Abstract
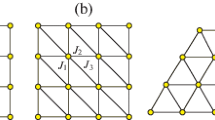
In the present paper we analyzed a change in the density of states of a two-dimensional Ising model when a next-next-neighbor interaction is introduced. In other words, we examined two-dimensional lattices with diagonal connections. The same as in a three-dimensional model in this case each spin has 6 connections. Since the model is planar, we can calculate the free energy and other characteristics of the system using a polynomial algorithm. We performed computer simulations using the Kasteleyn–Fisher algorithm, which allowed us to study changes of critical values and the density of states when a long-range interaction is taken into account. From the obtained results it follows that the interactions of the type analyzed here result in quantitative changes of the system’s characteristics, but they did not change them qualitatively. In particular, we again obtained a logarithmic divergence of the heat capacity in the critical point.












Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Onsager, L., Crystal statistics. I. A two-dimensional model with an order–disorder transition, Phys. Rev., 1944, vol. 65, nos. 3–4, pp. 117–149.
Kasteleyn, P., Dimer statistics and phase transitions, J. Math. Phys., 1963, vol. 4, no. 2.
Fisher, M., On the dimer solution of planar Ising models, J. Math. Phys., 1966, vol. 7, no. 11.
Karandashev, Ya.M. and Malsagov, M.Yu., Polynomial algorithm for exact calculation of partition function for binary spin model on planar graphs, Opt. Mem. Neural Networks, 2017, vol. 26, no. 2. https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.00922.
Schraudolph, N. and Kamenetsky, D., Efficient exact inference in planar Ising models, NIPS, 2008. https://arxiv.org/abs/0810.4401.
Karandashev, I.M., Kryzhanovsky, B.V., and Malsagov, M.Yu., The analytical expressions for a finite-size 2D Ising model, Opt. Mem. Neural Networks, 2017, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 165–171.
Kryzhanovsky, B.V., Malsagov, M.Yu., and Karandashev, I.M., Dependence of critical parameters of 2D Ising model on lattice size, Opt. Mem. Neural Networks, 2018, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 10–22.
Lundow, P.H. and Markström, K., The discontinuity of the specific heat for the 5D Ising model, Nucl. Phys. B, 2015, vol. 895, pp. 305–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nuclphysb.2015.04.013
Litinskii, L. and Kryzhanovsky, B., Spectral density and calculation of free energy, Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Its Appl., 2018, vol. 510, no. C, pp. 702–712.
Kryzhanovsky, B.V., Features of the spectral density of a spin system, Dokl. Math., 2018, vol. 97, no. 2, pp. 188–192.
Baxter, R.J., Exactly Solved Models in Statistical Mechanics, London: Academic Press, 1982.
Funding
The work financially supported by State Program of SRISA RAS no. 0065-2019-0003 (AAA-A19-119011590090-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Karandashev, I.M., Kryzhanovsky, B.V. Change in Density of States of 2D Ising Model when Next-Neighbor Interaction Is Introduced. Opt. Mem. Neural Networks 28, 165–174 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1060992X19030032
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1060992X19030032