Abstract
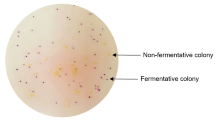
The diversity of cultured pathogenic bacteria in the bottled mineral water (BMW) was investigated using selective media. The pure isolates from these selective media, which showed hemolytic activity on the blood agar media and antibiotic resistance, were identified by 16S rRNA gene technique. The seven obtained strains were belonged to the genus Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Acinetobacter, Stenotrophomonas, and Exiguobacterium, and were mostly closed to the pathogenic strains. The increasing of ozone concentration from air-fed ozone generators eliminate the growth of bacteria included the pathogenic bacteria, but in other side it increases the amount of nitrates and nitrites in the final product of the BMW. These findings revealed that the BMW either has potential pathogenic bacteria or high levels of nitrates and all these products may effect on the health of the end user.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warburton, D.W., Can. J. Microbiol., 1993, vol. 39, pp. 158–168.
Ferreira, A.C., Morais, P.V., and da Costa, M., Ibid., 1994, vol. 40, pp. 72–77.
Papapetropoulou, M., Tsintzou, A., and Vantarakis, A., Ibid., 1997, vol. 43, pp. 499–502.
WHO. Division of emerging and ciommunicible deseases surveillance and control annual report, Geneva: World Health Organization, 1997.
Craun, G.F., Bwachuku, N., Calderon, R.L., and Craun, M.F., J. Environ. Health., 2002, vol. 65, pp. 16–23.
Magda, M.M., Abd El-Salam, E.M.A.E., Mohamed, M.M.K., J. Egypt. Public Health Assoc., 2008, vol. 83, pp. 468–486.
Camper, A.K., LeChevallier, M.W., Broadaway, S.C., and McFeters, G.A., Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1986, vol. 52, pp. 434–486.
Daood, N., J. Basic Sci., 2009, vol. 25, p. 1.
Burge, S.H. and Hunter, P.R., Rivista Ital. d’Igiene, 1990, vol. 50, pp. 401–406.
Eckmanns, T., Oppert, M., Martin, M., et al., Clinical Microbiol. Infection, 2008, vol. 14, pp. 454–458.
Palmera-Suarez, R., Garcia, P., Garcia, A., et al, Eutosurveillance, 2007, vol. 12, p. 3235.
Blake, P.A., Rosenberg, M.L., Bandeira Costa J., et al, Amer. J. Epidemiol., 1977, vol. 105, pp. 337–343.
Hunter, P.R.J., Appl. Bacteriol., 1993, vol. 74, pp. 345–352.
Ronald, M., Atlas Hand Book of Microbiol. Media, 14th ed., Boca Raton, USA: CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group, 2010.
APHA. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed., Washington: American. Public Health Assoc., 1998.
Ronald, M., Atlas Principles of Msicrobiology, Boston: Wm. C. Brown Publishers, 1997.
Raphael, S.S., Bryant, N.J., Hyde, T.A., et al., Lynch’ Medical Laboratory Technology, Philadephia: Saunders, 1983.
Chang, Y.J., Stephen, J.R., Richter, A.P., et al., J. Microbiol. Methods., 2000, vol 40, pp. 19–31.
Kumar, S., Tamura, K., and Nei, M., Brief Bioinform., 2004, vol. 5, pp. 150–163.
Zobell, C.E. and Anderson, D.Q., Biol. Bull., 1936, vol. 71. pp. 324–342.
Palmer, K.L., Brown, A., and Whiteley, M., J. Bacteriol., 2007, vol. 189, pp. 4449–4455.
Vander Mauven, C., Pierard, A., Kley-Raymann, M., and Haas, D., Ibid., 198, vol. 160, pp. 928–934.
Eliasson, B. and Kogelschatz, K., In. Proc. 18th Int. Symp. on Plasma Chem (Tokyo, 1987), Tokyo, 1987, pp. 736–740.
Kogelschatz, U. and Baessler, P., Ozone Sci. Eng., 1987, vol. 9, pp. 195–206.
Leclerc, H. and DaCosta, M.S., Technology of Bottled Water, Senior, D.A.G. and Ashurst, P., (Eds.), Stefield: Acad. Press. 1998, pp. 223–274.
Leclerc, H., Schwatzbrod, L., and Dei Cas, E., Crit Rev. Microbiol., 2002, vol. 28, pp. 371–409.
Griffith, F., J. Hygiene, 1928, vol. 27, pp. 113–159.
Kummerer, K., Antimicrob. Chemother., 2004, vol. 54, pp. 311–320.
Baguero, F., Martinez, J.L., and Canton, R., Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2008, vol. 19, pp. 260–265.
Cooke, M.D., Freshwater Res., 1975, vol. 10, pp. 391–397.
Goyal, S.M., Gerba, C.P., and Melnik, J.L., Water Res., 1979, vol. 13, pp. 349–356.
Klare, I., Heier, H., Claus, H., et al., Microbiol. Drug Resist., 1995, vol. 1, pp. 265–272.
Martinez, J.L., Science, 2008, vol. 321, pp. 365–367.
Zhang, Y., Marrs, C.F., and Siman, C., and Xi, C., Sci. Total Environ. 2009, vol. 407, pp. 3702–3706.
Armstrong, J.L., Shigeno, D.S., Colomiris, J.J., and Seidler, R., J. Appl. Emviron. Microbiol., 1981, vol. 42, pp. 277–283.
Schwartz, T., Kohnen, W., Jansen, B., and Obst, U., FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 325–335.
Cruickshank, R., Duguid, J.P., Marimon, B.P., and Swain, R.H.A., Medical Microbiology, 12nd ed., Edinburgh; London; New York: Churchill Livingstone, 1975.
Dibua, U.E., and Gideon, O., Animal Res. Int., 2006, vol. 3, pp. 439–447.
Palleroni, N.J., Doudoroff, M., and Steiner, R.Y., J. Gen. Microbiol., 1970, vol. 60, pp. 215–231.
Aragone, M.R., Maurizi, D.M., Clara, L.O., et al., J. Clinical Microbiol., 1992, vol. 30, pp. 1583–1584.
Oggioni, M.R., Pozzi, G., Balensin, P.E., et al., Ibid., 1998, vol. 36, pp. 325–326.
David, R.S., Clinical. Infect. Dis., 2008, vol.46, pp. 104–111.
Nitthya, V., Muthukumar, S.P., and Halami, P.M., Int. J.Toxicol, 2012, vol. 31, pp. 228–237.
Pepe, O., Blaiotta, G., Moschetti, G., et al., Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 69, pp. 2321–2329.
Tena, D., Martinez-Torres, J.A., Perez-Pomata, M.T., et al., J. Clinical. Infect. Dis, 2007, vol. 44, pp. 40–42.
From, C., Hormazabat, V., and Granum, P.E., Int. J. Food Microbiol., 2007, vol. 115, pp. 319–324.
Carraro, E., Bonetta, S., Palumbo, F., and Gilli, G., Annali dell’Instituto Superiore di Sanita, 2004, vol. 40, pp. 117–140.
Sakhnini, E., Weissmann, A., and Oren, I., Amer. J. Med. Sci., 2002, vol. 323, pp. 269–272.
Trautmann, M., Lepper, P.M., and Haller, M., Amer. J. Infect. Control., 2005, vol. 33, pp. 41–49.
Aumeran, C., Paillard, C., Robin, F., et al., J. Hosp. Infect., 2007, vol. 65, pp. 47–53.
Todar, K., Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Outline textbook of bacteriology, Kenneth Todar University of Wisconsin-Madison Department of Bacteriology. http://www.textbookofbacteriology.net.
Spencer, R.C., J. Hosp. Infect., 1995, vol. 30, pp. 453–464.
Funke, G., Von Graevenitz, A., Clarrige, J.E., and Bernard, K.A., Clinical Microbiol. Rev., 1997, vol. 10, pp. 125–159.
Levi, I. and Rubinstein, E., Acineytobacter: microbiology, epidemiology, infections, management, Bergogne-Berezin, M.L., Joly-Guillou, K.J., Towner (Eds.), New York: CRC Press, 1996, pp. 101–115.
Towner, K.J., J. Med. Microbiol. 1997, vol. 46, pp. 721–746.
Moralez-Suarez-Varela, M., Llopis-Gonzalez, A., Tejerizo-Perez, M.L., and Ferrandiz-Ferragud, J., J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol., 1993, vol. 12, pp. 229–236.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The text was submitted by the authors in English.
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, H.A., Mostfa, M.I. Monitoring the quality of mineral bottled water concerning to potential pathogenic bacteria and nitrate levels. J. Water Chem. Technol. 39, 116–124 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X17020102
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X17020102