Abstract
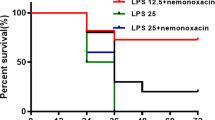
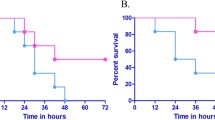
We studied tolerogenic properties of new nonpyrogenic low-endotoxic complex preparation composed of Shigella sonnei carbohydrate biopolymers under D-galactosamine and direct experimental endotoxic shock models. Pretreatment with complex preparation (exopolysaccharide + lipopolysaccharide) S. sonnei protects mice (CBA × C57B1/6)F1 against lipopolysaccharide (E. coli O:55)-mediated death. We demonstrate correlation between increasing preimmunization dose of complex preparation with rate of survival and reduction of TNF-α serum level under a direct endotoxic shock model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cross, A.S., Opal, S.M., Warren, H.S., Palardy, J.E., Glaser, K., Parejo, A., and Bhattacharjee, A.K., Active Immunization with a Detoxified Escherichia coli J5 Lipopolysaccharide Group B Meningococcal Outer Membrane Protein Complex Vaccine Protects Animals from Experimental Sepsis, J. Infect. Dis., 2001, no. 183, pp. 1079–1086.
Astiz, M.E. and Rackow, E.C., Septic Shock, Lancet, 1998, no. 361, pp. 1501–1505.
Dinarello, C., Cytokines As Mediators in the Pathogenesis of Septic Shock, Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immunol., 1996, no. 216, pp. 133–165.
Ulloa, L. and Tracey, K.J., The “Cytokine Profile”: A Code for Sepsis, Trends Mol. Med., 2005, no. 11, pp. 56–63.
Madonna, G.S., Peterson, J.E., Ribi, E.E., and Vogel, S.N., Early-Phase Endotoxin Tolerance: Induction by Detoxified Lipid A Derivative, Monophosphoryl Lipid A, Infect. Immun., 1986, vol. 1, no. 52, pp. 6–11.
Dinarello, C.A., Immediate Cytokine Responses to Endotoxin: Tumor Necrosis Factor α and Interleukin-1 Family, in Endotoxin in Health and Disease, Brade, H., Ed., New York: Marcell Dekker, 1999, pp. 817–830.
van Emersfoort, E.S., van Berkel, T.J., and Kuiper, J., Receptors, Mediators, and Mechanisms Involved in Bacterial Sepsis and Septic Shock, Clin. Microbial. Rev., 2003, vol. 3, no. 16, pp. 379–414.
Lehmann, B.V., Freudenberg, M.A., and Galanos, G., Lethal Toxicity of Lipopolysaccharide and Tumor Necrosis Factor in Normal and D-Galactosamine-Treated Mice, J. Exp. Med., 1987, no. 165, pp. 657–663.
Tiegs, G., Wolter, M., and Wendel, A., Tumour Necrosis Factor Is a Terminal Mediator in Galactosamine/Endotoxin-Induced Hepatitis in Mice, Biochem. Pharmacol., 1989, no. 38, pp. 627–631.
Mignon, A., Rouquet, N., Fabre, M., Martin, S., Pages, J.C., Dhainaut, J.F., Kahn, A., Briand, P., and Joulin, V., LPS Challenge in D-Galactosamine-Sensitized Mice Accounts for Caspase-Dependent Fulminant Hepatitis, Not for Septic Shock, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 1999, no. 159, pp. 1308–1315.
Johnston, C.A. and Greisman, S.E., Mechanism of Endotoxin Tolerance, in Handbook of Endotoxin, vol. 2: Pathophysiology of Endotoxin, Hishaw, L.B., Ed., New York: Elsevier, 1985, pp. 359–391.
Suffredini, A.F., Reda, D., Banks, S.M., Tropea, M., Agosti, J.M., and Miller, R., Effects of Recombinant Dimeric TNF-α Receptor on Human Inflammatory Responses Following Intravenous Endotoxin Administration, J. Immunol., 1995, no. 155, pp. 5038–5045.
Marano, M.A., Fong, Y., Moldawer, L.L., Wei, H., Calvano, S.E., Tracey, K.J., Barie, J.S., Manogue, K., Cerami, A., Shires, G.T.G., and Lowry, S.F., Serum Cachectin/Tumor Necrosis Factor in Critically Ill Patients with Burns Correlate with Infection and Mortality, Surg. Gynecol. Obstet., 1990, no. 170, pp. 32–38.
Christman, J.W., Lancaster, L.H., and Blackwell, T.S., Nuclear Factor B: A Pivotal Role in the Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome and New Target for Therapy, Intens. Care Med., 1998, no. 24, pp. 1131–1138.
Schade, F., Flach, R., Flohe, S., Majetschak, M., Kreuzfelder, E., Dominguez-Fernandes, E., Borgermann, J., Reuter, M., and Obertacke, U., Endotoxin Tolerance, in Endotoxin in Health and Disease, Brade, H., Ed., New York: Marcell Dekker, 1999, pp. 751–767.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.A. Markina, I.A. Kondratieva, 2013, published in Vestnik Moskovskogo Universiteta. Biologiya, 2013, No. 3, pp. 12–15.
About this article
Cite this article
Markina, A.A., Kondratieva, I.A. Investigation of protective properties of Shigella sonnei carbohydrate biopolymers under experimental endotoxic shock models. Moscow Univ. Biol.Sci. Bull. 68, 100–103 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0096392513020053
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0096392513020053