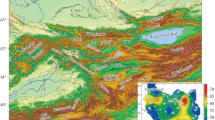
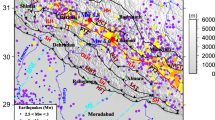
Abstract
The article presents a brief overview of the currently existing ideas about the seismotectonic situation in the Earth’s crust of Iran, which is experiencing intense compression in the northeastern direction as a result of collision of the Arabian and Eurasian lithospheric plates. The survey also involved geodetic data in the form of modern GPS measurements of horizontal surface displacements. The stress-strain state of the Earth’s crust of Iran (construction of the average focal mechanism) was assessed based on data on the total set of 945 focal mechanisms of earthquakes of average strength (4.4 ≤ MW ≤ 6.5) according to the ISC catalog, which occurred from 1975 to 2020, within 12 spatial samplings. The focal mechanisms of the strongest earthquakes in the last 50 years (MW = 6.0–7.4) for one event in each of these samplings are also considered. The calculated parameters of the average mechanisms and focal mechanisms of strong earthquakes are compared both with each other and with the surrounding tectonic situation and the distribution of deformation velocity vectors according to GPS observations. A satisfactory correspondence has been established between all the comparable values. The differences in the type of formation of the seismogenic layer of the Earth’s crust of Iran in different regions are demonstrated. These differences are manifested in different ratios of shear and thrust components in the reconstructed mean mechanism in different spatial samplings. A similar difference is noted in individual focal mechanisms of the strongest earthquakes. However, it is possible to describe the observed nature of deformation of the crust of Iran within a single concept of collisional tectonics, caused by collision of the Arabian and Eurasian plates in the last 5 Ma.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Allen, M.B., Ghassemi, M.R., Shahrabi, M., and Qorashi, M., Accommodation of late Cenozoic oblique shortening in the Alborz range, northern Iran, J. Struct. Geol., 2003, vol. 25, no. 5, pp. 659–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8141(02)00064-0
Allen, M.B., Jackson, J., and Walker, R., Late Cenozoic reorganization of the Arabia-Eurasia collision and the comparison of short-term and long-term deformation rates, Tectonics, 2004, vol. 23, no. 2, p. TC2008. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003TC001530
Allen, M.B., Kheirkhah, M., Emami, M.H., and Jones, S.J., Right-lateral shear across Iran and kinematic change in the Arabia–Eurasia collision zone, Geophys. J. Int., 2011, vol. 184, no. 2, pp. 555–574. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04874.x
Allen, M.B., Saville, C., Blanc, E.J.-P., Talebian, M., and Nissen, E., Orogenic plateau growth: Expansion of the Turkish-Iranian Plateau across the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt, Tectonics, 2013, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 171–190. https://doi.org/10.1002/tect.20025
Altamimi, Z., Rebischung, P., Métivier, L., and Collilieux, X., ITRF2014: A new release of the international terrestrial reference frame modeling nonlinear station motions, J. Geophys. Res., 2016, vol. 121, no. 8, pp. 6109–6131.https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JB013098
Ansari, S., Structural and stress heterogeneities along the 1997 Zirkuh earthquake fault, Eastern Iran, Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ., 2021, vol. 80, no. 11, pp. 8319–8337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02436-7
Authemayou, Ch., Bellier, O., Chardon, D., Benedetti, L., Malekzade, Z., Claude, Ch., Angeletti, B., Shabanian, E., and Abbassi, M.R., Quaternary slip-rates of the Kazerun and the Main Recent Faults: Active strike-slip partitioning in the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt, Geophys. J. Int., 2009, vol. 178, no. 1, pp. 524–540. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04191.x
Axen, G.J., Lam, P.S., Grove, M., Stockli, D.F., and Hassanzadeh, J., Exhumation of the west-central Alborz Mountains, Iran, Caspian subsidence, and collision-related tectonics, Geology, 2001, vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 559–562. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0559:EOTWCA>2.0.CO;2
Bachmanov, D.M., Zelenin, E.A., Kozhurina, A.I., and Trifonov, V.G., Using the active faults of Eurasia database for solving tectonic problems, Geodin. Tektonofiz., 2019, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 971–993. https://doi.org/10.5800/GT-2019-10-4-0453
Bayer, R., Chery, J., Tatar, M., Vernant, Ph., Abbassi, M., Masson, F., Nilforoushan, F., Doerflinger, E., Regard, V., and Bellier, O., Active deformation in Zagros–Makran transition zone inferred from GPS measurements, Geophys. J. Int., 2006, vol. 165, no. 1, pp. 373–381. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.02879.x
Berberian, M. and Walker, R., The Rudbār M w = 7.3 earthquake of 1990 June 20; seismotectonics, coseismic and geomorphic displacements, and historic earthquakes of the western ‘High-Alborz’, Iran, Geophys. J. Int., 2010, vol. 182, no. 3, pp. 1577–1602. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04705.x
Copley, A., Karasozen, E., Oveisi, B., Elliott, J.R., Samsonov, S., and Nisen, E., Seismogenic faulting of the sedimentary sequence and laterally variable material properties in the Zagros Mountains (Iran) revealed by the August 2014 Murmuri (E. Dehloran) earthquake sequence, Geophys. J. Int., 2015, vol. 203, no. 2, pp. 1436–1459. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggv365
DeMets, C., Gordon, R.G., Argus, D.F., and Stein, S., Effect of recent revisions to the geomagnetic reversal time-scale on estimates of current plate motions, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1994, vol. 21, no. 20, pp. 2191–2194. https://doi.org/10.1029/94GL02118
Djamour, Y., Vernant, Ph., Bayer, R., Nankali, H.R., Ritz, J.-F., Hinderer, J., Hatam, Y., Luck, B., Le Moigne, N., Sedighi, M., and Khorrami, F., GPS and gravity constraints on continental deformation in the Alborz mountain range, Iran, Geophys. J. Int., 2010, vol. 183, no. 3, pp. 1287–1301. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04811.x
Djamour, Y., Vernant, Ph., Nankali, H.R., and Tavakoli, F., NW Iran-eastern Turkey present-day kinematics: Results from the Iranian permanent GPS network, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2011, vol. 307, nos. 1–2, pp. 27–34.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2011.04.029
Donner, S., Ghods, A., Krüger, F., Rößler, D., Landgraf, A., and Ballato, P., The Ahar-Varzeghan earthquake doublet (Mw 6.4 and 6.2) of 11 August 2012: Regional seismic moment tensors and a seismotectonic interpretation, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am., 2015, vol. 105, pp. 791–807.
Engdahl, E.R., Jackson, J.A., Myers, S.C., Bergman, E.A., and Priestley, K., Relocation and assessment of seismicity in the Iran region, Geophys. J. Int., 2006, vol. 167, no. 2, pp. 761–778. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03127.x
Esmaeili, B., Almasian, M., and Zare, M., Dating of South Ahar Fault seismic activity by thermo lominesense with regard to August 11th earthquake, Second European Conference on Earthquake Engineering and Seismology, Istanbul, 2014.
Feng, W., Samsonov, S., Almeida, R., Yassaghi, A., Li, J., Qiu, Q., Li, P., and Zheng, W., Geodetic constraints of the 2017 Mw 7.3 Sarpol Zahab, Iran earthquake and its implications on the structure and mechanics of the Northwest Zagros thrust-fold belt, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2018, vol. 45, no. 14, pp. 6853–6861. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL078577
Frohling, E. and Szeliga, W., GPS constraints on interpolate locking within Makran subduction zone, Geophys. J. Int., 2016, vol. 205, no. 1, pp. 67–76. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggw001
Gao, L. and Wallace, T.C., The 1990 Rudbar-Tarom Iranian earthquake sequence: Evidence for slip partitioning, J. Geophys. Res., 1995, vol. 100, no. B8, pp. 15317–15332. https://doi.org/10.1029/95JB00320
Hessami, K., Nilforoushan, F., and Talbot, C., Active deformation within the Zagros Mountains deduced from GPS measurements, J. Geol. Soc., 2006, vol. 163, no. 1, pp. 143–148. https://doi.org/10.1144/0016-764905-031
Hollingsworth, J., Jackson, J., Walker, R., Gheitanchi, M.R., and Bolourchi, M.J., Strike-slip faulting, rotation, and along-strike elongation in the Kopeh Dagh mountains, NE Iran, Geophys. J. Int., 2006, vol. 166, no. 3, pp. 1161–1177. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.02983.x
Horton, B.K., Hassanzadeh, J., Stockli, D.F., Axen, G.J., Gillis, R.J., Guest, B., Amini, A., Fakhari, M.D., Zamanzadeh, S.M., and Grove, M., Detrital zircon provenance of Neoproterozoic to Cenozoic deposits in Iran: Implications for chronostratigraphy and collisional tectonics, Tectonophysics, 2008, vol. 451, nos. 1–4, pp. 97–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2007.11.063
International Seismological, Centre. http://www.isc.ac.uk/ registries/search/. Cited December 4, 2021.
Jackson, J. and McKenzie, D., Active tectonics of the Alpine–Himalayan Belt between western Turkey and Pakistan, Geophys. J. Int., 1984, vol. 77, no. 1, pp. 185–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1984.tb01931.x
Jackson, J., Priestley, K., Allen, M., and Berberian, M., Active tectonics of the South Caspian Basin, Geophys. J. Int., 2002, vol. 148, no. 2, pp. 214–245. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01588.x
Kalantari, A. and Parsizadeh, F., The M w = 6.4 and M w = 6.3 Iran earthquakes of August 11, 2012, EERI Special Earthquake Report, 2012.
Khorrami, F., Vernant, Ph., Masson, F., Nilfouroushan, F., Mousavi, Z., Nankali, H., Saadat, S.A., Walpersdorf, A., Hosseini, S., Tavakoli, P., Aghamohammadi, A., and Alijanzade, M., An up-to-date crustal deformation map of Iran using integrated campaign-mode and permanent GPS velocities, Geophys. J. Int., 2019, vol. 217, no. 2, pp. 832–843. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggz045
Koronovskii, N.B., Bryantseva, G.V., Arkhipov, E.V., and Anisimova, O.V., Structural-geomorphological analysis and seismicity of Iranian region, Byull. Mosk. O-va. Ispyt. Prir. Otd. Geol., 2017, vol. 92, no. 3, pp. 12–22.
Laane, J.L. and Chen, W.-P., The Makran earthquake of 1983 April 18: A possible analogue to the Puget Sound earthquake of 1965?, Geophys. J. Int., 1989, vol. 98, no. 1, pp. 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1989.tb05509.x
Lukk, A.A. and Rebetskii, Yu.L., Modern geodynamics and focal mechanisms of earthquakes in the neighborhood of Bushehr NPP, Geofiz. Protsessy Biosfera, 2018, vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 90–108. https://doi.org/10.21455/GPB2018.3-6
Maggi, A., Jackson, J.A., Priestley, K., and Baker, C., A re-assessment of focal depth distributions in southern Iran, the Tien Shan and northern India: do earthquakes really occur in the continental mantle?, Geophys. J. Int., 2000, vol. 143, no. 3, pp. 629–661. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246X.2000.00254.x
Mangino, S. and Priestley, K., The crustal structure of the southern Caspian region, Geophys. J. Int., 1998, vol. 133, no. 3, pp. 630–648. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246X.1998.00520.x
Masson, F., Chéry, J., Hatzfeld, D., Martinod, J., Vernant, P., Tavakoli, F., and Ghafory-Ashtiani, M., Seismic versus aseismic deformation in Iran inferred from earthquakes and geodetic data, Geophys. J. Int., 2005, vol. 160, no. 1, pp. 217–226. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02465.x
Masson, F., Djamour, Y., Van Gorp, S., Chéry, J., Tatar, M., Tavakoli, F., Nankali, H., and Vernant, P., Extension in NW Iran driven by the motion of the South Caspian Basin, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2006, vol. 252, nos. 1–2, pp. 180–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2006.09.038
Masson, F., Anvari, M., Djamour, Y., Walpersdorf, A., Tavakoli, F., Daignieres, M., Nankali, H., and Van Gorp, S., Large-scale velocity field and strain tensor in Iran inferred from GPS measurements: new insight for the present-day deformation pattern within NE Iran, Geophys. J. Int., 2007, vol. 170, no. 1, pp. 436–440. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03477.x
Masson, F., Lehujeur, M., Ziegler, Y., and Doubre, C., Strain rate tensor in Iran from a new GPS velocity field, Geophys. J. Int., 2014, vol. 197, no. 1, pp. 10–21. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggt509
Mousavi-Bafrouei, S.H. and Mahani, A.B., A comprehensive earthquake catalogue for the Iranian Plateau (400 B.C. to December 31, 2018), J. Seismol., 2020, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 709–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-020-09923-6
Mousavi, Z., Walpersdorf, A., Walker, R.T., Tavakoli, F., Pathier, E., Nankali, H., Nilfouroushan, F., and Djamour, Y., Global Positioning System constraints on the active tectonics of NE Iran and the South Caspian region, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2013, vols. 377–378, pp. 287–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.07.007
Mouthereau, F., Lacombe, O., and Vergés, J., Building the Zagros collisional orogen: Timing, strain distribution and the dynamics of Arabia/Eurasia plate convergence, Tectonophysics, 2012, vols. 532–535, pp. 27–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2012.01.022
Nilforoushan, F., Masson, F., Vernant, P., Vigny, C., Martinod, J., Abbassi, M., Nankali, H., Hatzfeld, D., Bayer, R., Tavakoli, F., Ashtiani, A., Doerflinger, E., Daignières, M., Collard, P., and Chéry, J., GPS network monitors the Arabia-Eurasia collision deformation in Iran, J. Geod., 2003, vol. 77, nos. 7–8, pp. 411–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-003-0326-5
Nissen, E., Yamini-Fard, F., Tatar, M., Gholamzadeh, A., Bergman, E., Elliott, J.R., Jackson, J.A., and Parsons, B., The vertical separation of mainshock rupture and microseismicity at Qeshm island in the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt, Iran, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2010, vol. 296, nos. 3–4, pp. 181–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2010.04.049
Peyret, M., Djamour, Y., Hessami, K., Regard, V., Bellier, O., Vernant, P., Daignières, M., Nankali, H., Van Gorp, S., Goudarzi, M., Chéry, J., Bayer, R., and Rigoulay, M., Present-day strain distribution across the Minab-Zendan-Palami fault system from dense GPS transects, Geophys. J. Int., 2009, vol. 179, no. 2, pp. 751–762. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04321.x
Raeesi, M., Zarifi, Z., Nilfouroushan, F., Boroujeni, S.A., and Tiampo, K., Quantitative analysis of seismicity in Iran, Pure Appl. Geophys., 2017, vol. 174, no. 3, pp. 793–833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-016-1435-4
Regard, V., Bellier, O., Thomas, J.-C., Abbassi, M.R., Mercier, J.L., Shabanian, E., Feghhi, Kh., and Soleymani, S., Accommodation of the Arabia-Eurasia convergence in the Zagros-Makran transfer zone, SE Iran: A transition between collision and subduction through a young deforming system, Tectonics, 2004, vol. 23, no. 4, p. TC4007. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003TC001599
Regard, V., Bellier, O., Thomas, J.C., Bourlès, D.L., Bonnet, S., Abbassi, M., Braucher, R., Mercier, J.L., Shabanian, E., Soleymani, Sh., and Feghhi, Kh., Cumulative right-lateral fault slip rate across the Zagros–Makran transfer zone: role of the Minab–Zendan fault system in accommodating Arabia–Eurasia convergence in southeast Iran, Geophys. J. Int., 2005, vol. 162, no. 1, pp. 177–203. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02558.x
Reilinger, R., McClusky, S., Vernant, Ph., Lawrence, S., Ergintav, S., Cakmak, R., Ozener, H., Kadirov, F., Guliev, I., Stepanyan, R., Nadariya, M., Hahubia, G., Mahmoud, S., Sakr, K., ArRajehi, A., Paradissis, D., Al-Aydrus, A., Prilepin, M., Guseva, T., Evren, E., Dmitrotsa, A., Filikov, S.V., Gomez, F., Al-Ghazzi, R., and Karam, G., GPS constraints on continental deformation in the Africa-Arabia-Eurasia continental collision zone and implications for the dynamics of plate interactions, J. Geophys. Res., 2006, vol. 111, no. B5, p. B05411. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JB004051
Ritz, J.-F., Nazari, H., Ghassemi, A., Salamati, R., Shafei, A., Solaymani, S., and Vernant, Ph., Active transtension inside central Alborz: A new insight into northern Iran–southern Caspian geodynamics, Geology, 2006, vol. 34, no. 6, pp. 477–480. https://doi.org/10.1130/G22319.1
Shahvar, M.P. and Zaré, M., The 27 august 2010 Mw 5.7 Kuh-Zar earthquake (Iran): Field investigation and strong-motion evidence, Nat. Hazards, 2013, vol. 66, no. 2, pp. 689–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0507-8
Sudhaus, H. and Jonsson, S., Source model for the 1997 Zirkuh earthquake (M w = 7.2) in Iran derived from JERS and ERS InSAR observations, Geophys. J. Int., 2011, vol. 185, no. 2, pp. 676–692. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.04973.x
Talebian, M. and Jackson, J.A., Offset on the main recent fault of the NW Iran and implications for the late Cenozoic tectonics of the Arabia–Eurasia collision zone, Geophys. J. Int., 2002, vol. 150, no. 2, pp. 422–439. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01711.x
Talebian, M. and Jackson, J.A., A reappraisal of earthquake focal mechanisms and active shortening in the Zagros mountains of Iran, Geophys. J. Int., 2004, vol. 156, no. 3, pp. 506–526. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02092.x
Tatar, M., Hatzfeld, D., Martinod, J., Walperdorf, A., Ghafori-Ashtiany, M., and Chéry, J., The present-day deformation of the central Zagros from GPS measurements, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2002, vol. 29, no. 19, pp. 33-1–33-4. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002GL015427
Tavakoli, F., Walpersdorf, A., Authemayou, C., Nankali, H.R., Hatzfeld, D., Tatar, M., Djamour, Y., Nilforoushan, F., and Cotte, N., Distribution of the right-lateral strike–slip motion from the Main Recent Fault to the Kazerun Fault System (Zagros, Iran): Evidence from present-day GPS velocities, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2008, vol. 275, nos. 3–4, pp. 342–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2008.08.030
Vernant, Ph., Nilforoushan, F., Hatzfeld, D., Abbassi, M.R., Vigny, C., Masson, F., Nankali, H., Martinod, J., Ashtiani, A., Bayer, R., Tavakoli, F., Chéry, J., Present-day crustal deformation and plate kinematics in Middle East constrained by GPS measurements in Iran and northern Oman, Geophys. J. Int., 2004a, vol. 157, no. 1, pp. 381–398. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02222.x
Vernant, Ph., Nilforoushan, F., Chéry, J., Bayer, R., Djamour, Y., Masson, F., Nankali, H., Ritz, J.-F., Sedighi, M., and Tavakoli, F., Deciphering oblique shortening of central Alborz in Iran using geodetic data, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2004b, vol. 223, nos. 1–2, pp. 177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2004.04.017
Walker, R.T. and Jackson, J., Active tectonics and late Cenozoic strain distribution in central and eastern Iran, Tectonics, 2004, vol. 23, no. 5, p. TC5010. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003TC001529
Walker, R.T., Gans, P., Allen, M.B., Jackson, J., Khatib, M., Marsh, N., and Zarrinkoub, M., Late Cenozoic volcanism and rates of active faulting in eastern Iran, Geophys. J. Int., 2009, vol. 177, no. 2, pp. 783–805. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.04024.x
Walpersdorf, A., Hatzfeld, D., Nankali, H., Tavakoli, F., Nilforoushan, F., Tatar, M., Vernant, P., Chéry, J., and Masson, F., Difference in the GPS deformation pattern of North and Central Zagros (Iran), Geophys. J. Int., 2006, vol. 167, no. 3, pp. 1077–1088. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03147.x
Walpersdorf, A., Manighetti, I., Mousavi, Z., Tavakoli, F., Vergnolle, M., Jadidi, A., Hatzfeld, D., Aghamohamma-di, A., Bigot, A., Djamour, Y., Nankali, H., and Sedighi, M., Present-day kinematics and fault slip rates in eastern Iran, derived from 11 years of GPS data, J. Geophys. Res., 2014, vol. 119, no. 2, pp. 1359–1383. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JB010620
Yunga, S.L., Metody i rezul’taty izucheniya seismotektonicheskikh deformatsii (Methods and Results of Studying Seismotectonic Deformations), Moscow: Nauka, 1990.
Zarifi, Z., Nilfouroushan, F., and Raeesi, M., Crustal stress map of Iran: Insight from seismic and geodetic computations, Pure Appl. Geophys., 2014, vol. 171, no. 7, pp. 1219–1236.
Funding
The study was carried out under the state task of the Schmidt Institute of Physics of the Earth, Russian Academy of Sciences (topic no. 0144-2019-0011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by A. Carpenter
About this article
Cite this article
Lukk, A.A., Leonova, V.G. Deformations, Stresses, and Strong Earthquakes in the Earth’s Crust of Iran. Seism. Instr. 58, 330–349 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0747923922030100
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0747923922030100