Abstract
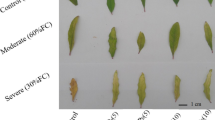
The sewage effluent is used as source of irrigation in developing as well as developed countries. The usage of the treated effluent for agricultural purpose and recreational activities are due to the demand of the water worldwide. This study aims to reveal the impact of various concentration of the treated sewage effluent on the germination and physiological parameters of green gram (Vigna radiata), red gram (Cajanus cajan) and paddy (Oryza sativa). Treated sewage effluents collected from three different sewage treatment plants of Mysore City (Kesere, Vidhyarayanapuram, Rayenakare) was used to cultivate the seedling with different concentrations (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 and 100%). It is concluded that the germination percentage of the seedlings are maximum at lower dilutions of 10–30% for all the treated water. The highest shoot length (27.53) and root length (26.91) was reported was for paddy cultivated with Kesare sewage water at an effluent concentration of 10%. The seedling cultivated in Kesare treated sewage effluent exhibited maximum shoot length and root length. The vigour index was reported to be higher for effluent concentration of 10%. This study concludes that the seed germination, root length, shoot length and vigour Index are dependable on the concentration of the effluent used. In 10% concentration of effluent is most effective and stresses the need of proper concentration of the effluent for irrigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Baki, A.A. and Anderson, J.D., Vigour determination of soya bean seed by multiple criteria, Crop Sci., 1973, no. 13, pp. 630–633.
Agarwal, P.K., Singh, V.P., and Kumar, D., Biochemical changes in seedling on B. nigra and L. usitatissimum under the stress of Mansurpur distillery effluents, J. Indian Bot. Soc., 1981, no. 2, pp. 60–95.
Ajmal, M. and Khan, A.U., Effects of sugar factory effluent on soil and crop plants, Environ. Pollut., 1983, no. 30, pp. 135–141.
APHA. Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, Washington, D.C., 2005. ed. 21.
Bakhsh, K. and Hassan, S., Use of sewage water for radish cultivation: A case study of Punjab, Pak. J. Agric. Soc. Sci., 2005, vol. 1, no. (4), pp. 322–326.
Bazai, Z.A. and Achakzai, A.K.K., Effect of waste water from Quetta city on germination and seedling growth of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.), J. App. Sci., 2006, vol. 6, no. (2), pp. 380–382.
Behera, B.K. and Mishra, B.N., Analysis of industrial effluent on growth and development of rice seedling, Environ. Res., 1982, no. 28, pp. 10–20.
Choudhury, S.K., Jha, A.N., and Srivastava, D.K., Effect of paper mill effluent on seed germination and seed germination and seedling growth in maize, Environ. Ecol., 1987, no. 5, pp. 285–287.
Czabator, F.J., Germination value: An index combining seed and completeness of pine seed germination, Forensic Sci., 1962, no. 8, pp. 386–396.
Doke, M.K., Khan, E.M., Rapoul, J., and Shaikh, A., Physico-chemical analysis of sugar industry effluent and its effect on seed germination of Vignangularis, Vigna cylindrical, and Sorghum cernum, 2011, no. 5, pp. 7–11.
Feigin, A., Ravina, I., and Shalhevet, J., Irrigation with treated sewage effluent management for environmental protection, J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci., 1991. vol. 154, no. 6, p. 446.
Hicks, R.W. and Hird, C., Soil and urban land use, in Soil: Their Properties and Management, Charman, P.E.V. and Murphy, B.W., Eds., Oxford University Press, 2000. ed. 2, p. 378–399.
Karunaichamy, K.S.T.K., Paliwal, K., and Swami, P.S., Effect of sewage water irrigation on dry matter yield and heavy metal concentration in three forage grasses, Int. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 1990, no. 16, pp. 151–160.
Khan, M.G., Danlel, G., Konjit, M., Thomas, A., Eyasu, S.S., and Awoke, G., Impact of textile waste water on seed germination and some physiological parameters in pea, Asian J. Plant Sci., 2011, no. 10, pp. 269–273.
Lubello, C., Gori, R., Paolo, N.F., and Ferrini, F., Municipal-treated waste water reuse for plant nurseries irrigation, Water Res., 2004, no. 38, pp. 2939–2947.
Nagajyothi, P.C., Dinakar, N., Suresh, S., Udaykiran, Y., Suresh, C., and Damodharam, T., Effect of industrial effluent on the morphological parameters and chlorophyll content of green gram (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.), J. Environ. Biol., 2009, vol. 30, no. (3), pp. 385–388.
Nagda, G.K., Diwan, A.M., and Ghole, V.S., Seed germination bioassays to assess toxicity of molasses fermentation based bulk drug industry effluent, Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem., 2006, vol. 5, no. (6), pp. 1598–1603.
Nath, K., Singh, D., Shyam, S., and Sharma, Y.K., Phytotoxic effects of chromium and tannery effluent on growth and metabolism of Phaseolus mungo Roxb., J. Environ. Biol., 2009, vol. 30, no. (2), pp. 227–234.
Otobbang, E., Sadovnikova, L., Lakimenko, O., Nilsson, I., and Persson, J., Sewage sludge: Soil conditioner and nutrient source. II. Availability of Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cd to barley in a pot experiment, Acta Agric. Scand., Soil Plant Sci., 1997, vol. 47, pp. 65–70.
Panasker, D.B. and Pawar, R.S., Effect of textile mill effluent on growth of Vigna unguiculata and Pisum sativum seedlings, Indian J. Sci. Technol., 2011., no. 4, pp. 266–272.
Pathak, H., Joshi, H.C., Chaudhary, A., Chaudhary, R., Kalra, N., and Dwivedi, M.K., Distillery. effluent as soil amendment for wheat and rice, J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci., 1998, no. 46, pp. 155–157.
Pathak, H., Joshi, H.C., Chaudhary, A., Chaudhary, R., Kalra, N., and Dwivedi, M.K., Soil amendment with distillery effluent for wheat and rice cultivation, Water, Air, Soil Pollut., 1999, vol. 113, no. (1–4), pp. 133–140.
Ramana, S., Biswas, A.K., Singh, A.B., and Yadava, R.B.R., Relative efficancy of different distillery effluents on growth, nitrogen fixation and yield of groundnut, Bioresour. Technol., 2001, no. 81, pp. 117–121.
Ramana, S., Biswas, A.K., Kundu, S., Saha, J.K., and Yadava, R.B., Effect of distillery effluent on seed germination in some vegetable crops, Bioresour. Technol., 2002, vol. 82, no. (3), pp. 273–275.
Rodosevich, S., Holt, J., and Ghersa, C., Weed Ecology, Implications for Management, New York: Wiley Publishers, 1997.
Saravanamoorthy, M.D. and Ranjitha Kumari, B.D., Effect of textile waste water on morphophysiology and yield on two varieties of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.), J. Agric. Technol., 2007, vol. 3, no. (2), pp. 335–343.
Shakunthala Bai, Shivanna Srikantaswamy, and Doddaiah Shivakumar, Urban wastewater characteristic and its management in urban areas–a case study of Mysore City, Karnataka, India, J. Water Resour. Prot., 2010, no. 2, pp. 717–726.
Singh, D.K., Kumar, D., and Singh, V.P., Studies of pollution effects of sugar mill and distillery effluents on seed germination and seedling growth in three varieties of rice, J. Environ. Biol., 1985, no. 6, pp. 31–35.
Subramani, A., Sundermoorti, P., Saravanan, S., Silvarju, M., and Lakshmanchary, A.S., Impact of biologically treated distillery effluent on growth behaviour of green gram (Viniga radiate), J. Ind. Pollut. Control, 1999, no. 15, pp. 281–286.
Ungar, L.A., Halophyte seed germination, Bot. Rev., 1987, no. 44, pp. 233–264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
About this article
Cite this article
Divya, L., George, J., Midhun, G. et al. Impacts of treated sewage effluent on seed germination and vigour index of monocots and dicot seeds. Russ. Agricult. Sci. 41, 252–257 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068367415040242
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068367415040242