Ann Surg 2011, 253: 484–7.
Dixon JB, O’Brien PE, Playfair J, et al. Adjustable gastric banding and conventional therapy for type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008, 299: 316–23.
Sesti G, Folli F, Perego L, Hribal ML, Pontiroli AE. Effects of weight loss in metabolically healthy obese subjects after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and hypocaloric diet. PLoS One 2011, 6: e17737.
Hanusch-Enserer U, Cauza E, Brabant G, et al. Plasma ghrelin in obesity before and after weight loss after laparoscopical adjustable gastric banding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004, 89: 3352–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castagneto-Gissey, L., Mingrone, G. Insulin sensitivity and secretion modifications after bariatric surgery. J Endocrinol Invest 35, 692–698 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3275/8470
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3275/8470