Abstract
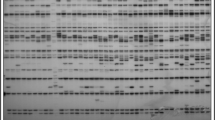
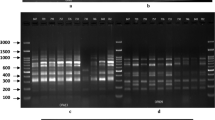
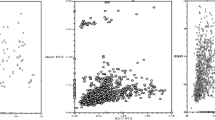
The tea is one of the most important products in the southern region of Azerbaijan Republic, and plays an essential role in the region’s economy. Assessing and describing genetic diversity in crop plants is a crucial first step toward their improvement. In this study the tea genotypes belonged southern region of Azerbaijan was studied using 10 random amplified polymorphic DNA in order to estimate their genetic diversity and to identify the relationships among their genotypes. The RAPD primers generated 132 amplification products and 113 of which were polymorphic. The polymorphic banding patterns with the number of amplified fragments varied from 4 (OPA-19) to 19 (OPAB-18). Percent polymorphism ranged from 50 to 95% with an average of 83.94%. The genetic similarity among the genotypes tested ranged 0.445 to 0.819 with an average of 0.512. The cluster analysis based on UPGMA and Jaccard similarity index revealed 5 main clusters for the RAPD data and the principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) supported the clustering result. According to our results, there is a relatively high genetic distance across tea genotypes in the southern of Azerbaijan Republic. Furthermore, it could be inferred that RAPD markers are suitable tools for the evaluation of genetic diversity and relationships within Camellia sinensis.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bandyopadhyay, T., Molecular marker technology in genetic improvement of tea, Int. J. Plant Breed. Genet., 2011, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 23–33.
Boonerjee, S., Islam, M.N., Hoque, M.I., and Sarker, R.H., Genetic diversity analysis of eighteen tea (Camellia sinensis L.) clones of Bangladesh through RAPD, Plant Tissue Cult. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 189–199.
Botstein, D., White, R.L., Skolnick, M., and Davis, R.W., Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 1980, vol. 32, pp. 314–331.
Chen, L., Gao, Q., Chen, D., and Xu, C.J., The use of RAPD markers for detecting genetic diversity, relationship and molecular identification of Chinese elite tea genetic resources [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze] preserved in a tea germplasm repository, Biodiversity Conserv., 2005, vol. 14, pp. 1433–1444.
Cheng-Wen, S., Yi-Huan, H., Jian-An, H., Jun-Wu, L., Chun-Lin, L., and De-Hua, L., RAPD analysis on genetic diversity of typical tea populations in Hunan Province, Chin. J. Agric. Biotechnol., 2008, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 67–72.
Fabriki-Ourang, S., and Karimi, H., Assessment of genetic diversity and relationships among Salvia species using gene targeted CAAT box-derived polymorphism markers, J. Genet., 2019, vol. 98, no. 75, pp. 1–10.
FAO, Country report on the state of plant genetic resources for food and agriculture: National report on the state of plant genetic resources for food and agriculture in Azerbaijan, 2016, pp. 1–58.
Govindaraj, M., Vetriventhan, M., and Srinivasan, M., Importance of genetic diversity assessment in crop plants and its recent advances: an overview of its analytical perspectives, Genet. Res. Int., 2015, art. ID 431487.
Gul, S., Ahmad, H., Khan, A., and Alam, M., Assessment of Genetic Diversity in Tea genotypes through RAPD Primers, Pak. J. Biol. Sci., 2007, vol. 10, no. 15, pp. 2609–2611.
Guliyev, N., Sharifova, S., Ojaghi, J., Abbasov, M., and Akparov, Z., Genetic diversity among melon (Cucumis melo L.) accessions revealed by morphological traits and ISSR markers, Turk. J. Agric. For., 2018, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 393–401.
Hammer, Ø., Harper, D.A.T., and Ryan, P.D., PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis, Palaeontologia Electronica, 2011, vol. 4, no. 1, art. ID 9.
Igwe, D.O., Afiukwa, C.A., Acquaah, G., and Ude, G.N., Genetic diversity and structure of Capsicum annuum as revealed by start codon targeted and directed amplified minisatellite DNA markers, Hereditas, 2019, vol. 156, art. ID 32.
Izzatullayeva, V., Akparov, Z., Babayeva, S., Ojaghi, J., and Abbasov, M., Efficiency of using RAPD and ISSR markers in evaluation of genetic diversity in sugar beet, Turk. J. Biol., 2014, vol. 38, pp. 429–438.
Jahangirzadeh Khiavi, S., Azadi Gonbad, R., and Falakro, K., Identification of genetic diversity and relationships of some Iranian tea genotypes using SRAP markers, J. Hortic. Postharvest Res., 2020, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 25–34.
Jaroslava, O., Daniela, R., Domenico, F., Eloy Fernández, C., Svobodova, E., and Luigi, M., Assessment of genetic diversity of Smallanthussonchifolius (Poepp. & Endl.) h. Robinson landraces by using AFLP markers, Genetika, 2018, vol. 50, no. 3, pp. 803–816.
Karak, T., and Bhagat, R.M., Trace Elements in tea leaves, made tea and tea infusion: A review, Food Res. Int., 2010, vol. 43, no. 9, pp. 2234–2252.
Karunarathna, K.H.T., Mewan, K.M., Weerasena, O.V.D.S.J., Perera, S.A.C.N., Edirisinghe, E.N.U., and Jayasoma, A.A, Understanding the genetic relationships and breeding patterns of Sri Lankan tea cultivars with genomic and EST-SSR markers, Sci. Hortic., 2018, vol. 240, no. 9, pp. 72–80.
Liu, B.Y., Li, Y.Y., Tang, Y.C., Wang, L.Y., Cheng, H., and Wang, P.S., Assessment of genetic diversity and relationship of tea germplasm in Yunnan as revealed by ISSR markers, Acta Agron. Sin., 2010, vol. 36, pp. 391–400.
Matsumoto, S., Kiriiwa, Y., and Yamaguchi, S., The Korean tea plant (Camellia sinensis): RFLP analysis of genetic diversity and relationship to Japanese tea, Breed. Sci., 2004, vol. 54, no. 3, pp. 231–237.
Mohammadi, S., and Prasanna, B., Analysis of genetic diversity in crop plants—salient statistical tools and considerations, Crop Sci., 2003, vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 1235–1248.
Murray, M.G., and Thompson, W.F., Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA, Nucleic Acids Res., 1980, vol. 8, no. 9, pp. 4321–4325.
Ojaghi, J., and Akhundova, E., Genetic diversity in doubled haploids wheat based on morphological traits, gliadin protein patterns and RAPD markers, Afr. J. Agric. Res., 2010, vol. 5, pp. 1701–1712.
Powell, W., Morgante, M., Andre, C., Hanafey, M., Vogel, J., Tingey, S., and Rafalski, A., The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers of germplasm analysis, Mol. Breed., 1996, vol. 2, pp. 225–238.
Roy, S.C., and Chakraborty, B.N., Genetic diversity and relationships among tea (Camellia sinensis) cultivars as revealed by RAPD and ISSR based fingerprinting, Indian J. Biotechnol., 2009, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 370–376.
Sadigova, S., Sadigov, H., Eshghi, R., Salayeva, S., and Ojaghi, J., Application of RAPD and ISSR markers to analyses molecular relationships in Azerbaijan wheat accessions (Triticum aestivum L.), Bulg. J. Agric. Sci., 2014, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 97–105.
Saghai-Maroof, M.A., Soliman, K.M., Jorgensen, R.A., and Allard, R.W., Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: mendelian inheritance, chromosome location and population dynamics, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1984, vol. 81, pp. 8014–8018.
Salayeva, S., Decroocq, S., Mariette, S., and Akhundova, E., Comparison of genetic diversity between cultivated and wild grape varieties originating from the Near-Caspian zone of Azerbaijan, J. Int. Sci. Vigne Vin, 2010, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 191–200.
Salayeva, S.J., Ojaghi, J.M., Pashayeva, A.N., Izzatullayeva, V.I., Akhundova, E.M., and Akperov, Z.I., Genetic diversity of Vitis vinifera L. in Azerbaijan, Russ. J. Genet., 2016, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 391–397.
Saravanan, M., Maria John, K.M., Raj Kumar, R., Pius, P.K., and Sasikumar, R., Genetic diversity of UPASI tea clones (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) on the basis of total catechins and their fractions, Phytochemistry, 2005, vol. 66, no. 5, pp. 561–565.
Sharma, A., Rajpurohit, D., Jain, D., Verma, P., and Joshi, A., Molecular characterization of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) genotypes using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers, J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem., 2019, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 4770–4775.
Shah, S., Yadav, R.N.S., and Borua, P.K., Molecular analysis by RAPD markers of popular tea (Camellia sinensis) varieties of North-East India infested by tea mosquito bug (Helopeltis theivora), Int. J. Biosci., 2015, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 318–325.
Shikhseyidova, G., Akhundova, E., Quliyev, R., Eshghi, R., Salayeva, S., and Ojaghi, J., Molecular diversity and genetic structure of durum wheat landraces, Albanian J. Agric. Sci., 2015, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 112–120.
Sornakili, A., Rathinam, P., Thiruvengadum, R., and Kuppusamy, P., Comparative assessment of RAPD and ISSR markers to study genetic polymorphism in Colletotrichum gloeosorioides isolates of mango, Asian J. Plant Pathol., 2017, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 130–138.
Vivodik, M., Balazova, Z., Galova, Z., and Petrovicova, L., Genetic diversity analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) using SCoT markers, J. Microbiol., Biotechnol. Food Sci., 2017, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 1170–1173.
Wambulwa, M.C., Meegahakumbura, M.K., Kamunya, S., Muchugi, A., Möller, M., Liu, J., Xu, J.C., Li, D.J., and Gao, L.M., Multiple origins and a narrow genepoolcharacterise the African tea germplasm: Concordant patterns revealed by nuclear and plastid DNA markers, Sci. Rep., 2017, vol. 7, art. ID 4053.
Wambulwa, M.C., Meegahakumbura, M.K., Chalo, R., Kamunya, S., Muchugi, A., Xu, J.C., Liu, J., Li, D.J., and Gao, L.M., Nuclear microsatellites reveal the genetic architecture and breeding history of tea germplasm of East Africa, Tree Genet. Genomes, 2016, vol. 12, no. 11.
Wei, C.L., Cheng, J.L., Khan, M.A., Yang, L.Q., Imani, S., Chen, H.C., and Fu, J.J., An improved DNA marker technique for genetic characterization using RAMP-PCR with high-GC primers, Genet. Mol. Res., 2016, vol. 15, no. 3, art. ID 15038721.
Yousefi, V., Najaphy, A., Zebarjadi, A., and Safari, H., Molecular characterization of thymus species using ISSR markers, J. Anim. Plant Sci., 2015, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 1087–1094.
Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., Chen, X., Sun, W., and Li, J., Genetic diversity and structure of tea plant in Qinba area in China by three types of molecular markers, Hereditas, 2018, vol. 155, art. ID 22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
About this article
Cite this article
Huseynov, M., Suleymanova, Z., Ojaghi, J. et al. Characterization and Phylogeny Analysis of Azerbaijan Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Genotypes by Molecular Markers. Cytol. Genet. 56, 285–291 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452722030057
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452722030057