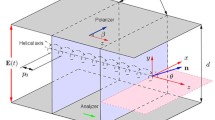
Abstract
The possibility of using a ferrielectric liquid crystal as an electro-optic medium for a phase spatial light modulator has been investigated. The electro-optic characteristics of a ferrielectric liquid crystal are measured, and a numerical simulation of a 12-sector spiral phase plate based on this crystal is performed. It is found that, at a sub-kilohertz frequency of phase shift switching modulation by 2π, the investigated liquid-crystal ferrielectric is a lower voltage electro-optic medium for space–time light modulators in comparison with ferroelectric liquid crystals.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H., Forbes A., et al., Roadmap on structured light, J. Opt., 2016, vol. 19, p. 013001. https://doi.org/10.1088/2040-8978/19/1/013001
Forbes. A., Dudley. A., and McLaren. M., Creation and detection of optical modes with spatial light modulators, Adv. Opt. Photon., 2016, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 200–227. https://doi.org/10.1364/AOP.8.000200
https://holoeye.com/spatial-light-modulators.
https://www.hamamatsu.com/eu/en/product/optical-components/lcos-slm/for-research-and-development/ lcos-slm/X-15213-01.html.
Yin, K., Hsiang, E.L., Zou, J., Li, Y., Yang, Z., Yang, Q., Lai, P.C., Lin, C.L., and Wu, S.T., Light: Science & Applications, 2022, vol. 11, no. 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-021-00680-w
Isomae, Y., Sugawara, N., Iwasaki, N., Honda, T., and Amari, K., Phase-only spatial light modulator having high reflectance, high-definition pixels and high photo-durability, Proc. SPIE, 2021, vol. 11788, p. 191. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2595136
Naumov, A.F., Loktev, M.Y., Guralnik, I.R., and Vdovin, G., Liquid-crystal adaptive lenses with modal control, Opt. Lett., 1998, vol. 23, pp. 992–994. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.23.000992
Vdovin, G.V., Guralnik, I.R., Kotova, S.P., Loktev M.Yu., and Naumov, A.F., Liquid-crystal lenses with a controlled focal length. I. Theory, Quantum Electronics, 1999, vol. 29, no. 3, p. 256. https://doi.org/10.1070/QE1999v029n03ABEH001463
Vdovin, G.V., Guralnik, I.R., Kotova, S.P., Loktev M.Yu., and Naumov, A.F., Liquid-crystal lenses with a controlled focal length. II. Numerical optimisation and experiments, Quantum Electron., 1999, vol. 29, no. 3, p. 261. https://doi.org/10.1070/QE1999v029n03ABEH001464
Lin, Y.H., Wang, Y.J., and Reshetnyak, V., Liquid crystal lenses with tunable focal length, Liq. Cryst. Rev., 2017, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 111–143. https://doi.org/10.1080/21680396.2018.1440256
Algorri, J.F., Zografopoulos, D.C., Urruchi, V., and Sanchez-Pena, J.M., Recent Advances in Adaptive Liquid Crystal Lenses, Crystals, 2019, vol. 9, no. 5, p. 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9050272
Kotova, S.P., Kvashnin, M.Y., Rakhmatulin, M.A., et al., Modal liquid crystal wavefront corrector, Opt. Express, 2002, vol. 10, no. 22, pp. 1258–1272. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.10.001258
Loktev, M., Vdovin, G., Klimov, N., and Kotova, S., Liquid crystal wavefront corrector with modal response based on spreading of the electric field in a dielectric material, Opt. Express, 2007, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 2770–2778. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.15.002770
Kotova, S.P., Patlan V.V., and Samagin S.A., Tunable liquid-crystal focusing device. 1. Theory, Quantum Electron., 2011, vol. 41, p. 58. https://doi.org/10.1070/QE2011v041n01ABEH014406
Kotova, S.P., Patlan V.V., and Samagin S.A., Tunable liquid-crystal focusing device. 2. Experiment, Quantum Electron., 2011, vol. 41, p. 65. https://doi.org/10.1070/QE2011v041n01ABEH014407
Kotova, S.P., Mayorova, A.M., and Samagin, S.A., Tunable 4-channel LC focusing device: summarized results and additional functional capabilities, J. Opt., 2015, vol. 17, no. 5, p. 055602. https://doi.org/10.1088/2040-8978/17/5/055602
Kotova S.P., Mayorova A.M., and Samagin S.A., Light fields generated by LC focusing device in different operational regimes, Proc. SPIE, 2016, vol. 10176, p. 1017626.
Kotova S.P., Mayorova A.M., and Samagin S.A., Ability of a four-channel liquid-crystal modulator to generate light fields with a complex intensity distribution, J. Opt. Technol., 2017, vol. 84, no. 5, pp. 323–330. https://doi.org/10.1364/JOT.84.000323
Xianyu, H., Wu, S.T., and Lin, C.L., Dual frequency liquid crystals: a review, Liq. Cryst., 2009, vol. 36, no. 6–7, pp. 717–726. https://doi.org/10.1080/02678290902755598
Peng, F., Chen, H., Tripathi, S., Twieg, R.J., and Wu, S.T., Fast-response infrared phase modulator based on polymer network liquid crystal, Opt. Mater. Express, 2015, vol. 5, pp. 265–273. https://doi.org/10.1364/OME.5.000265
Li, Y., Yang, Z., Chen, R., Mo, L., Li, J., Hu, M., and Wu, S.T., Submillisecond-response polymer network liquid crystal phase modulators, Polymers, 2020, vol. 12, no. 12, p. 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122862
Fan, Y.H., Lin, Y.H., Ren, H., Gauza, S., and Wu, S.T., Fast-response and scattering-free polymer network liquid crystals for infrared light modulators, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, vol. 84, pp. 1233–1235. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1649816
Sun, J. and Wu, S.T., Recent advances in polymer network liquid crystal spatial light modulators, J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys., 2014, vol. 52, pp. 183–192. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.23391
Love, G.D., Kirby, A.K., and Ramsey, R.A., Sub-millisecond, high stroke phase modulation using polymer network liquid crystals, Opt. Express, 2010, vol. 18, no. 7, pp. 7384–7389. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.18.007384
Hyman R.M., Lorenz A., and Wilkinson T.D., Phase modulation using different orientations of a chiral nematic in liquid crystal over silicon devices, Liq. Cryst., 2016, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 83–90. https://doi.org/10.1080/02678292.2015.1061146
Oton, E., Netter, E., Nakano, T., D-Katayama, Y., and Inoue, F., Monodomain Blue Phase Liquid Crystal Layers for Phase Modulation, Sci. Rep., 2017, vol. 7, no. 44575, p. 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44575
Beresnev, L.A., Chigrinov, V.G., Dergachev, D.I., Poshidaev, E.P., Fünfschilling, J., and Schadt, M., Deformed helix ferroelectric liquid crystal display: A new electrooptic mode in ferroelectric chiral smectic C liquid crystals, Liq. Cryst., 1989, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 1171–1177. https://doi.org/10.1080/02678298908026421
Pozhidaev, E.P., Kiselev, A.D., Srivastava, A.K., Chigrinov, V.G., Kwok, H.S., and Minchenko, M.V., Orientational Kerr effect and phase modulation of light in deformed-helix ferroelectric liquid crystals with subwavelength pitch, Phys. Rev. E, 2013, vol. 87, p. 052502. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.87.052502
Pozhidaev, E.P., Torgova, S.I., Molkin, V.M., Minchenko, M.V., Vashchenko, V.V., Krivoshey, A.I., and Strigazzi, A., New chiral dopant possessing high twisting power, The nano-scale pitch ferroelectric liquid crystal materials for modern display and photonic application employing highly effective chiral components: Trifluoromethylalkyl diesters of p-terphenyldicarboxylic acid, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 2009, vol. 509, no. 1, pp. 1042–1050. https://doi.org/10.1080/15421400903054667
Mikhailenko, V., Krivoshey, A., Pozhidaev, E., Popova, E., Fedoryako, A., Gamzaeva, S., Barbashov, V., Srivastava, A.K., Kwok, H.S., and Vashchenko, V., The nano-scale pitch ferroelectric liquid crystal materials for modern display and photonic application employing highly effective chiral components: Trifluoromethylalkyl diesters of p-terphenyldicarboxylic acid, J. Mol. Liq., 2019, vol. 281, pp. 186–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.02.047
Kotova, S.P., Samagin, S.A., Pozhidaev, E.P., and Kiselev, A.D., Light modulation in planar aligned short-pitch deformed-helix ferroelectric liquid crystals, Phys. Rev. E, 2015, vol. 92, no. 6, p. 062502. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.92.062502
Kotova, S.P., Pozhidaev, E.P., Samagin, S.A., Kesaev, V.V., Barbashov, V.A., and Torgova, S.I., Ferroelectric liquid crystal with sub-wavelength helix pitch as an electro-optical medium for high-speed phase spatial light modulators, Opt. Laser Technol., 2021, vol. 135, p. 106711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106711
Goodby, J.W., Patel, J.S., and Chin, E., Ferroelectric, ferrielectric and antiferroelectric properties in the (R)- and (S)-1-methylalkyl 4′-(4″-n-alkoxybenzoyloxy)biphenyl-4-carboxylate liquid crystals, J. Mater. Chem., 1992, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 197–207. https://doi.org/10.1039/JM9920200197
Pozhidaev, E.P., Minchenko, M.V., Kuznetsov, A.V., Tkachenko, T.P., and Barbashov, V.A., Broad temperature range ferrielectric liquid crystal as a highly sensitive quadratic electro-optical material, Opt. Lett., 2022, vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 1598–1601. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.450919
Pozhidaev, E., Torgova, S., Minchenko, M., Yednak, C.A.R., Strigazzi, A., and Miraldi, E., Phase modulation and ellipticity of the light transmitted through a smectic C* layer with short helix pitch, Liq. Cryst., 2010, vol. 37, no. 8, pp. 1067–1081. https://doi.org/10.1080/02678292.2010.486482
Pozhidaev, E.P., Srivastava, A.K., Kiselev, A.D., Chigrinov, V.G., Vashchenko, V.V., Krivoshey, A.I., Minchenko, M.V., and Kwok, H.S., Enhanced orientational Kerr effect in vertically aligned deformed helix ferroelectric liquid crystals, Opt. Lett., 2014, vol. 39, no. 10, pp. 2900–2903.
Emelyanenko, A.V., Pozhidaev, E.P., Molkin, V.E., and Shtykov, N.M., Antiferroelectric and ferrielectric liquid-crystal display: Electrically controlled birefringence color switch as a new mode, J. Soc. Inform. Display, 2008, vol. 16, no. 8, pp. 811–818. https://doi.org/10.1889/1.2966442
Gerard, A. and Burch, J.M., Introduction to Matrix Methods in Optics, New York: Wiley, 1975.
Beijersbergen, M.W., Coerwinkel, R.P., Kristensen, M., and Woerdman, J.P., Helical-wavefront laser beams produced with a spiral phaseplate, Opt. Commun., 1994, vol. 112, no. 5–6, pp. 321–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4018(94)90638-6
Ganic, D., Gan, X., Gu, M., Hain, M., Somalingam, S., Stankovic, S., and Tschudi, T., Generation of doughnut laser beams by use of a liquid-crystal cell with a conversion efficiency near 100%, Opt. Lett., 2002, vol. 27, no. 15, pp. 1351–1353.
Wang, Q., Sun, X.W., and Shum, P., Generating doughnut-shaped beams with large charge numbers by use of liquid-crystal spiral phase plates, Appl. Opt., 2004, vol. 43, no. 11, pp. 2292–2297. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.43.002292
Albero, J., Garcia-Martinez, P., Bennis, N., Oton, E., Cerrolaza, B., Moreno, I., and Davis, J.A., Liquid crystal devices for the reconfigurable generation of optical vortices, J. Lightwave Technol., 2012, vol. 30, p. 3055.
Goodman, J.W., Introduction to Fourier Optics, Englewood: Roberts, 2005.
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project nos. 20-02-00671, 20-02-00746 A, and 19-52-06005 MNTI_a).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by Yu. Sin’kov
About this article
Cite this article
Pozhidaev, E.P., Kotova, S.P. & Samagin, S.A. Ferrielectric Liquid Crystal with a Subwavelength Helix Pitch As an Electro-Optic Medium for Phase Spatial Light Modulators. Bull. Lebedev Phys. Inst. 50 (Suppl 1), S85–S95 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068335623130109
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068335623130109