Abstract
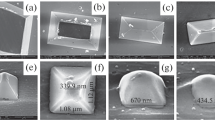
Results of the characterization and numerical analysis of InAsSbP composition strain-induced micro- and nanostructures shape transition are presented. Nucleation is performed from In-As-Sb-P quaternary composition liquid phase in Stranski–Krastanow growth mode. Geometric features and the shape transformation chronology of truncated pyramidal islands, lens-shape and pyramidal quantum dots (QDs) are under consideration, which opens up new possibilities at nanoscale engineering and nanoarchitecture of several types of nanostructures. High-resolution scanning electron (HR-SEM) and transmission electron (TEM) microscopes are used for micro- and nanostructures characterization. We show that as the islands volume decreases, the following succession of shape transitions are detected: truncated pyramid, {111} facetted pyramid, {111} and partially {105} facetted pyramid, completely unfacetted ‘pre-pyramid’, which gradually evolve to hemisphere and then again to pyramidal QD but with higher facet indexes. Critical sizes of islands shape transformation from ‘pre-pyramid’ to hemisphere (500–550 nm) and then from lens-shape again to pyramidal QDs (5–7 nm) are experimentally detected and theoretically evaluated. It is shown that theoretically calculated values coincide with experimentally obtained data.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bimberg, D., Grundmann, M., and Ledentsov, N.N., Quantum Dot Heterostructures, New York: Wiley, 1998.
Bhattacharya, P., Su, X.H., Chakrabarti, S., et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2005, vol. 86, p. 191106.
Rogalski, A., Acta Phys. Pol. A, 2009, vol. 116, p. 389.
Aroutiounian, V.M., Petrosian, S.G., Khachatryan, A., and Touryan, K., J. Appl. Phys., 2001, vol. 89, p. 2268.
Rudin, A.M., Guo, L.J., et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 1998, vol. 73, p. 3429.
Marquardt, O., Hickel, T., Neugebauer, J., Gambaryan, K.M., and Aroutiounian, V.M., J. Appl. Phys., 2011, vol. 110, p. 043708.
Gambaryan, K.M., Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2010, vol. 5, p. 587.
Aroutiounian, V.M., Gambaryan, K.M., and Soukiassian, P.G., Surface Science, 2010, vol. 604, p. 1127.
Ishikuro, H. and Hiramoto, T., Appl. Phys. Lett., 1997, vol. 71, p. 3691.
Gambaryan, K.M., Aroutiounian, V.M., and Harutyunyan, V.G., Infrared Phys. & Tech., 2011, vol. 54, p. 114.
Stranski, I. and Krastanow, L., Math.-Naturwiss., 1938, vol. 146, p. 797.
Gambaryan, K.M., Aroutiounian, V.M., Boeck, T., and Schulze, M., Phys. Status Solidi C, 2009, vol. 6, p. 1456.
Daruka, I., Tersoff, J., and Barabasi, A.-L., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1999, vol. 82, p. 2753.
Tersoff, J. and LeGoues, F.K., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1994, vol. 72, p. 3570.
Zinke-Allmang, M., Feldman, L.C., and Grabow, M.H., Surf. Sci. Rep., 1992, vol. 16, p. 377.
Ross, F.M., Tersoff, J., and Tromp, R.M., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1998, vol. 80, p. 984.
Tersoff, J., Spencer, B.J., Rastelli, A., and von Kanel, H., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2002, vol. 89, p. 196104.
Liu, N., Tersoff, J., Baklenov, O., Holmes, Jr., A.L., and Shih, C.K., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2000, vol. 84, p. 334.
Gambaryan, K.M., Aroutiounian, V.M., Boeck, T., et al., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2008, vol. 41, p. 162004.
Tersoff, J. and Tromp, R.M., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1993, vol. 70, p. 2782.
Safonov, K.L., Dubrovskii, V.G., Sibirev, N.V., and Trushin, Yu.V., Technical Physics Letters, 2007, vol. 33, p. 490.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors wish to thank to Dr. T. Boeck from Institute for Crystal Growth (IKZ), Berlin, Germany and Dr. A. Trampert from Paul Drude Institute for Solid State Electronics (PDI), Berlin, Germany for HR-SEM and TEM measurements, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by K.M. Gambaryan
About this article
Cite this article
Gambaryan, K.M., Aroutiounian, V.M. Geometric Features and Numerical Analysis of InAsSbP Composition Micro- and Nanostructures Shape Transformation at Nucleation from Liquid Phase. J. Contemp. Phys. 56, 133–138 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068337221020067
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068337221020067