Abstract
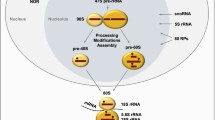
The rate of protein synthesis strictly correlates with the rRNA quantity in a cell. The rRNA synthesis is the first stage in the ribosomal synthesis process. It is actively regulated by such external factors as type of nutrition, growth factor, and cell stress. Thus, pre-rRNA transcription and maturation play a central role in processes of cell growth and proliferation. In recent years, numerous data have been obtained that make it possible to suggest that quantitative and qualitative changes in the rRNA synthesis are the most important molecular indicators of cell malignancy. The principle of suppressing activity of rRNA genes at various stages of their expression is used today in chemotherapeutic methods of treatment of oncological diseases. A number of data indicate that the adaptation of the nucleoli precedes the malignant transformation and is not the result of it. These data offer new possibilities for studying the relationship between the transcription of ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and cell proliferation. Understanding these subtle connections is necessary for the development of new approaches to the molecular characterization and subsequent therapy of neoplastic diseases. The aim of this work was to obtain a cellular model system that makes it possible to adequately estimate the activity of RNA polymerase I in vivo by measuring the expression level of the luciferase reporter gene. For this purpose, the regulatory region of the 6.7 kb rRNA gene preceding the transcriptional start point was recloned into the luciferase expression vector pGL4.77. The obtained construct was used to transfect the line HEK293, which resulted in the line pqA77.HEK293. The new model system opens wide prospects for studying transcription regulation mechanisms of human ribosomal genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moss, T., Langlois, F., Gagnon–Kugler, T., and Stefanovsky, V., A housekeeper with power of attorney: The rRNA genes in ribosome biogenesis, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2007, vol. 64, no. 1, pp. 29–49.
Stults, D.M., Killen, M.W., Pierce, H.H., and Pierce, A.J., Genomic architecture and inheritance of human ribosomal RNA gene clusters, Genome Res., 2007, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 13–18.
McStay, B. and Grummt, I., The epigenetics of rRNA genes: From molecular to chromosome biology, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 2008, vol. 24, pp. 131–157.
Santoro, R. and Grummt, I., Epigenetic mechanism of rRNA gene silencing: Temporal order of NoRC–mediated histone modification, chromatin remodeling, and DNA methylation, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2005, vol. 25, pp. 2539–2546.
Zentner, G.E., Saiakhova, A., Manaenkov, P., et al., Integrative genomic analysis of human ribosomal DNA, Nucleic Acids Res., 2011, vol. 39, no. 12, pp. 4949–4960.
Mayer, C., Schmitz, K.–M., Li, J., et al., Intergenic transcripts regulate the epigenetic state of rRNA genes, Mol. Cell, 2006, vol. 2, pp. 351–361.
Santoro, R., Li, J. and Grummt, I., The nucleolar remodeling complex NoRC mediates heterochromatin formation and silencing of ribosomal gene transcription, Nat. Genet., 2002, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 393–396.
Zhou, Y., Santoro, R., and Grummt, I., The chromatin remodeling complex NoRC targets HDAC1 to the ribosomal gene promoter and represses RNA polymerase I transcription, EMBO J., 2002, vol. 21, no. 17, pp. 4632–4640.
Jacob, S.T., Regulation of ribosomal gene transcription, Biochem. J., 1995, vol. 306, part 3, pp. 617–626.
Kuhn, A. and Grummt, I., A novel promoter in the mouse rDNA spacer is active in vivo and in vitro, EMBO J., 1987, vol. 6, no. 11, pp. 3487–3492.
Grummt, I., Life on a planet of its own: regulation of RNA polymerase I transcription in the nucleolus, Genes Dev., 2003, vol. 17, no. 14, pp. 1691–1702.
Gonzalez, I.L. and Sylvester, J.E., Complete sequence of the 43–kb human ribosomal DNA repeat: Analysis of the intergenic spacer, Genomics, 1995, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 320–328.
Gonzalez, I.L. and Sylvester, J.E., Human rDNA: Evolutionary patterns within the genes and tandem arrays derived from multiple chromosomes, Genomics, 2001, vol. 73, no. 3, pp. 255–263.
Netchvolodov, K.K., Boiko, A.V., Ryskov, A.P., and Kupriyanova, N.S., Evolutionary divergence of the pre–promotor region of ribosomal DNA in the great apes, DNA Sequence, 2006, vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 378–391.
Zomerdijk, C., Beckmann, H., Comai, L., and Tjian, R., Assembly of transcriptionally active RNA polymerase I initiation factor SL1 from recombinant subunits, Science, 1994, vol. 266, pp. 2015–2018.
Heix, J., Zomerdijk, J.C., Ravanpay, A., et al., Cloning of murine RNA polymerase I–specific TAF factors: Conserved interactions between the subunits of the species–specific transcription initiation factor TIFIB/SL1, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1997, vol. 94, no. 5, pp. 1733–1738.
Denissov, S., van Driel, M., Voit, R., et al., Identification of novel functional TBP–binding sites and general factor repertoires, EMBO J., 2007, vol. 26, pp. 944–954.
Bernstein, E. and Allis, C.D., RNA meets chromatin, Genes Dev., 2005, vol. 19, pp. 1635–1655.
Mayer, C., Schmitz, K.–M., Li, J., Grummt, I., and Santoro, R., Intergenic transcripts regulate the epigenetic state of rRNA genes, Mol. Cell, 2006, vol. 2, pp. 351–361.
Netchvolodov, K.K., Kurova, V.S., Kononikhin, A.S., et al., Complexes of DNA dependent protein kinase with single stranded oligo–(AGGG)6: Identification and possible role in modulation of ribosomal RNA transcription, Dokl. Biochem. Biophys., 2009, vol. 424, pp. 1–4.
Grandori, C., Gomez–Roman, N., Felton–Edkins, Z.A., Ngouenet, C., and Galloway, D.A., c–Myc binds to human ribosomal DNA and stimulates transcription of rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I, Nat. Cell Biol., 2005, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 311–318.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © K.K. Netchvolodov, T.A. Kurako, E.Y. Rybalkina, G.V. Pavlova, N.S. Kupriyanova, 2018, published in Molekulyarnaya Genetika, Mikrobiologiya i Virusologiya, 2018, No. 1, pp. 19–22.
About this article
Cite this article
Netchvolodov, K.K., Kurako, T.A., Rybalkina, E.Y. et al. A New Cellular Model System for Study of Regulatory Mechanisms of Human Ribosomal Gene Transcription. Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol. 33, 21–25 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416818010093
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416818010093