Abstract
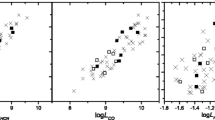
The paper aims at establishing relations between the parameters of methanol maser emission that originates in dense star-forming regions and parameters of a dense core using emission of the CS molecule. A total of 164 sources toward the positions of methanol masers using the RT-22 radio telescope at CrAO, Ukraine, have been observed. For 85 sources, the CS (J = 2–1) line emission was detected. Most of the sources have been selected from catalogs of the class I and class II methanol masers. For methanol masers, this is the most complete survey in the CS (J = 2–1) line on the northern sky. A comparative analysis of parameters of methanol masers spectra in the CS (J = 2–1) line, and methanol masers, luminosities of dense cores, and infrared sources, has been performed. The detection rates of the CS (J = 2–1) line emission, its intensities and widths, the differences between the systematic velocities and velocities of the maser line centers have been investigated. The radiation detection rates in the CS (J = 2–1) line are shown to differ for various source samplings. The form of the dependences lgLcs – lgLbol, lgLmas – lgLcs and lgLmas – lgLbol has been found for sources with which methanol masers are associated. Based on the luminosity of infrared sources, samples of sources in which the CS (J = 2–1) line emission is detected with a higher probability have been determined.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. V. Antyufeev, S. Yu. Zubrin, A. N. Korol’, A. M. Korolev, V. V. Myshenko, V. I. Pod’yachii, A. V. Poladich, V. I. Shkodil, and V. M. Shul’ga, “The instrumental complex for spectral observations at frequencies from 85 to 116 GHz at the CrAO RT-22 radio telescope,” Radiofiz. Radioastron. 15, 369–375 (2010).
A. V. Antyufeev and V. M. Shul’ga, “Spectral analyzer on the basis of personal computer,” Radiotekhnika 10, 145–148 (2005).
A. N. Patoka, V. M. Shul’ga, A. V. Antyufeev, S. Yu. Zubrin, V. V. Mishenko, A. M. Korolev, and V. I. Pod’yachii, “Regions of existence of the class II methanol masers. Statistical features of emission in CS (J = 2 – 1) line,” Radiofiz. Radioastron. 22, 173–200 (2017). doi 10.15407/rpra22.03.173
V. M. Shul’ga, A. V. Antyufeev, S. Yu. Zubrin, V. V. Mishenko, V. I. Pod’yachii, A. M. Korolev, and A. N. Patoka, “Observations of non typical masers at the RT-22 radio telescope in 2004–2013,” Radiofiz. Radioastron. 22, 112–122 (2004). doi 10.15407/rpra22.02.112
L. D. Anderson, D. S. Balser, V. Cunningham, and W. P. Armentrout, “The WISE catalog of galactic H II regions,” Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 212, 1 (2014). doi 10.1088/0067-0049/212/1/1
G. Anglada, R. Estalella, J. Pastor, L. F. Rodriguez, and A. D. Haschick, “A CS and NH3 survey of regions with H2O maser emission,” Astrophys. J. 463, 205–223 (1996). doi 10.1086/177235
Y. Ao, J. Yang, and K. Sunada, “13CO, C18O, and CS observations toward massive dense cores. Astron. J. 128, 1716–1732 (2004). doi 10.1086/423906
R. Bachiller, J. Gomez-Gonzalez, A. Barcia, and K. Menten, “The 44 GHz methanol masers — Results of an extensive survey in the 70 – 61A+ line,” Astron. Astrophys. 240,116–122 (1990).
J.-H. Bae, K.-T. Kim, S.-Y. Youn, W.-J. Kim, D.-Y. Byun, H. Kang, “A multi-epoch, simultaneous water and methanol maser survey toward intermediate-mass young stellar objects,” Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 196, 21 (2011). doi 10.1088/0067-0049/196/2/21
W. Batrla, H. E. Matthews, and K. Menten, “Detection of strong methanol masers towards galactic H II regions,” Nature 326, 49–51 (1987). doi 10.1038/326049a0
O. S. Bayandina, I. E. Val’tts, and G. M. Larionov, “Class I methanol maser emission in infrared clouds and the third version of the Astro Space Center MMI/SFR catalog,” Astron. Rep. 56, 553–563. doi 10.1134/S1063772912060029
H. Beuther, P. Schilke, K. M. Menten, F. Motte, T. K. Sridharan, and F. Wyrowski, “High-mass protostellar candidates. II. Density structure from dust continuum and CS emission,” Astrophys. J. 566, 945–965 (2002). doi 10.1086/338334
L. Kus and A. J. Blaszkiewicz, “12.2 GHz survey towards 6.7 GHz methanol masers. A comparison of 12.2 GHz and 6.7 GHz spectra,” Astron. Astrophys. 413, 233–240 (2004). doi 10.1051/0004-6361:20031451
S. L. Breen, S. P. Ellingsen, J. L. Caswell, J. A. Green, G. A. Fuller, M. A. Voronkov, L. J. Quinn, and A. Avison, “Statistical properties of 12.2 GHz methanol masers associated with a complete sample of 6.7 GHz methanol masers,” Astrophys. J. 733, 80 (2011). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/733/2/80
S. L. Breen, S. P. Ellingsen, J. L. Caswell, J. A. Green, M. A. Voronkov, A. Avison, G. A. Fuller, and L. J. Quinn, “12.2-GHz methanol maser MMB follow-up catalogue — IV. Longitude range 20º – 60º,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 459, 4066–4087 (2016). doi 10.1093/mnras/stw965
S. L. Breen, S. P. Ellingsen, J. L. Caswell, J. A. Green, M. A. Voronkov, G. A. Fuller, L. J. Quinn, and A. Avison, “12.2-GHz methanol maser methanol multibeam follow-up catalogue — II. Longitude range 186º – 330º,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 426, 2189–2207 (2012). doi 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21759.x
S. L. Breen, S. P. Ellingsen, and J. L. Caswell, “12.2-GHz methanol masers towards 1.2-mm dust clumps: Quantifying high-mass star formation evolutionary schemes,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 401, 2219–2244 (2010). doi 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15831.x
S. L. Breen and S. P. Ellingsen, “Masers as evolutionary tracers of high-mass star formation,” Proc. IAU Symp. 287, 156–160. doi 10.1017/S1743921312006837
L. Bronfman, L.-A. Nyman, and J. May, “A CS (2-1) survey of IRAS point sources with color characteristics of ultra-compact H II regions,” Astron. Astrophvs., Suppl. Ser. 115, 1–81 (1996).
R. A. Burns, K. Sunada, and T. Omodaka, “H2O masers in a jet-driven bow shock: Episodic ejection from a massive young stellar object,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 460, 283–290 (2016). doi 10.1093/mnras/stw958
R. A. Burns, H. Imai, A. Nakagawa, and Y. Ueno, “'Water Spout’ maser jet in S235AB-MIR,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 453, 3163–3173 (2015). doi 10.1093/mnras/stvl836
D.-Y. Byun, K.-T. Kim, and J.H. Bae, “44-GHz class I methanol maser survey towards 6.7-GHz class II methanol masers,” Proc. Int. Astron. Union 8, 284–285 (2012). doi 10.1017/S1743921312007156
J. L. Caswell, G. A. Fuller, J. A. Green, A. Avison, S. L. Breen, K. J. Brooks, M. G. Burton, A. Chrysostomou, J. Cox, P. J. Diamond, S. P. Ellingsen, M. D. Gray, M. G. Hoare, M. R. W. Masheder, N. M. McClure-Griffiths, M. R. Pestalozzi, S. J. Philips, L. Quinn, M.A. Thompson, and M. A. Voronkov, “The 6-GHz methanol multibeam maser catalogue — I. Galactic centre region, longitudes 345º to 6º,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 404, 1029–1060 (2010). doi 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16339.x
J. L. Caswell, R. A. Vaile, S. P. Ellingsen, and R. P. Norris, “Galactic methanol masers at 12 GHz,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 274, 1126–1152 (1995). doi 10.1093/mnras/274.4.1126
J. L. Caswell, J. Yi, R. S. Booth, and D. M. Cragg, “Methanol masers at 107.0 and 156.6 GHz,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 313, 599–616 (2000). doi 10.1046/ j.1365-8711.2000.03277.x
M. Catarzi, L. Moscadelli, and D. Panella, “Observation of methanol maser sources with the Arcetri 12 GHz receiver,” Astron. Astrophys., Suppl. Ser. 98, 127–135 (1993).
X. Chen, S. P. Ellingsen, Z.-Q. Shen, A. Titmarsh, and C.-G. Gan, “A 95 GHz class I methanol maser survey toward glimpse Extended Green Objects (EGOs),” Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 196, 9 (2011). doi 10.1088/0067-0049/196/1/9
X. Chen, S. P. Ellingsen, and Z.-Q. Shen, “Class I methanol masers: Masers with extended green objects,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 396, 1603–1609 (2009). doi 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.14818.x
Y. K. Choi, K. Hachisuka, M. J. Reid, Y. Xu, A. Brunthaler, K. Menten, “Trigonometric parallaxes of star forming regions in the Perseus spiral arm,” Astrophys. J 790, 99 (2014). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/790/2/99
M. S. Connelley and A. T. Tokunaga, “The evolution of the multiplicity of embedded protostars. I. Sample properties and binary detections,” Astron. J. 135, 2496–2525 (2008). doi 10.1088/0004-6256/135/6/2496
C. J. Cyganowski, C. L. Brogan, T. R. Hunter, and E. Churchwell, “A class I and class II CH3OH maser survey of EGOs from the GLIMPSE survey,” Astrophys. J. 702, 1615–1647 (2009). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/702/2/1615
J. Koda, E. Rosolowsky, S. Towers, J. D. Meyer, F. Egusa, R. Momose, T. P. Robitaille, “A water maser and NH3 survey of glimpse extended green objects,” Astrophys. J. 764, 61 (2013). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/764/1/61
S. Dzib, L. Loinard, L. F. Rodriguez, A. J. Mioduszewski, and R. M. Torres, “VLBA Determination of the distance to nearby star-forming regions. VI. The distance to the young stellar object HW 9 in Cepheus A,” Astrophys. J. 733, 71 (2011). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/733/1/71
S. P. Ellingsen, “The relationship between class I and class II methanol masers,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc 359, 1498–1516 (2005). doi 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09010.x
S. P. Ellingsen, S. L. Breen, M. A. Voronkov, and J. R. Dawson, “Testing maser-based evolutionary schemes: A new search for 37.7-GHz methanol masers,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 429, 3501–3516 (2013). doi 10.1093/mnras/sts621
S. Faundez, L. Bronfman, G. Garay, R. Chini, L.-C. Nyman, and J. May, “SIMBA survey of southern high-mass star forming regions. I. Physical parameters of the 1.2 mm/IRAS sources,” Astron. Astrophys. 426, 97–103 (2004). doi 10.1051/ 0004-6361:20035755
V. L. Fish, T. C. Muehlbrad, P. Pratap, L. O. Sjouwerman, V. Strelnitski, Y. M. Pihlstrom, and T. L. Bourke, “First interferometric images of the 36 GHz methanol masers in the DR21 Complex,” Astrophys. J. 729, 14 (2011). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/729/1/14
F. Fontani, R. Cesaroni, and R. S. Furuya, “Class I and class II methanol masers in high-mass star-forming regions,” Astron. Astrophys. 517, A56 (2010). doi 10.1051/ 0004-6361/200913679
J. Foster, J. M. Jackson, P. J. Barnes, E. Barris, K. Brooks, M. Cunningham, S. C. Finn, G. A. Fuller, S. N. Longmore, J. L. Mascoop, N. Peretto, J. Rathborne, P. Sanhueza, F. Schuller, and F. Wyrowski, “The millimeter astronomy legacy team 90 GHz (MALT90) pilot survey,” Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 197, 25 (2011). doi 10.1088/0067-0049/197/2/25
C.-G. Gan, X. Chen, Z.-Q. Shen, Y. Xu, and B.-G. Ju, “A search for 95 GHz class I methanol masers in molecular outflows,” Astrophys. J. 763, 2 (2013). doi 10.1088/ 0004-637X/763/1/2
D. Gibson, R. Plume, E. Bergin, S. Ragan, and N. Evans, “Molecular line observations of infrared dark clouds. II. Physical conditions,” Astrophys. J. 705, 123–134 (2009). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/705/1/123
A. I. Gomez-Ruiz, S. E. Kurtz, E. D. Araya, P. Hofner, and L. Loinard, “A catalog of methanol masers in massive star-forming regions. III. The molecular outflow sample,” Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 222, 18 (2016). doi 10.3847/0067-0049/222/2/18
J. Harju, K. Lehtinen, R. S. Booth, and I. Zinchenko, “A survey of SiO emission towards interstellar masers. I. SiO line characteristics,” Astron. Astrophys., Suppl. Ser. 132, 211–231 (1998). doi 10.1051/aas:1998448
A. D. Haschick, K. Menten, and W. A. Baan, “Detection of widespread strong methanol masers at 44 GHz,” Astrophys. J. 354, 556–567 (1990). doi 10.1086/168715
J. H. He, S. Takahashi, and X. Chen, “A 1 mm spectral line survey toward glimpse Extended Green Objects (EGOs),” Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 202, 1 (2012). doi 10.1088/0067-0049/202/1/1
J. Hennen, Master of Science Thesis (College of Science and Health, DePaul Univ., Chicago, IL, 2012).
T. Hirota, K. Ando, T. Bushimata, Y.K. Choi, M. Honma, H. Imai, K. Iwadate, T. Jike, S. Kameno, O. Kameya, R. Kamohara, Y. Kan-Ya, H. Kawaguchi, S. Kuji, T. Kurayama, S. Manabe, M.M.N. Matsui, T. Miyaji, A. Miyazaki, T. Nagayama, A. Nakagawa, D. Namikawa, D. Nyu, C.S. Oh, T. Omodaka, T. Oyama, S. Sakai, T. Sasao, K. Sato, M. Sato, K.M. Shibata, Y. Tamura, K. Ueda, and K. Yamashita, “Astrometry of H2O masers in nearby star-forming regions with VERA III. IRAS 22198+6336 in Lyndsl204G,” Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 60, 961–974 (2008). doi 10.1093/pasj/60.5.961
T. Hirota, T. Bushimata, Y. K. Choi, M. Honma, H. Imai, K. Iwadate, T. Jike, S. Kameno, O. Kameya, R. Kamohara, Y. Kan-Ya, N. Kawaguchi, M. Kijima, M. K. Kim, H. Kobayashi, S. Kuji, T. Kurayama, S. Manabe, K. Maruyama, M. Matsui, N. Matsumoto, T. Miyaji, T. Nagayama, A. Nakagawa, K. Nakamura, C. S. Oh, T. Omodaka, T. Oyama, S. Sakai, T. Sasao, K. Sato, M. Sato, K. M. Shibata, M. Shintani, Y. Tamura, M. Tsushima, and K. Yamashita, “Distance to Orion KL measured with VERA,” Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 59, 897–903 (2007). doi 10.1093/pasj/59.5.897
M. Honma, T. Bushimata, Y. K. Choi, T. Hirota, H. Imai, K. Iwadate, T. Jike, O. Kameya, R. Kamohara, Y. Kan-Ya, N. Kawaguchi, M. Kijima, H. Kobayashi, S. Kuji, T. Kurayama, S. Manabe, T. Miyaji, T. Nagayama, A. Nakagawa, C. S. Oh, T. Omodaka, T. Oyama, S. Sakai, K. Sato, T. Sasao, K. M. Shibata, M. Shintani, H. Suda, Y. Tamura, M. Tsushima, and K. Yamashita, “Astrometry of galactic star-forming region sharpless 269 with VERA: Parallax measurements and constraint on outer rotation curve,” Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 59, 889–895 (2007). doi 10.1093/pasj/59.5.889
L. G. Hou and J. L. Han, “The observed spiral structure of the Milky Way,” Astron. Astrophys. 569, 125 (2014). doi 10.1051/0004-6361/201424039
B. Hu, K. M. Menten, Y. Wu, A. Bartkiewicz, K. Rygl, M. J. Reid, J. S. Urquhart, and X. Zheng, “On the relationship of UC H II regions and class II methanol masers. I. Source catalogs,” Astrophys. J. 833, 18 (2016). doi 10.3847/0004-637X/833/1/18
V. A. Hughes and G. C. MacLeod, “A comparison of the infrared luminosity and ionizing luminosity of selected star forming regions,” Astron. J. 105, 1495–1504 (1993). doi 10.1086/116528
J. Jijina, P. C. Myers, and F. Adams, “Dense cores mapped in ammonia: A database,” Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 125, 161–236 (1999). doi 10.1086/313268
C. H. Jordan, A. J. Walsh, S. L. Breen, S. P. Ellingsen, M. A. Voronkov, and L. J. Hyland, “MALT-45: A 7 mm survey of the southern galaxy. II. ATCA follow-up observations of 44 GHz class I methanol masers,” Mon. Notic. R. Astron. Soc. 471, 3915–3954 (2017). doi 10.1093/mnras/stxl776
S. V. Kalenskii, T. Liljestroem, I. E. Val’tts, V. I. Vasil’kov, V. I. Slysh, and S. Urpo, “Observations of methanol masers at 95 GHz,” Astron. Astrophys., Suppl. Ser. 103, 129–134 (1994).
S. V. Kalenskii, V. G. Promyslov, V. I. Slysh, P. Bergman, and A. Winnberg, “The detection of class I methanol masers towards regions of low-mass star formation,” Astron. Rep. 50, 289–297 (2006). doi 10.1134/S1063772906040032
H. Kang, K.-T. Kim, D.-Y. Byun, S. Lee, and Y.-S. Park, “Simultaneous observation of water and class I methanol masers toward class II methanol maser sources,” Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 221, 6 (2015). doi 10.1088/0067-0049/221/1/6
J. Kang, D. -Y. Byun, K. -T. Kim, J. Kim, A. -R. Lyo, and W. H. T. Vlemmings, “Linear polarization of class I methanol masers in massive star-forming regions,” Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 227, 17 (2016). doi 10.3847/0067-0049/227/2/17
M. S. Kirsanova, A. M. Sobolev, and M. Thomasson, “Gas kinematics in high-mass star-forming regions from the Perseus Spiral Arm,” Astron. Rep. 61, 760–774. doi 10.1134/S1063772917090025
S. Kurtz, P. Hofner, and C.V. Alvarez, “A catalog of CH3OH 70–61A+ maser sources in massive star-forming regions,” Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 155, 149–165 (2004). doi 10.1086/423956
M. L. Kutner and B. L. Ulich, “Recommendations for calibration of millimeter-wavelength spectral line data,” Astrophys. J. 250, 341–348 (1981). doi 10.1086/159380
G. M. Larionov and I. E. Val’tts, “The methanol emission of isolated maser condensations: statistical velocity distribution,” Astron. Rep. 51, 756–772 (2007). doi 10.1134/S1063772907090065
G. M. Larionov, I. E. Val’tts, A. Winnberg, L. E. Johansson, R. S. Booth, and V. V. Golubev, “Survey of bipolar outflows and methanol masers in the C32S (2–1) and C34S (2–1) lines in the northern sky,” Astron. Astrophys., Suppl. Ser. 139, 257–275 (1999). doi 10.1051/aas:1999392
J.-E. Lee, E. A. Bergin, and N. J. Evans II, “Evolution of chemistry and molecular line profiles during protostellar collapse,” Astrophys. J. 617, 360–383 (2004). doi 10.1086/425153
F. C. Li, Y. Xu, Y. W. Wu, J. Yang, D. R. Lu, K. M. Menten, “Ammonia and CO outflow around 6.7 GHz methanol masers,” Astrophys. J. 152, 92 (2016). doi 10.3847/0004-6256/152/4/92
S. Liechti and T. L. Wilson, “Maps of the 36GHz methanol emission,” Astron. Astrophys. 314, 615–624 (1996).
W. Lim, A.-R. Lyo, K.-T. Kim, and D.-Y. Byun, “Candidates for the young stellar outflows: Water and methanol masers from young stellar objects,” Astron. J. 144, 151 (2012). doi 10.1088/0004-6256/144/5/151
I. D. Litovchenko, A. V. Alakoz, I. E. Val’tts, and G. M. Larionov, “Search for class I methanol maser emission in various types of objects in the interstellar medium,” Astron. Rep. 55, 1086–1095 (2011). doi 10.1134/S1063772911120080
S. L. Lumsden, M. G. Hoare, J. S. Urquhart, R. D. Oudmaijer, J. C. Mottram, H. D. Cooper, T. J. T. Moore, “The red MSX source survey: The massive young stellar population of our galaxy,” Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 208, 11 (2013). doi 10.1088/0067-0049/208/1/11
D. M. Mehringer, S. Zhou, and H. R. Dickel, “BIMA array observations of the, 107 GHz methanol masers in Cepheus A,” Astrophys. J., Lett. 475, L57–L60 (1997). doi 10.1086/310462
K. Menten, “Methanol masers and submillimeter wavelength water masers in star-forming regions,” in Atoms, Ions and Molecules: New Results in Spectral Line Astrophysics (Astron. Soc. Pac., San Francisco, CA, 1991), in Ser.: ASP Conference Series, Vol. 16, pp. 119–136.
V. Minier, J. E. Conway, and R. S. Booth, “VLBI observations of 6.7 and 12.2 GHz methanol masers toward high mass star-forming regions. II. Tracing massive protostars,” Astron. Astrophys. 369, P. 278–290 (2001). doi 10.1051/0004-6361:20010124
G. A. Moellenbrock, M. J. Claussen, and W. M. Goss, “A precise distance to IRAS 00420+5530 via H2O maser parallax with the VLBA,” Astrophys. J. 694, 192–204 (2009). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/694/1/192
A. P. Moises, A. Damineli, E. Figueredo, R. D. Blum, and P. S. Conti, “Spectrophotometric distances to galactic HII regions,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 411, 705–760 (2011). doi 10.1111/J.1365-2966.2010.17713.X
S. Molinari, J. Brand, R. Cesaroni, and F. Palla, “A search for precursors of ultracompact HII regions in a sample of luminous IRAS sources. I. Association with ammonia cores,” Astron. Astrophys. 308, 573–587 (1996).
L. Moscadelli, R. Cesaroni, M. J. Rioja, R. Dodson, and M. J. Reid, “Methanol and water masers in IRAS 20126+4104: The distance, the disk, and the jet,” Astron. Astrophys. 526, A66 (2011). doi 10.1051/0004-6361/201015641
L. Moscadelli, M. J. Reid, K. M. Menten, A. Brunthaler, X. W. Zheng, and Y. Xu, “Trigonometric parallaxes of massive star-forming regions. II. Ser A and NG, C 7538,” Astrophys. J. 693, 406–412 (2009). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/693/1/406
J. C. Mottram, M. G. Hoare, J. S. Urquhart, S. L. Lumsden, R. D. Oudmaijer, T. P. Robitaille, T. J. Moore, and J. Stead, “The red MSX source survey: The bolometric fluxes and luminosity distributions of young massive stars,” Astron. Astrophys. 525 (2011). doi 10.1051/0004-6361/201014479
H. S. P. Miiller, K. Menten, and H. Mader, “Accurate rest frequencies of methanol maser and dark cloud lines,” Astron. Astrophys. 428, 1019–1026 (2004). doi 10.1051/0004-6361:20041384
K. Niinuma, M. Honma, K. Motogi, A. Nakagawa, Y. Kan-Ya, N. Kawaguchi, H. Kobayashi, and Y. Ueno, “Astrometry of H2O masers in the massive star-forming region IRAS 06061+2151 with VERA,” Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 63, 9–16 (2011). doi 10.1093/pasj/63.1.9
H. Kobayashi, M. Honma, K. Sato, and Y. Ueno, “VERA Observations of H2O maser sources in three massive star-forming regions and galactic rotation measurements,” Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 62, 101–114 (2010). doi 10.1093/ pasj/62.1.101
F. Palla, J. Brand, R. Cesaroni, G. Comeretto, and M. Felli, “Water masers associated with dense molecular clouds and ultracompact H II regions,” Astron. Astrophys. 246, 249–263 (1991).
J. D. Pandian, P. F. Goldsmith, and A. A. Deshpande, “The Arecibo methanol maser galactic plane survey. I. Data,” Astrophys. J. 656, 255–274 (2007). doi 10.1086/510512
O. Patoka, “Spectral characteristics of molecule CS emission in regions containing methanol masers,” in Proc. 2015 Int. Young Scientists Forum on Applied Physics (YSF), Dnipropetrovsk, Sept. 29 – Oct. 2, 2015 (IEEE, New York, 2015) pp. 1–2. doi 10.1109/YSF.2015.7333259
M. R. Pestalozzi, V. Minier, and R. S. Booth, “A general catalogue of 6.7-GHz methanol masers: I. Data,” Astron. Astrophys. 432, 737–742 (2005). doi 10.1051/0004-6361:20035855
M. R. Pestalozzi, V. Minier, F. Motte, and J. E. Conway, “Discovery of two new methanol masers in NGC 7538. Locating of massive protostars,” Astron. Astrophys., 448, L57–L60 (2006). doi 10.1051/0004-6361:200600006
V. I. Piddyachiy, V. M. Shulga, A. M. Korolev, and V. V. Myshenko, “High doping density Schottky diodes in the 3 mm wavelength cryogenic heterodyne receiver,” Int. J. Infrared Millimeter Waves 26, 1307–1315 (2005). doi 10.1007/s10762-005-7605-6
R. L. Plambeck and K. M. Menten, “95 GHz methanol masers near DR 21 and DR 21 (OH),” Astrophys. J. 364, 555–560 (1990). doi 10.1086/169437
S. E. Ragan, E. A. Bergin, R. Plume, D. L. Gibson, D. J. Wilner, S. O’ Brien, and E. Hails, “Molecular line observations of infrared dark clouds: seeking the precursors to intermediate and massive star formation,” Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 166, 567–584 (2006). doi 10.1086/506594
S. E. Kurtz, A. I. Gomez-Ruiz, P. Hofner, E. D. Araya, S. V. Kalenskii, “A Catalog of 44 GHz methanol masers in massive star-forming regions. IV. The high-mass protostellar object sample,” Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 233, 4 (2017). doi 10.3847/1538-4365/aa8f4e
D. Russeil, “Star-forming complexes and the spiral structure of our galaxy,” Astron. Astrophys. 397, 133–146 (2003). doi 10.1051/0004-6361:20021504
K. L. J. Rygl, A. Brunthaler, M. J. Reid, K. M. Menten, H. J. van Langevelde, and Y. Xu, “Trigonometric parallaxes of 6.7 GHz methanol masers,” Astron. Astrophys. 511, A2 (2010). doi 10.1051/0004-6361/200913135
K. L. J. Rygl, A. Brunthaler, A. Sanna, K. M. Menten, M. J. Reid, J. H. van Langevelde, M. Honma, K. J. E. Torstensson, and K. Fujisawa, “Parallaxes and proper motions of interstellar masers toward the Cygnus X star-forming complex. I. Membership of the Cygnus X region,” Astron. Astrophys. 539, A79 (2012). doi 10.1051/0004-6361/201118211
N. Sakai, M. Sato, K. Motogi, T. Nagayama, K. M. Shibata, M. Kanaguchi, and M. Honma, “Absolute proper motion of IRAS 00259+5625 with VERA: Indication of super-bubble expansion motion,” Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 66, 3 (2014). doi 10.1093/ pasj/pst005
M. Sato, T. Hirota, M. Honma, H. Kobayashi, T. Sasao, T. Bushimata, Y. K. Choi, H. Imai, K. Iwadate, T. Jike, S. Kameno, O. Kameya, R. Kamohara, Y. Kan-Ya, N. Kawaguchi, M. K. Kim, S. Kuji, T. Kurayama, S. Manabe, M. Matsui, N. Matsumoto, T. Miyaji, T. Nagayama, A. Nakagawa, K. Nakamura, C. S. Oh, T. Omodaka, T. Oyama, S. Sakai, K. Sato, K. M. Shibata, Y. Tamura, and K. Yamashita, “Distance to NGC 281 in a galactic fragmenting superbubble: Parallax measurements with VERA,” Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 60, 975–989 (2008). doi 10.1093/pasj/60.5.975
D. E. Schenck, Y. L. Shirley, M. Reiter, and S. Juneau, “Testing the global star formation relation: an HCO+ (3-2) mapping study of red MSX sources in the Bolocam Galactic Plane Survey,” Astron. J. 142, 94 (2011). doi 10.1088/0004-6256/142/3/94
W. M. Schlingman, Y. L. Shirley, D. E. Schenk, E. Rosolowsky, J. Bally, C. Battersby, M. K. Dunham, T. P. Ellsworth-Bowers, N. J. Evans II, A. Ginsburg, and G. Stringfellow, “The Bolocam Galactic Plane Survey. V. HCO+ and N2H+ spectroscopy of 1.1 mm dust continuum sources,” Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 195, 14 (2011). doi 10.1088/0067-0049/195/2/14
V. I. Slysh, S. V. Kalenskii, I. E. Val’tts, and V. V. Golubev, “Detection of a new methanol maser line with the Kitt Peak 12 meter telescope by remote observing from Moscow,” Astrophys. J., Lett. 478, L37–L40 (1997). doi 10.1086/310548
V. I. Slysh, I. E. Val’tts, S. V. Kalenskii, M. A. Voronkov, F. Palagi, G. Tofani, and M. Catarzi, “The Medicina survey of methanol masers at 6.7 GHz,” Astron. Astrophys., Suppl. Ser. 134, 115–128 (1999). doi 10.1051/aas:1999127
Y. Sun, Y. Xu, X. Chen, B. Zhang, Y.-W. Wu, C. Henkel, A. Brunthaler, Y. K. Choi, and X.-W. Zheng, “6.7 GHz methanol maser survey toward GLIMPSE point sources and BGPS 1.1 mm dust clumps,” Astron. Astrophys. 563, A130 (2014). doi 10.1051/0004-6361/201323047
M. Szymczak, A. Bartkiewicz, and A. M. S. Richards, “A multi-transition molecular line study of candidate massive young stellar objects associated with methanol masers,” Astron. Astrophys. 468, 617–625 (2007). doi 10.1051/0004-6361:20077289
M. Szymczak, G. Hrynek, and A. J. Kus, “A survey of the 6.7 GHz methanol maser emission from IRAS Sources. I. Data,” Astron. Astrophys., Suppl. Ser. 143, 269–301 (2000). doi 10.1051/aas:2000334
M. Szymczak, A. J. Kus, G. Hrynek, A. Kepa, and E. Pazderski, “6.7 GHz Methanol masers at sites of star formation. A blind survey of the Galactic plane between 20° ≤ l ≤ 40° and |b| ≤ 0.52°,” Astron. Astrophys. 392, 277–286 (2002). doi 10.1051/0004-6361:20020907
M. Szymczak, T. Pillai, K. M. Menten, “Masers as signposts of high-mass protostars. A water maser survey of methanol maser sources,” Astron. Astrophys. 434, 613–621 (2005). doi 10.1051/0004-6361:20042437
M. Szymczak, P. Wolak, A. Bartkiewicz, and K. Borkowski, “The Torun catalogue of 6.7 GHz methanol masers,” Astron. Nachr. 333, 634–639 (2012). doi 10.1002/ asna.201211702
A. Traficante, G. A. Fuller, N. Peretto, J. E. Pineda, and S. Molinari, “The initial conditions of stellar protocluster formation. II. A catalogue of starless and protostellar clumps embedded in IRDCs in the Galactic longitude range 15° ≤ l ≤ 55°” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 451, 3089–3106 (2015). doi 10.1093/mnras/stv1158
J. S. Urquhart, T. J. Moore, M. G. Hoare, S. L. Lumsden, R. D. Oudmaijer, J. M. Rathborne, J. C. Mottram, and J. J. Stead, “The red MSX source survey: Distribution and properties of a sample of massive young stars,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 410, 1237–1250 (2011). doi 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17514.x
J. S. Urquhart, T. J. Moore, K. M. Menten, C. Konig, F. Wyrowski, M. A. Thompson, S. Leurini, and D. J. Eden, “The almost ubiquitous association of 6.7-GHz methanol masers with dust,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 446. 3461–3477 (2015). doi 10.1093/mnras/stu2300
I. E. Val’tts, A. M. Dzura, S. V. Kalenskii, V. I. Slysh, R. S. Booth, and A. Winnberg, “The discovery of methanol masers at 107 GHz,” Astron. Astrophys. 294, 825–830(1995).
I. E. Val’tts, S. P. Ellingsen, V. I. Slysh, S. V. Kalenskii, R. Otrupcek, and G. M. Larionov, “Detection of new sources of methanol emission at 95 GHz with the Mopra Telescope,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 317, 315–332(2000). doi 10.1046/ j.1365-8711.2000.03518.x
I. E. Val’tts and G. M. Larionov, “A general catalog of class I methanol masers,” Astron. Rep. 51, 519–530 (2007). doi 10.1134/S1063772907070013
H. M. de Villiers, A. Chrysostomou, M. A. Thompson, S. P. Ellingsen, J. S. Urquhart, S. L. Breen, M. G. Burton, T. Csengeri, and D. Ward-Thompson, “Methanol maser associated outflows: Detection statistics and properties,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 444, 566–585 (2014). doi 10.1093/mnras/stu1474
T. L. Wilson, C.M. Walmsley, P. R. Jewell, and L. E. Snyder, “Detection of a new type of methanol maser,” Astron. Astrophys. 134, L7–L10 (1984).
J. G. A. Wouterloot and J. Brand, “IRAS sources beyond the solar circle. I. CO observations,” Astron. Astrophys., Suppl. Ser. 80, 149–187 (1989).
J. Wu, N. J. Evans, and Y. L. Shirley, “The properties of massive, dense clumps: Mapping surveys of HCN and CS,” Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 188, 313–357 (2010). doi 10.1088/0067-0049/188/2/313
Y. Wu, M. Huang, and J. He, “A Catalogue of high velocity molecular outflows,” Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 115, 283–284 (1996).
Y. Wu, J. Wu, and J. Wang, “A search for massive dense cores with 13CO J = l–0 line,” Astron. Astrophys. 380, 665–672 (2001). doi 10.1051/0004-6361:20011498
Y. W. Wu, M. Sato, M. J. Reid, L. Moscadelli, Y. Xu, A. Brunthaler, K. Menten, and X. W. Zheng, “Trigonometric parallaxes of star-forming regions in the Sagittarius spiral arm,” Astron. Astrophys. 566, A17 (2014). doi 10.1051/0004-6361/ 201322765
Y. W. Wu, Y. Xu, J. D. Pandian, J. Yang, C. Henkel, K. M. Menten, and S. B. Zhang, “Ammonia and CO observations toward low-luminosity 6.7 GHz methanol masers,” Astrophys. J. 720, 392–408 (2010). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/720/1/392
Y.-W. Wu, Y. Xu, and J. Yang, “Multiwavelength study of low-luminosity 6.7-GHz methanol masers,” Res. Astron. Astrophys. 11, 137–155 (2011). doi 10.1088/1674-4527/11/2/002
Y. Xu, J. J. Li, M. J. Reid, K. Menten, X. W. Zheng, A. Brunthaler, L. Moscadelli, and B. Zhang, “On the nature of the local spiral arm of the Milky Way,” Astrophys. J. 769, 15 (2013). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/769/1/15
Y. Xu, M. J. Reid, K. Menten, A. Brunthaler, X. W. Zheng, L. Moscadelli, “Trigonometric parallaxes of massive star-forming regions: III. G59.7+0.1 and W51IRS2,” Astrophys. J. 693, 413–418 (2009). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/693/1/413
Y. Xu, X.-W. Zheng, and D. -R. Jiang, “Statistical properties of 6.7 GHz methanol maser sources,” Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. 3, 49–68 (2003).
W. Yang, Y. Xu, X. Chen, S. P. Ellingsen, D. Lu, and Y. Li, “A new 95 GHz methanol maser catalog. I. Data,” Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 231, 20 (2017). doi 10.3847/1538-4365/aa6ff3
L. Moscadelli, M. Sato, M. J. Reid, K. Menten, X. W. Zheng, A. Brunthaler, T. M. Dame, Y. Xu, and K. Immer, “The parallax of W43: A massive star-forming complex near the galactic bar,” Astrophys. J. 781, 89 (2014). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/781/2/89
M. J. Reid, K. Menten, X. W. Zheng, A. Brunthaler, and Y. Xu, “Parallaxes for W49N and G048.60+0.02: Distant star forming regions in the Perseus spiral arm,” Astrophys. J. 775, 79 (2013). doi 10.1088/0004-637X/775/1/79
I. Zinchenko, V. Forsstroem, A. Lapinov, and K. Mattila, “Studies of dense molecular cores in regions of massive star formation. CS (J = 2–1) and HCN (J = l–0) observations of 11 northern cores,” Astron. Astrophys. 288, 601–616 (1994).
S. Y. Zubrin and V. M. Shulga, “The 95 GHz methanol maser towards the supernova remnant Kes 79” in Proc. 15th Young Scientists’ Conf. on Astronomy and Space Physics, Kyiv, Ukraine, Apr. 14–19, 2008 (Kyiv. Nats. Univ. Im. T. Shevchenka, Kyiv, 2008), pp. 41–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by G. Dedkov
About this article
Cite this article
Patoka, O.M., Shulga, V.M., Antyufeyev, O.V. et al. Survey of Regions with Methanol Masers in the CS (J = 2–1) Line: Statistical Characteristics of Radiation. Kinemat. Phys. Celest. Bodies 34, 217–257 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0884591318050033
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0884591318050033