Abstract
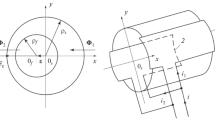
The damping winding of the synchronous machine is practically activated in transient conditions and the electromagnetic parameters of its equivalent diametrical circuits having magnetic axes d and q are adapted to the peculiarities of transients. It is necessary to distinguish between two types of the most common transients associated with asynchronous and synchronous motion of the rotors. Two sets of electromagnetic parameters of the equivalent damping winding can be found for them. On the basis of mathematical modeling of a synchronous machine with a full damping winding containing ten rods at each pole, a mathematical model of 15 differential equations in the Cauchy form is obtained, which allows the currents of all the rods of the real damping winding to be determined. On the basis of this model, the electromagnetic parameters of the equivalent damping winding for the two above-mentioned types of transients were determined. The traditional method of determining the parameters of the equivalent damping winding, which is based on the nonsynchronous steady-state motion of the rotor, yields ambiguous results depending on the location of the amplitude of the current layer of the rotor on its surface. Formulas for calculation of parameters of equivalent damping winding by this method were specified. The methods associated with the transient in synchronous mode give approximately the same values of the parameters of the equivalent damping winding.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Gradshtein, I.S. and Ryzhik, I.M., Tablitsy integralov, summ, ryadov i proizvedenii (Tables of Integrals, Sums, Series, and Products), Moscow: Fizmatgiz, 1963.
Abramov, A.I. and Ivanov-Smolenskii, A.V., Proektirovanie gidrogeneratorov i sinkhronnykh kompensatorov (Design of Hydrogenerators and Synchronous Capacitor), Moscow: Vysshaya Shkola, 1978.
Danilevich, Ya.B., Dombrovskii, V.V., and Kazovskii, E.Ya., Parametry elektricheskikh mashin peremennogo toka (Parameters of AC Electric Machine), Moscow: Nauka, 1965.
Dombrovskii, V.V., Eremeev, A.S., Ivanov, N.P., et al., Proektirovanie gidrogeneratorov (Design of Hydrogenerators), Moscow: Energiya, 1965, part 1.
Afanas’ev, A.A., Metod sopryazheniya konformnykh otobrazhenii v zadachakh elektromekhaniki (Conjugation Method for Conformal Mapping in Electromechanical Problems), Cheboksary: Chuvash. Gos. Univ., 2011.
Ivanov-Smolenskii, A.V., Elektricheskie mashiny (Electrical Machines), Moscow: Energiya, 1980.
Arakelyan, A.K. and Afanas’ev, A.A., Ventil’nye elektricheskie mashiny i reguliruemyi elektroprivod. Kniga 1. Ventil’nye elektricheskie mashiny (Valve Electric Machines and Adjustable Electric Drive, Book. 1: Valve Electrical Machines), Moscow: Energoatomizdat, 1997.
Danilevich, Ya.B. and Kulik, Yu.A., Teoriya i raschet dempfernykh obmotok sinkhronnykh mashin (Theory and Calculation of Damper Windings of Synchronous Machines), Moscow: Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1962.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by S. Avodkova
About this article
Cite this article
Afanas’ev, A.A. For Calculating the Parameters of the Equivalent Damping Winding of a Single-Pole Synchronous Machine. Russ. Electr. Engin. 91, 772–780 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068371220120020
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068371220120020