Abstract
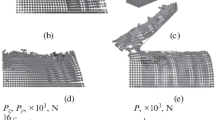
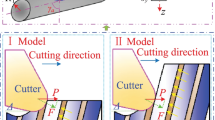
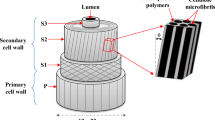
The machining of composites is of great interest in manufacturing today. To that end, it is necessary to calculate the cutting forces required and to predict the surface quality obtained. In the present work, the cutting zone of a unidirectional fiber-reinforced composite is simulated by the SPH method. The calculation results—specifically, the equivalent stress and the strain distribution—are compared with results obtained previously by the finite-element method and also with experimental data. The good agreement with experimental data indicates that the SPH method may expediently be used in simulating the cutting of composites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Teti, R., Machining of composite materials, CIRP Ann., 2002, vol. 51, no. 2, pp. 611–634.
Koshin, A.A., D’yakonov, A.A., and Shmidt, I.V., The modular structure of polymer-composite technologies, Vestn. Yuzh.-Ural. Gos. Univ., Mashinostr., 2015, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 51–60.
Jahromi, S.A. and Bahr, B., An analytical method for predicting cutting forces in orthogonal machining of unidirectional composites, Composites Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 70, pp. 2290–2297.
Gururaja, S. and Ramulu, M., Analytical formulation of subsurface stresses during orthogonal cutting of FRPs, Composites, Part A, 2010, vol. 41, pp. 1164–1173.
Beletskii, E.N., The rheological models used in the simulation of cutting processes of antifriction carbon plastics used in power engineering, Instrum. Tekhnol., 2009, no. 32, pp. 180–185.
Mkaddem, A. and Mansori, M.E., Finite element analysis when machining UGF-reinforced PMCs plates: chip formation, crack propagation and induced-damage, Mater. Des., 2009, no. 30, pp. 3295–3302.
Zhou, L., Huang, S.T., Wang, D., and Yu, X.L., Finite element and experimental studies of the cutting process of SiCp/Al composites with PCD tools, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2011, no. 52, pp. 619–626.
Soldani, X., Santiuste, C., Mucoz-Sánchez, A., and Miguélez, M.H., Influence of tool geometry and numerical parameters when modeling orthogonal cutting of LFRP composites, Composites, Part A, 2011, no. 42, pp. 1205–1216.
Mkaddem, A.A., Demirci, I., and Mansori, M., Micro-macro combined approach using FEM for modeling of machining of FRP composites: cutting forces analysis, Composites Sci. Technol., 2008, vol. 68, pp. 3123–3127.
Dandekar, C.R. and Shin, Y.C., Multi-step 3-D finite element modeling of subsurface damage in machining particulate reinforced metal matrix composites, Composites, Part A, 2009, vol. 40, pp. 1231–1239.
Rao, G.V.G., Mahajan, P., and Bhatnagar, N., Threedimensional macromechanical finite element model for machining of unidirectional-fiber reinforced polymer composites, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, vol. 498, pp. 142–149.
Rao, G.V.G., Mahajan, P., and Bhatnagar, N., Micromechanical modeling of machining of FRP composites cutting force analysis, Composites Sci. Technol., 2007, no. 46, pp. 579–593.
Rao, G.V.G., Mahajan, P., and Bhatnagar, N., Machining of UD-GFRP composites chip formation mechanism, Composites Sci. Technol., 2007, vol. 67, pp. 2271–2281.
Shchurov, I.A. and Boldyrev, I.S., Simulation of the cutting of workpieces made of composite materials using the finite element method, Vestn. Yuzh.-Ural. Gos. Univ., Mashinostr., 2012, no. 12, pp. 143–147.
Johnson, G.R. and Cook, W.H., Fracture characteristics of three metals subjected to various strains, strain rates, temperatures and pressures, Eng. Fract. Mech., 1985, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 31–48.
Corbett, B.M., Numerical simulations of target hole diameters for hypervelocity impacts into elevated and room temperature bumpers, Int. J. Impact Eng., 2006, vol. 33, pp. 431–440.
Gray, G.T., Chen, S.R., Wright, W., and Lopez, M.F., Constitutive equations for metals under compression at high strain rates and high temperatures, in LA-12669-MS, IS-4 Report Section, New Mexico: Los Alamos Natl. Lab., 1994.
Tan, P., Lee, B., and Tsangalis, C., FEA modeling prediction of the transmitted overpressure and particle acceleration within a frame subjected to shock tube blast loadings, 18th World IMACS/MODSIM Congr., Cairns, Australia, July 13–17, 2009, Cairns, 2009, pp. 1657–1663.
Arola, D. and Ramulu, M., Orthogonal cutting of fiber-reinforced composites: a finite element analysis, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 1997, vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 597–613.
Rao, G.V.G., Mahajan, P., and Bhatnagar, N., Threedimensional macromechanical finite element unidirectional-fiber reinforced polymer composites, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, vol. 498, pp. 142–149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.A. Shchurov, A.V. Nikonov, I.S. Boldyrev, D.V. Ardashev, 2016, published in STIN, 2016, No. 3, pp. 36–40.
About this article
Cite this article
Shchurov, I.A., Nikonov, A.V., Boldyrev, I.S. et al. SPH modeling of chip formation in cutting unidirectional fiber-reinforced composite. Russ. Engin. Res. 36, 883–887 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068798X1610018X
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068798X1610018X