Abstract
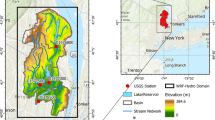
An object-oriented framework called GIS and Hydrologic Information System Modeling Object (GHISMO) that is tightly coupled with a prototype geographic information system (GIS), is presented in this research. The proposed GHISMO framework is used to simulate a hydrologic system on the base of the storage-release concept and with multiple weather data such as gage and NEXRAD data. Both quantitative and qualitative results of simulation for the Pleasant Run Creek and Little Buck Creek watersheds in Indiana (USA) demonstrate the method prospects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Yu. Abakumova, “A Study of Spatial Structure of Conditions of the River Network Formation,” Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol., No. 8, 38 (2013).
M. H. Ajward, A Spatially Distributed Unit Hydrograph Model Using a Geographic Information System, Ph. Doctoral Dissertation (Civil Engineering Department, University of Calgary, Calgary, 1996).
L. E. Band, C. L. Tague, S. E. Brun, et al., “Modeling Watersheds as Spatial Object Hierarchies: Structure and Dynamics,” Trans. in GIS, No. 3, 4 (2000).
J. F. Boyer, C. Berkhoff, and E. Servat, “Object-oriented Programming for a Simulation of the Rainfall-discharge Relationship,” in Proceedings of Hydroinformatics 96, Ed. by A. A. Balkema (Zurich, Switzerland, 1996).
H. Chen and R. Beschta, “Dynamic Hydrologic Simulation of the Bear Brook Watershed in Maine (BBWM),” Environ. Mon. Assess., 55 (1999).
J. Du, H. Xie, Y. Xu, and C. Xu, “Development and Testing of a New Storm Runoff Routing Approach Based on Time Variant Spatially Distributed Travel Time Method,” J. Hydrol., 369 (2009).
A. N. Gelfan, J. W. Pomeroy, and L. S. Kuchment, “Modeling Forest Cover Influences on Snow Accumulation Sublimation and Melt,” J. Hydrometeorol., No. 5, 5 (2004).
L. Garrote and I. Becchi, “Object-oriented Software for Distributed Rainfall-runoff Models,” J. Comput. Civil Eng., 11 (1997).
V. G. Kalinin and S. V. Pyankov, “Hydrological Geoinformation System “Basin of Votkinsk Reservoir,” Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol., No. 5 (2002).
K. Kang and V. Merwade, “Development and Application of a Storage-Release Based Distributed Hydrologic Modeling Using GIS,” J. Hydrol., 403 (2011).
G. A. Kiker, D. J. Clark, C. J. Martinez, and R. E. Schulz, “A Java Based, Object-oriented Modeling System for Southern African Hydrology,” Trans. of ASABE, No. 5, 49 (2006).
S. Kralisch, P. Krause, and O. David, “Using the Object Modeling System for Hydrological Model Development and Application,” Adv. Geosci., 4 (2005).
L. S. Kuchment and V. N. Demidov, “Modeling of Influence of Hydrological Processes on the Carbon Cycle of a Forest Ecosystem,” Environ. Model. Softw., 21 (2006).
L. S. Kuchment, A. N. Gelfan, and V. N. Demidov, “Modeling of the Hydrological Cycle of a Forest River Basin and Hydrological Consequences of Forest Cutting,” Open Hydrol. J., 5 (2011).
Y. B. Liu, S. Gebremeskel, F. Smedt, et al., “A Diffusive Transport Approach for Flow Routing in GIS-based Flood Modeling,” J. Hydrol., No. 1-4, 283 (2003).
D. R. Maidment, “GIS and Hydrologic Modeling,” in Environmental Modeling with GIS, Ed. by M. Goodchild, B. Parks, and L. Steyaert (Oxford University Press, New York, USA, 1993).
S. V. Pyankov and V. G. Kalinin, “Methodological Aspects of Spatial Analysis of the River Runoff Formation by Using Mathematical Cartographic Modeling,” Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol., No. 1, 34 (2009).
J. Wang, J. M. Hassett, and T. A. Endreny, “An Object Oriented Approach to the Description and Simulation of Watershed Scale Hydrologic Processes,” Comput. Geosci., No. 4, 31 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © K. Kang, J.H. Lee, 2017, published in Meteorologiya i Gidrologiya, 2017, No. 1, pp. 101-109.
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, K., Lee, J.H. Identification of the optimal integration of the hydrologic model with meteorology data using the advanced GIS object-oriented programming. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 42, 71–76 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068373917010095
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068373917010095