Abstract
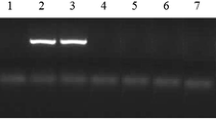
Studying the heterogeneity of internal fragments of the aur gene coding a proteolytic enzyme aureolysin in strains of Staphylococcus aureus with different enzymatic activity isolated from the affected skin of patients with atopic dermatitis was the aim of this study. The study included 125 patients from 1 to 35 years old diagnosed with atopic dermatitis. One hundred clinical strains of Staphylococcus aureus were studied in monoculture. Identification of the strains was performed by standard classical methods and obtained results were confirmed by specific biochemical microtests using a set of APIs Staph 20 (bioMerieux SA, France). Reference strains of S. aureus ATCC 29213 and NCTC 8325 were used in the work. Specific aur loci were detected by the method of multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Proteolytic ability of supernatants was determined by the ability to split the substrates (human IgG, Sigma) into fragments using as inhibitors of metalloproteases 0.01–0.1 M solutions of sodium EDTA. Sequencing of the amplified fragments of aur gene, including preliminary stages of separation and purification of DNA, was performed by Syntol (Moscow). Different strains of the conservative plot amplicon fragment of aur gene contain up to nine polymorphic nucleotides. The index of nucleotide diversity for proteolytic active strains was less (Pi = 0.04) than for proteolytic inactive (Pi = 0.07), p < 0.05. It should be noted that all proteolytically active strains were isolated from the skin of patients with high and moderate severity of atopic dermatitis (67.8 ± 5.4 points on the SCORAD scale) with erythematous form of the disease. The inactive strains were allocated in elderly patients with reduced severity of atopic dermatitis (with the dry form of skin lesions).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dmitrenko, O.A., Belokrysenko, S.S., Lavrova, N.V., Prokhorov, V.Ya., and Gintsburg, A.L., Klin. Mikrobiol. Antimikrob. Khimioter., 2006, vol. 8, no. 2, suppl. 1, p. 15.
Tyurin, J.A., Kulikov, S.N., Fassahov, R.S., et al., RF Patent No. 2373538, Byull. Izobret., 2009, no. 32.
Arvidson, S., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1973, vol. 302, pp. 149–157.
Banbula, A., Potempa, J., Travis, J., Fernandez-Catalan, C., Mann, K., Huber, R., Bode, W., and Medrano, F., Structure, 1998, vol. 6, pp. 1185–1193.
Hirasawa, Y., Takai, T., Nakamura, T., Mitsuishi, K., Gunawan, H., Suto, H., et al., J. Invest. Dermatol., 2010, vol. 130, pp. 614–617.
Kubica, M., Guzik, K., Koziel, J., Zarebski, M., Richter, W., et al., PLoS One, 2008, vol. 1, no. 1, p. e1409.
Lee, S.E., Jeong, S.K., and Lee, S.H., Yonsei Med. J., 2010, vol. 51, no. 6, pp. 808–822.
McAleese, F.M., Walsh, E.J., Sieprawska, M., Potempa, J., and Foster, T.J., J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, pp. 29969–29978.
Ohnemus, U., Kohrmeyer, K., Houdek, P., Rohde, H., Wladykowsi, E., Vidal, S., et al., J. Invest. Dermatol., 2008, vol. 128, pp. 906–916.
Sabat, A.J., Wladyka, B., Kosowska-Shick, K., Grundmann, H., van Dijl, J.M., Kowal, J., et al., BMC Microbiol., 2008, vol. 8, p. 129.
Sabat, A., Kosowska, K., Poulsen, K., Kasprowicz, A., Sekowska, A., van den Burg, B., et al., Infect. Immun., 2000, vol. 68, pp. 973–976.
Shaw, L., Golonka, E., Potempa, J., and Foster, S.J., Microbiol., 2004, vol. 150, pp. 217–228.
Sieprawska-Lupa, M., Mydel, P., Krawczyk, K., Wojcik, K., Puklo, M., Lopa, B., et al., Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2004, vol. 8, pp. 4673–4679.
Karlsson, A. and Arvidson, S., Infect. Immun., 2002, pp. 4239–4246.
Enright, M.C., Day, N.P.J., Davies, C.E., Peacock, S.J., and Spratt, B.G., J. Clin. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 1008–1015.
Severity scoring of atopic dermatitis: The SCORAD index. Consensus Report of the European task Force on Atopic Dermatitis, Dermatology, 1993, vol. 186, no. 1, pp. 23–31.
Nei, M. and Miller, J.C., Simple method for estimating average number of nucleotide substitutions within and between populations from restriction data, Genetics, 1990, vol. 125, pp. 873–879.
Kuhn, G., Francioli, P., and Blanc, D.S., Evidence for clonal evolution among highly polymorphic genes in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, J. Bacteriol., 2006, vol. 188, pp. 169–178.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © J.A. Tyurin, A.F. Shamsutdinov, R.S. Fassahov, 2014, published in Molekulyarnaya Genetika, Mikrobiologiya i Virusologiya, 2014, No. 1, pp. 5–7.
About this article
Cite this article
Tyurin, J.A., Shamsutdinov, A.F. & Fassahov, R.S. A Study of single nucleotide polymorphism fragments of the aur gene metalloprotease strains of Straphylococcus aureus isolated from the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol. 29, 4–7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416814010078
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416814010078