Abstract
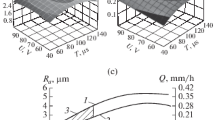
In the electric discharge machining (EDM) of VZhL14 alloy and ЭП517Ш steel, tensile residual stress appears in the surface layer. With increase in current, the residual stress increases; with increase in pulse duration, it falls. The influence of the current on the residual stress is greater than the influence of the pulse duration. Hence, in selecting the EDM conditions, the current is the key parameter. Mechanical removal of the defective layer is recommended so as to prevent microcrack propagation. In that case, useful compressive residual stress appears.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Świercz, R., Oniszczuk-Świercz, D., and Chmielew-ski, T., Multi-response optimization of electrical discharge machining using the desirability function, Micromachines, 2019, vol. 10, art. ID 72.
Liu, J.F., Guo, Y.B., Butler, T.M., and Weaver, M.L., Crystallography, compositions, and properties of white layer by wire electrical discharge machining of nitinol shape memory alloy, Mater. Des., 2016, vol. 109, pp. 1‒9.
Mehmood, Sh., Sultan, A., Anjum, N.A., et al., Determination of residual stress distribution in high strength aluminum alloy after EDM, Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J., 2017, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 29–35.
Lee, H.-T., Rehbach, W.P., Hsu, F.-C., et al., The study of EDM hole-drilling method for measuring residual stress in SKD11 tool steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2004, vol. 149, no. 1, pp. 88–93.
Herbert, C., Axinte, D., Hardy, M., and Brown, P.D., Investigation into the characteristics of white layers produced in a nickel-based superalloy from drilling operations, Mach. Sci. Technol., 2012, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 40–52.
García Navas, V., Ferreres, I., Marañón, J.A., et al., Electro-discharge machining (EDM) versus hard turning and grinding—Comparison of residual stresses and surface integrity generated in AISI O1 tool steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, vol. 195, nos. 1–3, pp. 186–194.
Funding
Financial support was provided by the Russian Ministry of Science and Higher Education (project FNSM-2020-0028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by B. Gilbert
About this article
Cite this article
Ablyaz, T.R., Osinnikov, I.V., Shiryaev, A.A. et al. Residual Stress after Electric Discharge Machining. Russ. Engin. Res. 42, 850–852 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068798X22080044
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068798X22080044