Abstract
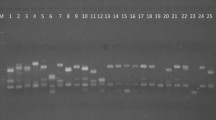
Genetic diversity of Ralstonia solanacearum, on seeds of tomato from different seed sources in Bangladesh was studied by using Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. The primers viz., OPA02, OPA08, OPA09, OPA10, OPA18 and OPE19 were tested in this experiment and were also evaluated on the basis of intensity and resolution of the band. Of these, the specific marker (OPA18) of RAPD in molecular characterisation of R. solanacearum produced distinct twenty bands with 100% polymorphism at base pair of 100–2000. Segregation of isolates of R. solanacearum was determined in unweighted pair group method with arithmetic means. In cluster analysis, isolate of Metal seed company Ltd. was very near with United seed company limited and Mallika seed company with the least genetic distance. Metal seed company Ltd. was also close to Lal Teer seed company Ltd. with lower genetic distance (0.1625). Coefficient of gene differentiation (1.0000) in R. solanacearum marked high genetic variations indicating adequate polymorphism. The highest (1.204) genetic distance was found in Namdhari seed company limited vs. Bangladesh Institute of Nuclear Agriculture (BINA). Moreover genetic identity was obtained as higher (0.8500) in United seed company limited vs. Metal seed company Ltd., and the lowest genetic identity (0.3000) was noted in BINA vs. Namdhari seed company limited. Banding pattern, gene differentiation, genetic distance and genetic identity showed the distinct genetic variations which were associated with each isolate of R. solanacearum.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Mansfield, J., Genin, S., Magori, S., Citovsky, V., Sriariyanum, M., and Ronald, P., et al., Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology, Mol. Plant Pathol., 2012, vol. 13, pp. 614–629.
Yabuuchi, E., Kosako, Y., Yano, I., Hotta, H., and Nishiuchi, Y., Transfer of two burkholderia and an alcaligenes species to Ralstonia gen. nov.: Proposal of Ralstonia pickettii (Ralston, Palleroni and Doudoroff 1973) comb. nov., Ralstonia solanacearum (Smith 1896) comb. nov. and Ralstonia eutropha (Davis 1969) comb. nov., Microb. Immun., 1995, vol. 39, pp. 897–904.
Hayward, A.C., The hosts of Pseudomonas solanacearum, in Bacterial Wilt, the Disease and Its Causative Agent, Pseudomonas solanacearum, Hayward, A.C. and Hartman, G.L., Eds., Wallingford, UK: CAB Int., 1994, pp. 9–25.
Fegan, M. and Prior, P., How complex is the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex?, in Bacterial Wilt: The Disease and the Ralstonia solanacearum Species Complex, Allen, C., Prior, P., and Hayward, A.C., Eds., St Paul, MN: APS Press, 2005, pp. 449–461.
Ramesh, R., Achari, G.A., and Gaitonde, S., Genetic diversity of Ralstonia solanacearum infecting solanaceous vegetables from India reveals the existence of unknown or newer sequevars of Phylotype I strains, Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2014, vol. 140, pp. 543–562.
Roy, C. and Sansonetti, P., Host-microbe interactions: Bacteria host- pathogen interactions: Interpreting the dialogue, Curr. Opin. Microb., 2004, vol. 7, pp. 1–3.
McGee, D.C., Epidemiology approach to disease management through seed technology, Ann. Rev. Phytopathol., 1995, vol. 33, pp. 445–466.
Vanitha, S.C., Niranjana, S.R., Mortensen, C.N., and Umesha, S., Bacterial wilt of tomato in Karnataka and its management by Pseudomonas fluorescens, Bio Control, 2009, vol. 54, pp. 685–695.
Popoola, A.R., Ganiyu, S.A., Enikuomehin, O.A., Bodunde, J.G., Adedibu, O.B., Durosomo, H.A., and Karunwi, O. A., Isolation and characterization of Ralstonia solanacearum causing bacterial wilt of tomato in Nigeria, Nigerian J. Biotech., 2015, vol. 29, pp. 1–10.
Hanson, P.M., Wang, J.-F., Lucardo, O., Hanudin, S.Y.M., Hartman, G.L., Lin, Y.C., and Chen, J.T., Variable reactions of tomato lines to bacterial wilt evaluated at several locations in South-East Asia, Hortic. Sci., 1996, vol. 31, pp. 143–146.
Williams, J.G.K., Kubelik, A.R., Livak, K.J., Rafalski, J.A., and Tingey, S.V., DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as generic markers, Nucl. Acids Res., 1990, vol. 18, no. 22, pp. 6531–6535.
Grover, A., Azmi, W., Gadewar, A.V., Pattanayak, D., Naik, P.S., Shekhawat, G.S., and Chakrabarti, S.K., Genotypic diversity in a localized population of Ralstonia solanacearum as revealed by random amplified polymorphic DNA markers, J. App. Microb., 2006, vol. 101, no. 4, pp. 798–806.
Singh, D., Sinha, S., Chaudhary, G., Yadav, D.K., and Mondal, K.K., Genetic diversity of biovar 3 and 4 of Ralstonia solanacearum causing bacterial wilt of tomato using BOX- PCR, RAPD and hrp gene sequences, Indian J. Agric. Sci., 2014, vol. 84, no. 3, pp. 391–395.
Sumangala, K., Lingaraju, S., Hegde, Y.R., and Byadagi, A.S., Genetic diversity of Ralstonia solanacaerum from major tomato growing areas of Karnataka, Int. J. Plant Prot., 2012, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 324–328.
Kelman, A., The relationship of pathogenicity in Pseudomonas solanacearum to colony appearance on a tetrazolium medium, Phytopathology, 1954, vol. 44, pp. 693–695.
Kovacs, N., Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction, Nature, 1956, vol. 178, p. 703.
Lelliott, R.A. and Stead, D.E., Methods for the diagnosis of bacterial diseases of plants, in Methods in Plant Pathology, Preece, T.F., Ed., London, UK: Blackwell Sci. Press, 1987, vol. 2.
Kiraly, Z., Methods in Plant Pathology, Budapest: Akad. Kiado, 1970.
Klement, Z., Rapid detection of the pathogenicity of phytopathogenic pseudomonads, Nature, 1963, vol. 199, pp. 299–300.
Ausubel, F. M., Brent, R., and Kingston, R.E., et al., Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1987.
Khayamie, S., Niknejad, K.N., Rabie, B., Sassanie, S., and Ebadie, A.A., Genetic characterization of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae strains from stone fruits based on RAPD analysis in Iran, Agric. Trop. Subtrop., 2009, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 162–166.
Nei, M., Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1973, vol. 70, no. 12, pp. 3321–3323.
Yeh, F.C., Yang, R.C., and Boyle, T., POPGENE 32-Version 1.31. Population Genetics Software, 1999.
Sharma, N. and Sharma, D.K., Incidence and seed transmission of Ralstonia solanaceurm (Smith) in brinjal (Solanum melongena L.) seeds, Int. J. Plant Pathol., 2014, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 63–69.
Sharma, D.K. and Agrawal, K., Incidence and histopathology of Ralstonia solanaceurm in tomato seeds, J. Mycol. Plant Pathol., 2010, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 115–119.
Kumar, S., Kedar, N., Hamsaveni, N., Gowda, P.H.R., Rohini, I.B., Rangaswamy, K.T., and Achari, R., Isolation and characterization of Ralstonia solanacearum causing bacterial wilt of Solanaceae crops, Int. J. Curr. Microb. Appl. Sci., 2017, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 1173–1190.
Perez, A.S., Mejia, L., Fegan, M., and Allen, C., Diversity and distribution of Ralstonia solanacearum strains in Guatemala and rare occurrence of tomato fruit infection, Plant Pathol., 2008, vol. 57, no. 2, pp. 320–331.
Ramsubhag, A., Lawrence, D., Cassie, D., Fraser, R., Umaharan, P., Prior, P., and Wicker, E., Wide genetic diversity of Ralstonia solanacearum strains affecting tomato in Trinidad, West Indies, Plant Pathol., 2012, vol. 61, no. 5, pp. 844–857.
Jeong, Y., Kim, J., Kang, Y., Lee, S., and Hwang, I., Genetic diversity and distribution of Korean isolates of Ralstonia solanacearum, Plant Dis., 2007, vol. 91, no. 10, pp. 1277–1287.
Nishat, S., Hamim, I., Khalil, M.I., Ali, M.A., Hossain, M.A., Meah, M.B., and Islam, M.R., Genetic diversity of the bacterial wilt pathogen Ralstonia solanacearuma using a RAPD marker, Comp. Ren. Biol., 2015, vol. 338, no. 11, pp. 757–767.
Dey, P., Hossain, I., Hossain, M.D., Mahmud, H., and Dey, S.K., Assessment of genetic diversity of seed borne Ralstonia solanacearuma of eggplant in Bangladesh, J. Plant Physiol. Pathol., 2020, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 1–7.
Castillo, J.A. and Greenberg, J.T., Evolutionary dynamics of Ralstonia solanacearuma, Appl. Environ. Microb., 2007, vol. 73, no. 4, pp. 1225–1238.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors acknowledge the financial support and scholarship granted by the Bangabandhu fellowship on Science, Information and Communication Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Dhaka and also acknowledge the Professor Golam Ali Fakir Seed Pathology Centre and Molecular Plant Pathology Laboratory, Department of Plant Pathology, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh to provide laboratory facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
About this article
Cite this article
Purnima Dey, Hossain, I., Mahmud, H. et al. Tomato Seed Borne Ralstonia solanacearum in Bangladesh. Russ. Agricult. Sci. 47, 386–393 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068367421040157
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068367421040157