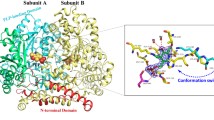
Abstract
Site-directed mutagenesis of the N-terminal catalytic module of Bos taurus tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (mini-BtTyrRS) with the substitution of three Trp residues by Ala residues in its structure using the modified QuikChange method was performed to study structural dynamic and functional properties of the protein by fluorescence spectroscopy. Point substitutions of tryptophan codons TGG with alanine codons GCG in the cDNA nucleotide sequence of the tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase catalytic module cloned in expression plasmid pET-30a were obtained during sequential PCR reactions using the developed primers. As a result, mini-BtTyrRS cDNAs, whose sequences contain only one tryptophan codon in each of the three positions in the protein structure, were obtained.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Pang, Y.L.J., Poruri, K., and Martinis, S.A., tRNA synthetase: tRNA aminoacylation and beyond, WIREs RNA, 2014, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 461–480. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1224
Kornelyuk, A.I., Structural and functional investigation of mammalian tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase, Biopolym. Cell, 1998, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 349–359.https://doi.org/10.7124/bc.0004DF
Gnatenko, D.V., Kornelyuk, A.I., Kurochkin, I.V., Ribkinska, T.A., and Matsuka, G.Kh., Isolation and characteristics of functionally active proteolytically modified form of tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase from the bovine liver, Ukr. Biochim. J., 1991, vol. 63, no. 4, pp. 61–67.
Greenberg, Y., King, M., Kiosses, W.B., Ewalt, K., Yang, X., Schimmel, P., Reader, J.S., and Tzima, E., The novel fragment of tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase, mini-TyrRS, is secreted to induce an angiogenic response in endothelial cells, FASEB J., 2008, vol. 22, no. 5, pp. 1597–1605. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.07-9973com
Kornelyuk, A.I., Maarten, P.R., Dubrovsky, A.L., and Murray, J.C., Cytokine activity of the non-catalytic EMAP-2-like domain of mammalian tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase, Biopolym. Cell, 1999, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 168–172.https://doi.org/10.7124/bc.000516
Guo, M. and Schimmel, P., Essential non-translational functions of tRNA synthetases, Nat. Chem. Biol., 2013, vol. 9, pp. 145–153. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1158
Ladokhin, A.S., Fluorescence spectroscopy in peptide and protein analysis, in Meyers, R.A., Ed., Chichester: John Wiley and Sons Ltd., 2002, pp. 5762–5779.
Chatttopadhyay, A. and Haldar, S., Dynamic insight into protein structure utilizing red edge excitation shift, Acc. Chem. Res., 2013, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 12–19. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar400006z
Rochamare, S.B. and Gaikwad, M., Tryptophan environment and functional characterization of a kinetically stable serine protease containing a polyproline II fold, J. Fluoresc., 2014, vol. 24, pp. 1363–1370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-014-1445-5
Kordysh, M. and Kornelyuk, A., Conformational flexibility of cytokine-like C-module of tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase monitored by Trp144 intrinsic fluorescence, J. Fluoresc., 2006, vol. 16, pp. 705–711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-006-0113-9
Turoverov, K.K. and Kuznetsova, I.M., The intrinsic fluorescence of globular actin: peculiarities in the location of tryptophan residues, Bioorg. Chem., 1998, vol. 24, no. 12, pp. 893–898.
Vallee-Belisle, A. and Michnick, S.W., Visualizing transient protein-folding intermediates by tryptophan-scanning mutagenesis, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 2012, vol. 19, no. 7, pp. 731–737. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2322
Kordysh, M.A. and Kornelyuk, A.I., Monitoring of the conformational change in the environment of the Trp144 fluorophore in the C-module of tyrosyltRNA synthetase during thermal denaturation, Dop. Nac. Acad. Nauk Ukraine, 2004, no. 1, pp. 156–161.
Kordysh, M.A. and Kornelyuk, A.I., Investigation of the interaction between isolated C-module of tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase and tRNA by fluorescence spectroscopy, Biopolym. Cell, 2006, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 283–298.https://doi.org/10.7124/bc.00073B
Klimenko, I.V., Gushcha, T.O., and Kornelyuk, A.I., Properties of tryptophan fluorescence of two forms of tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase from the liver, Biopolym. Cell, 1991, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 83–88.https://doi.org/10.7124/bc.000303
Kornelyuk, A.I., Klimenko, I.V., and Odynets, K.A., Conformational change of mammalian tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase induced by tyrosyladenylate formation, Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int., 1995, vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 317–322.
Kordysh M.O., Kyryushko G.V., Mely, Y., and Kornelyuk O.I. Conformational mobility investigation of TyrRS N-module and its complex with tRNA using the methods of time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy, Biopolym. Cell, 2007, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 130–136.https://doi.org/10.7124/bc.00075F
Ling, M.M. and Robinson, B.H., Approaches to DNA mutagenesis: an overview, Anal. Biochem., 1997, vol. 254, pp. 157–178. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1997.2428
Inoue, H., Nojima, H., and Okayama, H., High efficiency transformation of Escherichia coli plasmids, Gene, 1990, vol. 96, pp. 23–28.https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(90)90336-P
Miller, E.M. and Nickoloff, J.A., Escherichia coli electrotransformation, Methods Mol. Biol., 1995, vol. 47, pp. 105–113. https://doi.org/10.1385/0-89603-310-4:105
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., and Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed., New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989.
Morrison, K.L. and Weiss, G.A., Combinatorial alanine scanning, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2001, vol. 5, pp. 302–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1367-5931(00)00206-4
Liu, H. and Naismith, J.H., An efficient one-step site-directed deletion, insertion, single and multiple-site plasmid mutagenesis protocol, BMC Biotechnol., 2008, vol. 8, no. 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-8-91
Vovis, G.F. and Lacks, S., Complementary action of restriction enzymes endo R-DpnI and endo R-DpnII on bacteriophage fI DNA, J. Mol. Biol., 1977, vol. 115, no. 3, pp. 525–538. doi.org/ (77)90169-3https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836
Edelheit, O., Hanukoglu, A., and Hanukoglu, I., Simple and efficient site-directed mutagenesis using two single-primer reaction in parallel to generate mutants for protein structure-function studies, BMC Biotechnol., 2009, vol. 9, no. 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-9-61
Qui, D. and Scholthof, R.-B.G., A one-step PCR-based method for rapid and efficient site-directed fragment deletion, insertion, and substitution mutagenesis, J. Virol. Methods, 2008, vol. 149, no. 1, pp. 85–90.
Salerno, J.C., Jones, R.J., and Erdogan, E., A single-stage polymerase-based protocol for the introduction of deletions and insertion without subcloning, Mol. Biotechnol., 2005, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 225–232.
Tregan, A., Kielbus, M., Czapinski, J., Stepulak, A., Huhtaniemi, I., and Rivero-Muller, A., REPLACR-mutagenesis, a one-step method for site-directed mutagenesis by recombineering, Sci. Rep., 2016, vol. 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19121
Tseng, W.-Chi., Lin, J.-W., Wei, T.-Yu., and Fang, T.-Yu., A novel megaprimed and ligase-free, PCR-based, site-directed mutagenesis method, Anal. Biochem., 2008, vol. 375, no. 2, pp. 376–378.
Zheng, L., Bauman, U., and Reymnd, J.-L., An efficient one-step site-directed and site-saturation mutagenesis protocol, Nucleic Acids Res., 2004, vol. 32, no. 14. e115.https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gnh110
Blocquel, D., Li Sh, Wei N., Daub H., Sajish M., Erfurth M.-L., Kooi G., Zhou J., Bai G., Schimmel P., Jordanova A., and Yang X.-L. Alternative stable conformation capable of protein misinteraction links tRNA synthetase to peripheral neuropathy, Nucleic Acids Res., 2017, vol. 45, no. 13, pp. 8091–8104. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx455
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by D. Novikova
About this article
Cite this article
Zayets, V.N., Tsuvarev, A.Y., Kolomiiets, L.A. et al. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Tryptophan Residues in the Structure of the Catalytic Module of Tyrosyl-tRNA Synthetase from Bos taurus. Cytol. Genet. 53, 219–226 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3103/S009545271903006X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S009545271903006X