Abstract
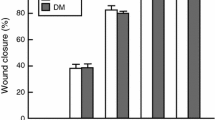
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is one of the main factors that can affect the condition and rate of skin regeneration process. Morphological and molecular biological investigations were carried out to study skin wounds of wild-type FVB mice and transgenic K14/mIGF-1 animals with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Increases in the IGF-1 expression, the area and thickness of regenerated epithelium, and number of Mac-1+ cells per wound were shown in transgenic animals compared with wild-type animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
auf dem Keller, U., Kumin, A., Braun, S., and Werner, S., Reactive oxygen species and their detoxification in healing skin wounds, J. Invest. Dermatol. Symp. Proc., 2006, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 106–111.
Martin, P., Wound healing-aiming for perfect skin regeneration, Science, 1997, vol. 276, no. 5309, pp. 75–81.
Grazul-Bilska, A., Johnson, M., Bilski, J., et al., Wound healing: the role of growth factors, Drugs Today, 2003, vol. 39, no. 10, pp. 787–795.
Cummings, D. and Merriam, G., Growth hormone therapy in adults, Ann. Rev. Med., 2003, vol. 54, pp. 513–533.
Green, H., Morikawa, M., and Nixon, T., A dual effector theory of growth-hormone action, Differentiation, 1985, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 195–198.
Eming, S., Snow, R., Yarmush, M., and Morgan, J., Targeted expression of insulin-like growth factor to human keratinocytes: modification of the autocrine control of keratinocyte proliferation, J. Invest. Dermatol., 1996, vol. 107, no. 1, pp. 113–120.
Barreca, A., De Luca, M., Del Monte, P., et al., In vitro paracrine regulation of human keratinocyte growth by fibroblast-derived insulin-like growth factors, J. Cell Physiol., 1992, vol. 151, no. 2, pp. 262–268.
Blenis, J., Signal transduction via the map kinases: proceed at your own risk, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1993, vol. 90, no. 13, pp. 5889–5892.
Guler, H., Zapf, J., Scheiwiller, E., and Froesch, E., Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth and has distinct effects on organ size in hypophysectomized rats, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1988, vol. 85, no. 13, pp. 4889–4893.
Tavakkol, A., Elder, J., Griffiths, C., et al., Expression of growth hormone receptor, insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-1) and IGF-1 receptor mRNA and proteins in human skin, J. Invest. Dermatol., 1992, vol. 99, no. 3, pp. 343–349.
Johansson, O. and Liu, P.O., Gamma-melanocyte stimulating hormone (Γ-MSH)-like immunoreactivity is present in certain normal human keratinocytes, Exp. Dermatol., 1993, vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 204–208.
Philpott, M., Sanders, D., and Kealey, T., Effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factors on cultured human hair follicles: IGF-1 at physiologic concentrations in an important regulator of hair follicle growth in vitro, J. Invest. Dermatol., 1994, vol. 102, no. 6, pp. 857–861.
Rudman, S., Philpott, M., Thomas, G., and Kealey, T., The role of IGF-1 in human skin and its appendages: morphogen as well as mitogen? J. Invest. Dermatol., 1997, vol. 109, no. 6, pp. 770–777.
Blakytny, R., Jude, E.B., Martin, GibsonJ., et al., Lack of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) in the basal keratinocyte layer of diabetic skin and diabetic foot ulcers, J. Pathol., 2000, vol. 190, no. 5, pp. 589–594.
Wetzler, C., Kampfer, H., Stallmeyer, B., et al., Large and sustained induction of chemokines during impaired wound healing in the genetically diabetic mouse: prolonged persistence of neutrophils and macrophages during the late phase of repair, J. Invest. Dermatol., 2000, vol. 155, p. 245–253.
Semenova, E., Koegel, H., Hasse, S., et al., Overexpression of mIGF-1 in keratinocytes improves wound healing and accelerates hair follicle formation and cycling in mice, Am. J. Pathol., 2008, vol. 173, no. 5, pp. 1295–1310.
Werner, S. and Grose, R., Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines, Physiol. Rev., 2003, vol. 83, no. 3, pp. 835–870.
Brown, D.L., Kane, C.D., Chernausek, S.D., and Greenhalgh, D.G., Differential expression and localization of insulin-like growth factors I and II in cutaneous wounds of diabetic and nondiabetic mice, Am. J. Pathol., 1997, vol. 151, no. 3, pp. 715–724.
Telasky, C., Tredget, E.E., Shen, Q., et al., IFN-2b suppresses the fibrogenic effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 in dermal fibroblasts, J. Interferon Cytokine Res., 1998, vol. 18, no. 8, pp. 571–577.
Neely, E.K., Morhenn, V.B., Hintz, R.H., et al., Insulin-like growth factors are mitogenic for human keratinocytes and a squamous cell carcinoma, J. Invest. Dermatol., 1991, vol. 96, no. 1, pp. 104–110.
Gartner, M.H., Benson, J.D., and Caldwell, M.D., Insulin-like growth factors I and II expression in the healing wound, J. Surg. Res., 1992, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 389–394.
Ando, Y. and Jensen, P.J., Epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I enhance keratinocyte migration, J. Invest. Dermatol., 1993, vol. 100, no. 5, pp. 633–639.
Bhora, F.Y., Dunkin, B.J., Batzri, S., et al., Effect of growth factors on cell proliferation and epithelialization in human skin, J. Surg. Res., 1995, vol. 59, no. 2, pp. 236–244.
Roesel, J.F. and Nanney, L.B., Assessment of differential cytokine effects on angiogenesis using an in vivo model of cutaneous wound repair, J. Surf. Res., 1995, vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 449–459.
Ghahary, A., Tredget, E.E., and Shen, Q., Insulin-like growth factor-II/mannose 6 phosphate receptors facilitate the matrix effects of latent transforming growth factor-βl released from genetically modified keratinocytes in a fibroblast/keratinocyte co-culture system, J. Cell Physiol., 1999, vol. 180, no. 1, pp. 61–70.
Bitar, M.S., Pilcher, C.W., Khan, I., and Waldbillig, R.J., Diabetes-induced suppression of IGF-1 and its receptor mRNA levels in rat superior cervical ganglia, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract., 1997, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 73–80.
Nakao-Hayashi, J., Ito, H., Kanayasu, T., et al., Stimulatory effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I on migration and tube formation by vascular endothelial cells, Atherosclerosis, 1992, vol. 92, nos. 2/3, pp. 141–149.
Nicosia, R.F., Nicosia, S.V., and Smith, M., Vascular endothelial growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor-1 promote rat aortic angiogenesis in vitro, Am. J. Pathol., 1994, vol. 145, no. 5, pp. 1023–1029.
Frystyk, J., Ledet, T., Moller, N., et al., Cardiovascular disease and insulin-like growth factor I, Circulation, 2002, vol. 106, pp. 893–895.
Sunderkotter, C., Steinbrink, K., Goebeler, M., et al., Macrophages and angiogenesis, J. Leukocyte Biol., 1994, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 410–422.
Dvorak, H.F., Brown, L.F., Detmar, M., and Dvorak, A.M., Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis, Am. J. Pathol., 1995, vol. 146, p. 146.
Werner, S. and Grose, R., Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines, Physiol. Rev., 2003, vol. 83, no. 3, pp. 835–870.
Gosain, A. and DiPietro, L.A., Aging and wound healing, World J. Surg., 2004, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 321–326.
Campos, A.C., Groth, A.K., and Branco, A.B., Assessment and nutritional aspects of wound healing, Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care, 2008, vol. 11, pp. 281–288.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Ukrainian Text © Yu.I. Leonov, M.S. Shkumat, P.P. Klymenko, M.Yu. Hovorun, M.M. Guzyk, T.M. Kuchmerovska, I.M. Pishel, 2015, published in Tsitologiya i Genetika, 2015, Vol. 49, No. 1, pp. 26–34.
About this article
Cite this article
Leonov, Y.I., Shkumat, M.S., Klymenko, P.P. et al. Effect of insulin-like growth factor transgene on wound healing in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Cytol. Genet. 49, 19–26 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452715010065
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452715010065