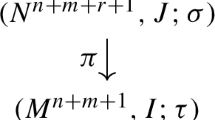Abstract
In this paper, we proceed with studying matrix equations over “skew series”. We establish conditions for splitting a Lagrange matrix equation into a set of scalar differential equations. We consider diagonal, triangular, nil-triangular, and dual-diagonal forms of its solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zaitsev, V. F. and Polyanin A. D. Handbook of Exact Solutions for Ordinary Differential Equations (Fizmatlit,Moscow, 2001; CRC Press, Boca Raton–New York, 2003).
DerevenskiiV. P. Quadratic Equations overMatrix Skew Series, RussianMathematics (Iz.VUZ) 58, No. 1, 14–26 (2014).
Serre J.-P. Lie Algebras and Lie Groups (W. A. Benjamin, Inc., New York–Amsterdam, 1965; Mir, Moscow, 1969).
Gantmacher F. R. The Theory of Matrices (Nauka, Moscow, 1959; Chelsea Publishing, Providence, RI, 1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.P. Derevenskii, 2015, published in Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii. Matematika, 2015, No. 12, pp. 14–26.
About this article
Cite this article
Derevenskii, V.P. Lagrange matrix equations. Russ Math. 59, 10–20 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1066369X15120026
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1066369X15120026