Abstract
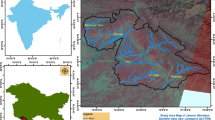
Around one-third of the world’s population drinks water from groundwater resources. Of this, about 10 percent, approximately 300 million people, obtains water from groundwater resources. This study identify and mapping of groundwater potential zone for growing population, irrigation and industrial development, combining with remote sensing (RS), geographical information system (GIS) and field data for hydrological research in Kalmykia, Russia. Various thematic layers (i.e. land use/cove, soil, geomorphology, lithology, elevation, slope, rainfall, normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), drainage density, lineament density, degraded land, forest, relief, vegetation, surface water body, land use, agriculture, flow accumulation, flow direction and base map) wear used along with existing maps to prepare groundwater potential zone (GWPZ) map. Weights were assigned to all above factors according to their effectiveness, sensitivity and relevance to ground water potentiality. Furthermore the resulting GWPZ map has been classified into five classes, named very high, high, moderate, low and very low based on hydro-geomorphological condition, covering 0.93, 11.65, 35.45, 43.20 and 8.77% area respectively. The results show that most part of areas with favorable lithology, soil texture, vegetation, slope, optimum rainfall condition has a high potential for groundwater. The results provide significant information and can be use by local authorities for groundwater exploitation and management.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Laishram Kanta Singh, Madan K. Jha, and Chowdary, V.M., Assessing the accuracy of GIS-based Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis approaches for mapping groundwater potential, Ecol. Indic., 2018, vol. 91, pp. 24–37.
Boori, M.S., Choudhary, K., Paringer, R.A., and Evers, M., Food vulnerability analysis in the central dry zone of Myanmar, Comput. Opt., 2017, vol. 41, no. 4, pp. 552–558. https://doi.org/10.18287/2412-6179-2017-41-4-552-558
Mogaji, K.A. and Lim, H.S., Application of a GIS-/remote sensing-based approach for predicting groundwater potential zones using a multi-criteria data mining methodology, Environ. Monit. Assess., 2017, vol. 189, p. 321.
Selvam, S., Dar, F.A., Magesh, N.S., et al., Application of remote sensing and GIS for delineating groundwater recharge potential zones of Kovilpatti Municipality, Tamil Nadu using IF technique, Earth Sci. Inf., 2016, vol. 9, p. 137.
Boori, M.S., Choudhary, K., Evers, M., and Paringer, R., A review of food security and flood risk dynamics in Central Dry Zone area of Myanmar, Procedia Eng., 2017, vol. 201, pp. 231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.09.600
Haleh, N., Biswajeet, P., and Mohammad, A.M., Application of GIS based data driven evidential belief function model to predict groundwater potential zonation, J. Hydrol., 2014, vol. 513, pp. 283–300.
Thapa, R., Gupta, S., Gupta, A., et al., Use of geospatial technology for delineating groundwater potential zones with an emphasis on water-table analysis in Dwarka River basin, Birbhum, India, Hydrogeol. J., 2018, vol. 26, p. 899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1683-0
Boori, M.S., Choudhary, K., and Kupriyanov, A., Vulnerability evaluation from 1995 to 2016 in Central Dry Zone area of Myanmar, Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr., 2017, vol. 32, pp. 139–154. doi 10.4028/www.scientific.net/JERA.32.139
Krishna, R., Iqbal, J., Gorai, A.K., Pathak, G., Tuluri, F., and Tchounwou, P.B., Groundwater vulnerability to pollution mapping of Ranchi district using GIS, Appl. Water Sci., 2015, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 345–358.
Saaty, T.L., The Analytic Hierarchy Process, New York: McGraw Hill, 1980.
Dasho, O.A., Ariyibi, E.A., Akinluyi, F.O., et al., Application of satellite remote sensing to groundwater potential modeling in Ejigbo area, Southwestern Nigeria, Earth Syst. Environ., 2017, vol. 3, p. 615.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Boori, M.S., Choudhary, K. & Kupriyanov, A. Mapping of Groundwater Potential Zone Based on Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques: A Case Study of Kalmykia, Russia. Opt. Mem. Neural Networks 28, 36–49 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1060992X1901003X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1060992X1901003X