Abstract
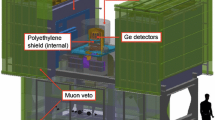
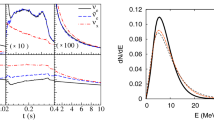
The results from measurements of thermal neutron flux in the EDELWEISS II experiment aimed at the direct detection of WIMPs (weakly interacting massive particles) by means of cryogenic germanium bolometers are described. Detailed knowledge of the neutron background is of crucial importance for the experiment, since neutrons with the MeV energy range of scattering seem to be hard to distinguish from the expected WIMP signal within the bolometers. Monitoring of the thermal neutron flux is performed using a mobile detection system with a low background proportional 3He counter. The neutron flux measurements were performed both outside and inside the device’s shielding, in the direct proximity of a cryostat with built-in germanium detectors. The sensitivity of the created thermal neutron detection system is on the level of 10−9 neutron (cm2 s)−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spergel, D.N., et al. (WMAP Collaboration), Astrophys. J. Suppl., 2007, vol. 170, p. 377.
Bertone, G., Hooper, D., Silk, J., Phys. Rep., 2005, vol. 405, p. 279.
Sanglard, V., et al., (EDELWEISS Collaboration), Phys. Rev. D, 2005, vol. 71, p. 122002.
Firestone, R.B., et al., Tables of Isotopes, New York: Wiley, 1998.
Vidyakin, G.S., et al., Pribory i Tekhnika Eksperimenta, 1989, no. 4, p. 70.
Feldman, G.J. and Cousins, R.D., Phys. Rev. D, 1998, vol. 57, p. 3873.
Agostinelli, S., et al., Nucl. Instr. Meth. A, 2003, vol. 506, p. 250, Available from http://www.geant4.org/geant4/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.V. Rozov, V.B. Brudanin, A.V. Lubashevskiy, S.S. Semikh, D.V. Filosofov, E.A. Yakushev (on behalf of EDELWEISS Collaboration), 2010, published in Izvestiya Rossiiskoi Akademii Nauk. Seriya Fizicheskaya, 2010, Vol. 74, No. 4, pp. 500–502.
About this article
Cite this article
Rozov, S.V., Brudanin, V.B., Lubashevskiy, A.V. et al. Monitoring of the thermal neutron flux in the EDELWEISS II dark matter direct search experiment. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. Phys. 74, 464–466 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1062873810040088
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1062873810040088