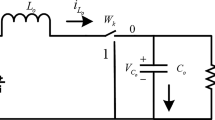
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a new sensor error anticipation method applied to switched systems. Once a small performance degradation is detected, the concerned sensor is identified before getting errors. Hybrid bond graph is employed to model the system by taking into account the continuous and discrete parts of the switching system. After modeling, observers are used to estimate the system’s parameters, and their outputs serve as inputs for the control charts, which aim to detect abnormal fluctuations and warn about sensor degradation. The proposed approach improves the system reliability and avoid errors that can causes delays in industrial production systems.











Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Liberzon, D., Switching in Systems and Control, Systems & Control: Foundations & Applications, Boston: Springer, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-0017-8
Liberzon, D., Switched systems, Handbook of Networked and Embedded Control Systems, Hristu-Varsakelis, D. and Levine, W.S., Eds., Control Engineering, Boston: Birkhäuser, 2005, pp. 559–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-8176-4404-0_24
Thirumarimurugan, M., Bagyalakshmi, N., and Paarkavi, P., Comparison of fault detection and isolation methods: A review, 10th Int. Conf. on Intelligent Systems and Control (ISCO), Coimbatore, India, 2016, IEEE, 2016, pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCO.2016.7726957
Isermann, R., Model-based fault-detection and diagnosis-status and applications, Annu. Rev. Control, 2005, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 71–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcontrol.2004.12.002
Patton, R.J. and Chen, J., A review of parity space approaches to fault diagnosis, IFAC Proc. Vol., 1991, vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 65–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-6670(17)51124-6
Bachir, S., Tnani, S., and Trigeassou, J.-C., and Champenois, G., Diagnosis by parameter estimation of stator and rotor faults occurring in induction machines, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 2006, vol. 53, no. 3, pp. 963–973. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2006.874258
Abboudi, A., and Belmajdoub,F., A new diagnosis approach of hybrid systems through observers and hybrid automata, Int. J. Autom. Smart Technol., 2020, vol. 10, no. 1. https://doi.org/10.5875/ausmt.v10i1.2169
Simani, S., Fantuzzi, C., and Patton, R.J., Model-based fault diagnosis techniques, Model-based Fault Diagnosis in Dynamic Systems Using Identification Techniques, Advances in Industrial Control, London: Springer, 2003, pp. 19–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-3829-7_2
Ruiz-Carcel, C., and Starr,A., Data-based detection and diagnosis of faults in linear actuators, IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., 2018, vol. 67, no. 9, pp. 2035–2047. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2018.2814067
Rosenber, R.C. and Karnopp, D.C., A definition of the bond graph language, J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 1972, vol. 94, no. 3, pp. 179–182. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3426586
Roychoudhury, I., Daigle, M.J., Biswas, G., and Koutsoukos, X., Efficient simulation of hybrid systems: A hybrid bond graph approach, Simulation, 2011, vol. 87, no. 6, pp. 467–498. https://doi.org/10.1177/0037549710364478
Mosterman, P.J., Hybrid dynamic systems: A hybrid bond graph modeling paradigm and its application in diagnosis, PhD Thesis, Nashville, Tenn.: Vanderbilt Univ., 1997.
Low, C.B., Wang, D., Arogeti, Sh., and Zhang, J.B., Causality assignment and model approximation for hybrid bond graph: Fault diagnosis perspectives, IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng., 2010, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 570–580. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2009.2026731
Oueslati, F.E. and Zanzouri, N., Hybrid dynamical system monitoring based on bond graph, 3th Int. Conf. on Automation, Control, Engineering and Computer Science (ACECS’16), 2016, pp. 332–337.
Abboudi, A. and Belmajdoub, F., Hybrid diagnosis method applied to switched mechatronic systems, J. Eur. Syst., Autom., 2021, vol. 54, no. 5, pp. 683–691. https://doi.org/10.18280/jesa.540503
Kohavi, Z. and Jha, N.K., Switching and Finite Automata Theory, Cambridge Univ. Press, 2009.
Wong, T. and Cormier, G., Bond graph causality assignment and evolutionary multi-objective optimization, Advances and Innovations in Systems, Computing Sciences and Software Engineering, Elleithy, K., Dordrecht: Springer, 2007, pp. 433–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6264-3_75
Roberts, S.W., A comparison of some control chart procedures, Technometrics, 1966, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 411–430. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1966.10490374
Nelson, L.S., The Shewhart control chart—Tests for special causes, J. Qual. Technol., 1984, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 237–239. https://doi.org/10.1080/00224065.1984.11978921
Jensen, W.A., Jones-Farmer, L.A., Champ, C.W., and Woodall, W.H., Effects of parameter estimation on control chart properties: A literature review, J. Qual. Technol., 2006, vol. 38, no. 4, pp. 349–364. https://doi.org/10.1080/00224065.2006.11918623
Chen, G., and Cheng, S.W., Max chart: Combining X-bar chart and S chart, Stat. Sin., 1998, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 263–271.
Smith, A.E., X-bar and R control chart interpretation using neural computing, Int. J. Prod. Res., 1994, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 309–320. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207549408956935
Abboudi, A., and Belmajdoub, F., Dynamic thresholds for a reliable diagnosis of switched systems, J. Eur. Syst. Autom., 2021, vol. 54, no. 6, pp. 827–833. https://doi.org/10.18280/jesa.540604
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Abboudi, A., Belmajdoub, F. Sensor Degradation Detection in Switched Systems. J. Mach. Manuf. Reliab. 52, 246–255 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1052618823030020
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1052618823030020