Abstract
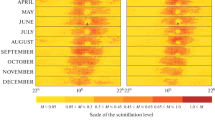
According to the data on the 20–24 solar activity cycles, long-term variations in the annual average solar wind speed and interplanetary scintillation index are compared to Wolf number variations. It is shown that the scintillation parameters at mid- and high heliolatitudes exhibit a slow nonmonotonic trend with a characteristic scale of the order of the secular cycle. For long-term data series since 1610 to the present, the correlation of variations of Wolf numbers and air temperature anomalies is analyzed. The possible application of the results to the global climate problem is discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Vlasov, V.I., Chashei, I.V., Shishov, V.I., and Shishova, T.D., Interplanetary plasma from radioastronomical data (Review), Geomagn. Aeron., 1979, vol. 19, pp. 269–282.
Vlasov, V.I., Interplanetary plasma during solar cycles 20, 21, and 22 from radio astronomical data, Sol. Syst. Res., 2000, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 103–106.
Vlasov, V.I., Long-term solar wind variations in the 20th–23rd solar activity cycles according to radio-astronomical data, Geomagn. Aeron., 2011, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 28–38. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793211010166
Tokumaru, M., Kojima, M., and Fujiki, K., Long-term evolution in the global distribution of solar wind speed and density fluctuations during 1997–2000, J. Geophys. Res., 2012, vol. 117, no. 6, p. 06108. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JA017379
Zerbo, J.-L. and Richardson, J.D., The solar wind during current and past solar minima and maxima, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys., 2015, vol. 120, p. 10, 250–10, 256. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JA021407
McComas, D.J., Elliott, H.A., Schwadron, N.A., Goslig, J.T., Skoug, R.M., and Goldstein, B.E., The three-dimensional solar wind around solar maximum, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2003, vol. 30, no. 10, pp. 1517–1520. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL017136
Dergachev, V.A., Solar activity, cosmic rays, and earth temperature reconstructions for the past two millennia, Geomagn. Aeron., 2015, vol. 55, no. 2, pp. 139–151. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793215020036
Humlum, O., Stordal, K., and Solheim, J.-E., The phase relation between atmospheric carbon dioxide and global temperature, Global Planet. Change, 2013, vol. 100, pp. 51–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.08.008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by A. Kazantsev
About this article
Cite this article
Vlasov, V.I., Dagkesamanskii, R.D., Potapov, V.A. et al. On Long-Term Variations in Solar Wind and Solar Activity Parameters with Possible Application to the Global Climate Problem. Bull. Lebedev Phys. Inst. 49, 6–9 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S106833562201002X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S106833562201002X