Abstract
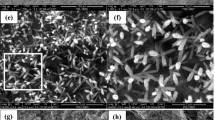
The anodization process was applied to 17-4PH stainless steel to modify its surface and to enhance hydrophobicity. The effects of various H2SO4/glycerin electrolytes and applied voltages on the water contact angle, the surface morphology (roughness), and corrosion resistance were investigated. It was observed that a high ratio of an H2SO4/glycerin electrolyte and high applied potentials resulted in an increase of a contact angle and an enhancement of the surface roughness. The highest contact angle was found to be up to 122.3°, when anodizing at 40 V using 70/30 of H2SO4/glycerin as electrolyte. Any further increase in the ratio of H2SO4/glycerin tended to reduce the contact angle. An electrochemical test showed that corrosion resistance was dependent on the hydrophobicity and surface roughness.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Costa, I., Franco, C.V., Kunioshi C.T., and Rossi, J.L., Corrosion resistance of injection-molded 17-4PH steel in sodium chloride solution, Corrosion, 2006, vol. 62, p. 357.
Liu, D., Liu, D., Zhang, X., Lui, C., et al., Surface nanocrystallization of 17-4 precipitation-hardening stainless steel subjected to ultrasonic surface rolling process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2018, vol. 726, p. 69.
Zhang, M. and Chu, Q., Heat treatment of 17-4PH stainless steel, Heat Treat. Met., 2012, vol. 37, no. 9, p. 8.
Suri, P., Smarslok, B.P., and German, R.M., Impact properties of sintered and wrought 17-4 PH stainless steel, Powder Metall., 2006, vol. 49, no. 1, p. 40.
Szewczyk-Nykiel, A., The effect of the addition of boron on the densification, microstructure and properties of sintered 17-4 PH stainless steel, Tech. Trans., 2014, vol. 13, p. 85.
Gülsoy, H.Ö., Salman, S., and Özbek, S., Effect of FeB additions on sintering characteristics of injection moulded 17-4PH stainless steel powder, J. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 39, no. 15, p. 4835.
Sobral, A.V.C., Ristow, W., Correa, O.V., Franco, C.V., et al., Corrosion behaviour of injection moulded 316L and 17-4PH stainless steels in a sodium chloride solution, Key Eng. Mater., 2001, vols. 189–191, p. 667.
Zhao, E., Li, Y., Gao, L., Yang, S., et al., Anti-corrosion properties of a bioinspired superhydrophobic surface on stainless steel, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2017, vol. 12, p. 9855.
Wu, Y., Zhao, F., Zhang Z., and Li, L., Study on the preparation and properties of micro-nano structure on the surface of 304 stainless steel by one-step anodizing, J. Nano Res., 2019, vol. 60, p. 42.
Ajeel, S., Ahmed, B., and Baker, Y.M., Electro-chemical measurements of anodizing stainless steel type Aisi 304, Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol., 2013, vol. 4, p. 63.
Latthe, S.S., Sudhagar, P., Devadoss, A., Kumarb, A.M., et al., A mechanically bendable superhydrophobic steel surface with its self-cleaning and corrosion-resistant properties, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, vol. 3, no. 27, p. 14263.
Rafieazad, M., Jaffer, J.A., Cui, C., Duan, X., et al., Nanosecond laser fabrication of hydrophobic stainless steel surfaces: The impact on microstructure and corrosion resistance, Materials, 2018, vol. 11, no. 9, p. 1577.
Minagar, S., Berndt, C.C., Wang, J., Ivanova, E., et al., A review of the application of anodization for the fabrication of nanotubes on metal implant surfaces, Acta Biomater., 2012, vol. 8, no. 8, p. 2875.
Martin, F., Del Frari, D., Cousty, J., and Bataillon, C., Self-organisation of nanoscaled pores in anodic oxide overlayer on stainless steels, Electrochim. Acta, 2009, vol. 54, no. 11, p. 3086.
Supriadi, S., Suharno, B., Widjaya, T., Ayuningtyas, S.T., et al., Development of superhydrophobic material SS 17-4 PH for bracket orthodontic application by metal injection molding, IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2018, vol. 299, no. 1, p. 012096.
Wang, J.H., Duh, J.G., and Shih H.C., Corrosion characteristics of coloured films on stainless steel formed by chemical, INCO and a.c. processes, Surf. Coat. Technol., 1996, vol. 78, nos. 1–3, p. 248.
Pochon, M. and Mantel, M., Improvement of stainless steels adhesive bonding using anodizing treatments, Rev. Métall., 2000, vol. 97, no. 5, p. 627.
Muratore, F., Baron-Wiecheć, A., Gholinia, A., Hashimoto, T., et al., Comparison of nanotube formation on zirconium in fluoride/glycerol electrolytes at different anodizing potentials, Electrochim. Acta., 2011, vol. 58, no. 1, p. 389.
Vera, M., Colaccio, Á., Rosenberger, M., Schvezov, C., et al., Influence of the electrolyte concentration on the smooth TiO2 anodic coatings on Ti–6Al–4V, Coatings, 2017, vol. 7, no. 3, p. 39.
Lee, B.G., Choi, J.W., Lee, S.E., Jeong, Y.S., et al., Formation behavior of anodic TiO2 nanotubes in fluoride containing electrolytes, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc., 2009, vol. 19, no. 4, p. 842.
Bervian, A., Ludwig, G.A., Kunst, S.R., Beltrami, L.V.R., et al., The influence of the glycerin concentration on the porous structure of ferritic stainless steel obtained by anodization, Dyna, 2015, vol. 82, no. 190, p. 46.
Khadiri, M., Elyaagoubi, M., Idouhli, R., Koumya Y., et al., Electrochemical study of anodized titanium in phosphoric acid, Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2020, vol. 2020, p. 5769071. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5769071
Ajeel, S.A., Puteh, R., and Baker, Y.M., Experimental study of anodizing process for stainless steel type 304, Wulfenia, 2013, vol. 20, no. 3, p. 347.
Domínguez-Jaimes, L.P., Arenas Vara, M.Á., Cedillo-González, E.I., Ruiz Valdés, J.J., et al., Corrosion resistance of anodic layers grown on 304L stainless steel at different anodizing times and stirring speeds, Coatings, 2019, vol. 9, no. 11, p. 706. .https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9110706
Zhang, B., Ni, H., Chen, R., Zhan, W., et al., A two-step anodic method to fabricate self-organised nanopore arrays on stainless steel, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, vol. 351, p. 1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.06.083
Poinern, G.E.J., Ali, N., and Fawcett, D., Progress in nano-engineered anodic aluminum oxide membrane development, Materials, 2011, vol. 4, p. 487.
Lin, Y., Lin, Q., Liu, X., Gao, Y., et al., A highly controllable electrochemical anodization process to fabricate porous anodic aluminum oxide membranes, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2015, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 495. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-1202-y
Zhang, D., Wang, L., Qian, H., and Li, X., Superhydrophobic surfaces for corrosion protection: A review of recent progresses and future directions, J. Coat. Technol. Res., 2016, vol. 13, no. 1, p. 11.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors express their gratitude to Dr. Aunchalee Manonukul from the National Metal and Materials Technology Center, Thailand, for providing the 17-4 PH stainless steel samples.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the research fund of Mae Fah Luang University, Thailand, grant no. 631B01014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Kosasang, O., Rattanawong, S. & Chumphongphan, S. Influence of Anodization Condition on Hydrophobicity, Morphology, and Corrosion Resistance of 17-4PH Stainless Steel. Surf. Engin. Appl.Electrochem. 58, 393–401 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375522040081
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375522040081