Abstract
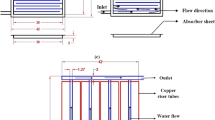
This study deals with the energy and exergy analyses of natural circulation solar water heating (SWH) systems. The system comprises of a single glazed flat plate solar collector (FPSC) with absorber plate of 2 m2, and a separate insulated well-mixed vertical water storage tank (WST) of 125 liters. The variable heat transfer coefficients, water inlet and outlet temperatures of the FPSC; and temperature of heated water stored in the WST are predicted theoretically for each interval. The daily energy and exergy efficiency of the FPSC, WST and SWH system are estimated to be about 39 and 4.36%, 67 and 38.55%, 27 and 1.01%, respectively. It is found that the water inlet temperature, optical efficiency and the solar radiation strongly influence the performance of the FPSC both energetically and exergetically. It is observed that change in the mass flow rate of water improves the exergy efficiency of the FPSC significantly. FPSC has been identified as a critical component of the system where exergy destruction of 308 W/m2 takes place daily as compared to 24 W/m2 in the WST against available solar exergy of about 663 W/m2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalogirou, S.A., Progr. Energy Combust. Sci., 2004, vol. 30, pp. 231–295.
Hossain, M.S., Saidur, R., Fayaz, H., et al., Renew. Sust. Energy Rev., 2011, vol. 15, pp. 3801–3812.
Jaisankar, S., Ananth, J., Thulasi, S., et al., Renew. Sust. Energy Rev., 2011, vol. 15, pp. 3045–3050.
Shukla, R., Sumathy, K., Erickson, P., and Gong, J., Renew. Sust. Energy Rev., 2013, vol. 19, pp. 173–190.
Gupta, G.L. and Garg, H.P., Solar Energy, 1968, vol. 12, pp. 163–182.
Ong, K.S., Solar Energy, 1974, vol. 16, pp. 137–147.
Ong, K.S., Solar Energy, 1976, vol. 18, pp. 183–191.
Wolf, D., Tamir, A., and Kudish, A.I., Energy, 1980, vol. 5, pp. 191–205.
Sodha, M.S. and Tiwari, G.N., Energy Convers. Manag., 1981, vol. 21, pp. 283–288.
Morrison, G.L. and Braun, J.E., Solar Energy, 1985, vol. 34, pp. 389–405.
Kudish, A.I., Santamaura, P., and Beaufort, P., Solar Energy, 1985, vol. 35, pp. 167–173.
Hobson, P.A. and Norton, B., Solar Energy, 1989, vol. 43, pp. 89–95.
Ayompe, L.M. and Duffy, A., Appl. Therm. Eng., 2013, vol. 58, pp. 447–454.
Essabbani, T., Moufekkir, F., Mezrhab, A., and Naji, H., Appl. Solar Energy, 2015, vol. 51, pp. 22–23.
Redpath, D.A.G., Solar Energy, 2012, vol. 86, pp. 705–715.
Fazilati, M.A. and Alemrajabi, A.A., Energy Convers. Manag., 2013, vol. 71, pp. 138–145.
Zhang, X., You, Sh., Xu, W., et al., Energy Convers. Manag., 2014, vol. 78, pp. 386–392.
Sudhishkumar, S. and Balusamy, T., Renew. Sust. Energy Rev., 2014, vol. 37, pp. 191–198.
Sathyamurthy, R., Samuel, D.G.H., Nagarajan, P.K., and Jaiganesh, V., Appl. Solar Energy, 2015, vol. 51, pp. 95–98.
Luminosu, I. and Fara, L., Energy, 2005, vol. 30, pp. 731–747.
Xiaowu, W. and Ben, H., Renew. Sust. Energy Rev., 2005, vol. 9, pp. 638–645.
Gunerhan, H. and Hepbasli, A., Energy Buildings, 2007, vol. 39, pp. 509–516.
Farahat, S., Sarhaddi, F., and Ajam, H., Renew. Energy, 2009, vol. 34, pp. 1169–1174.
Ceylan, I., Energy Buildings, 2012, vol. 47, pp. 630–635.
Kulkarni, G.N., Kedare, S.B., and Bandyopadhyay, S., Solar Energy, 2007, vol. 81, pp. 958–968.
Duffie, J.A. and Beckman, W.A., Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes, Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2006.
Indian Standard no. 12933: Part 1 and 2, New Delhi: Bureau of Indian Standards, 2003.
Kalogirou, S.A., Solar Energy Engineering: Processes and Systems, San Diego: Acad. Press, Elsevier, 2009.
Sukhatme, S.P. and Nayak, J.K., Solar Energy: Principles of Thermal Collection and Storage, New Delhi: Tata McGraw Hill, 2011.
Rezaie, B., Reddy, B., and Rosen, M.A., Proc. eSin the Canadian Conf. on Building Simulation, Halifax Nova Scotia, May 1–4, 2012. http://esimca. Assessed May 02, 2014.
Xu, C., Wang, Z., Li, X., and Sun, F., Appl. Therm. Eng., 2011, vol. 31, pp. 3904–3913.
Panwar, N.L., Kaushik, S.C., and Kothari, S.J., Energy, 2012, vol. 4, p. 023111.
Singh, O.K. and Kaushik, S.C., Appl. Therm. Eng., 2013, vol. 51, pp. 787–800.
Reddy, V.S., Kaushik, S.C., and Tyagi, S.K., Clean Techn. Policy, 2013, vol. 15, pp. 133–145.
Panwar, N.L., Appl. Solar Energy, 2014, vol. 50, pp. 133–137.
Kotas, T.J., The Exergy Method of Thermal Plant Analysis, Malabar, FL: Krieger Publishing Company, 1995, pp. 29–56.
Bejan, A., Advanced Engineering Thermodynamics, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2006, pp. 204–221.
Moran, M.J. and Shapiro, H.N., Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics, New Delhi: Wiley India (P) Ltd., 2010, pp. 272–315.
Petela, R., Engineering Thermodynamics of Thermal Radiation: for Solar Power Utilization, New York: McGraw Hill, 2010, pp. 68, 208–300.
Hepbasli, A., Renew. Sust. Energy Rev., 2008, vol. 12, pp. 593–661.
Petela, R., ASME J. Heat Transf., 1964, vol. 86, pp. 187–192.
Dincer, I. and Rosen, M.A., Exergy: Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development, Elsevier, 2007, pp. 23–34.
Dincer, I. and Rosen, M.A., Thermal Energy Storage: Systems and Applications, John Wiley & Sons, 2011, p. 15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaushik, S.C., Ranjan, K.R. Energetic and exergetic performance evaluation of natural circulation solar water heating systems. Appl. Sol. Energy 52, 16–26 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0003701X16010059
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0003701X16010059