Abstract
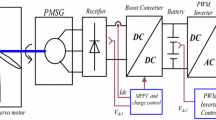
The principle of this article is to derive a numerical model of a wind energy system (WES) with transient speed wind rotary turbine with mechanical drive, pitch angle adjustment, Permanent magnet synchronised generator (PMSG), and power switched converter. The model uses low-solidity rotors which is necessary for a WES when used for power generation. The important features of the WES model is that it is designed to have maximum value of coefficient of performance in line with Betz limit, uses power electronic based connection between the generator and the dc bus paving way for dynamic control, has a good specific rated capacity (SRC) and uses a Permanent magnet synchronous generator instead of conventional induction generator. Simulation models are presented and the output is compared with conventional WES system.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Slootweg, J.G., de Haan, S.W.H., Polinder, H., and Kling, W.L., General model for representing variable speed wind turbines in power system dynamics simulations, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., 2003, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 1312–1322.
Ezhilarasan, G., et al., An improved buck boost converter using auxiliary resonance for photo voltaic based dynamic voltage restorer, Proc. ICPERES 2014 “Power Electronics and Renewable Energy Systems,” Lecture Notes Electr. Eng. Ser. vol. 326, New York: Springer-Verlag, 2014.
Kim, S.-K., Kim, E.-S., and Ahn, J.-B., Modeling and control of a grid-connected wind/PV hybrid generation system, Proc. 2003 IEEE PES Transmission and Distribution Conf. and Exposition, Piscataway, NJ: Inst. Elec-tr. Electron. Eng., 2003, pp. 1202–1207.
Kaderbhai, M. and Yuvarajan, S., Power electronics and control for wind power systems, Proc. 2009 IEEE Conf. on Power Electronics and Machines in Wind Applications, Piscataway, NJ: Inst. Electr. Electron. Eng., 2009, pp. 1–4.
El Moursi, M.S., Goweily, K., Kirtley, J.L., Jr., and Abdel-Rahman, M., Application of series voltage boosting schemes for enhanced fault ridethrough performance of fixed speed wind turbines, IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, 2014, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 61–71.
Jiang, Z. and Yu, X., Modeling and control of an integrated wind power generation and energy storage system, Proc. 2009 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Piscataway, NJ: Inst. Electr. Electron. Eng., 2009, pp. 212–221.
Onara, O.C., Uzunoglu, M., and Alam, M.S., Dynamic modeling, design and simulation of a wind/fuel cell/ultra-capacitor-based hybrid power generation system, J. Power Sources, 2006, vol. 161, pp. 707–722.
Iqbal, M T., Modeling and control of a wind fuel cell hybrid energy system, Renewable Energy, 2003, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 223–237.
Polinder, H., van der Pijl, F.F.A., de Vilder, G.-J., and Tavner, P., Comparison of direct-drive and geared generator concepts for wind turbines, IEEE Trans. Energy Convers., 2006, vol. 21, pp. 725–733.
Ezhilarasan, G. and Prakash, K., DC UPS for critical loads, Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res., 2015, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 3616–3622.
Xia, Y., Ahmed, K.H., and Williams, B.W., A new maximum power point tracking technique for permanent magnet synchronous generator based wind energy conversion systems, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., 2011, vol. 26, no. 12, pp. 3609–3620.
Kazmi, S.M.R., Goto, H., Guo, H.J., and Ichinokura, O., A novel algorithm for fast and efficient speed-sensorless maximum power point tracking in wind energy conversion systems, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 2011, vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 29–36.
Yazdani A. and Dash, P.P., A control methodology and characterization of dynamics for a photovoltaic (PV) system interfaced with a distribution network, IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, 2009, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 1538–1551.
Ezhilarasan, G. and Jayasree, K.S., Isolated buck-boost converter for a photovoltaic energy harvest system, Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res., 2015, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 3775–3781.
Huang, N., Simulation of power control of a wind turbine permanent magnet synchronous generator system, MSc Thesis, Milwaukee, WI: Marquette Univ., 2013.
Bang, D., Polinder, H., Shrestha, G., and Ferreira, G.A., Review of generator systems for direct-drive wind turbines, Proc. European Wind Energy Conf. and Exhibition, Brussels, 2008, pp. 109–119.
Zhang, S., Tseng, K.J., Vilathgamuwa, D.M., Nguyen, T.D., and Wang, X.Y., Design of a robust grid interface system for PMSG-based wind turbine generators, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 2011, vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 316–328.
Bhende, C.N., Mishra, S., and Malla, S.G., Permanent magnet synchronous generator-based standalone wind energy supply system, IEEE Trans. Sustainable Energy, 2011, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 361–373.
Ezhilarasan, G. and Prakash, K., Multi string converters for photovoltaic cell, Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res., 2015, vol. 10, no. 33, pp. 25790–25795.
Yang, J., Fletcher, J.E., and Reilly, J.O., A series dynamic resistor based converter protection scheme for doubly-fed induction generator during various fault conditions, IEEE Trans. Energy Convers., 2010, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 422–432.
Garcia-Hernandez, R. and Garduno-Ramirez, R., Modeling a Wind Turbine Synchronous Generator, Int. J. Energy Power, 2013, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 989–997.
Ezhilarasan, G. and Dash, S.S., A new approach in modeling and control of distributed energy resources for performance optimization and reliability improvement in a micro grid, Int. Rev. Model. Simul., 2015, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 26–40.
Li, S., Haskew, T.A. Swatloski, R.P. and Gathings, W., Optimal and direct-current vector control of direct-driven PMSG wind turbines, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., 2012, vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 2325–2337.
Wu, B., Lang, Y., Zargari, N. and Kouro, S., Power converters in wind energy conversion systems, in Power Conversion and Control of Wind Energy Systems, Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ezhilarasan, G., Gowda, N.D. & Saranya, D. Mathematical and Simulation Model of a Wind Energy System for a Grid Integrated Distributed Generation. Russ. Electr. Engin. 91, 792–798 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068371220120068
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068371220120068